Présentation PowerPoint
... close vicinity IEC Limits Pulsed Radio frequency B1 field: Patient tissue heating SAR IEC Limits ...
... close vicinity IEC Limits Pulsed Radio frequency B1 field: Patient tissue heating SAR IEC Limits ...
Effect of a Magnetic Field on an Atomic Orbital
... mentioned (without derivation) that if one assumes constant speed while the radius changes then he would get a change in the magnetic moment which is twice its magnitude for the case of fixed radius and change in speed. When an atomic electron is subject to an external magnetic field, most authors a ...
... mentioned (without derivation) that if one assumes constant speed while the radius changes then he would get a change in the magnetic moment which is twice its magnitude for the case of fixed radius and change in speed. When an atomic electron is subject to an external magnetic field, most authors a ...
Physics 1252 Exam #3E Instructions:
... This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your formula sheet, except for your name: it must be handed in, signed but clean, with your exam. There is space after each question to sh ...
... This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your formula sheet, except for your name: it must be handed in, signed but clean, with your exam. There is space after each question to sh ...
Electron Spin Resonance
... known B and . You will create a known uniform B field with a set of Helmholtz coils and create an oscillating EM field of known frequency by using smaller coils carrying an AC current of known frequency. Then, by placing the electrons inside the small coils and the small coils inside the Helmholt ...
... known B and . You will create a known uniform B field with a set of Helmholtz coils and create an oscillating EM field of known frequency by using smaller coils carrying an AC current of known frequency. Then, by placing the electrons inside the small coils and the small coils inside the Helmholt ...
Magnetic Head Pulleys
... Immediately after installation, it begins removing metal from your product stream - protecting crushers, grinders, pulverizers, screens and other processing equipment. tion irec It also helps insure product purity by removing rD o y ve lley Con metal contamination from foods, chemicals, Pu tic e n g ...
... Immediately after installation, it begins removing metal from your product stream - protecting crushers, grinders, pulverizers, screens and other processing equipment. tion irec It also helps insure product purity by removing rD o y ve lley Con metal contamination from foods, chemicals, Pu tic e n g ...
The Earth`s B-Field
... Magnetic fields extend infinitely, though they are weaker further from their source. The Earth's magnetic field, which effectively extends several tens of thousands of km’s into space, is called the magnetosphere. ...
... Magnetic fields extend infinitely, though they are weaker further from their source. The Earth's magnetic field, which effectively extends several tens of thousands of km’s into space, is called the magnetosphere. ...
8J Magnets and electromagnets
... Not all magnetic materials are magnets. A magnet is a piece of magnetic material with a north and south pole. Magnetism is the force that pulls the opposite poles of two magnets together or pushes the same poles of two magnets apart. ...
... Not all magnetic materials are magnets. A magnet is a piece of magnetic material with a north and south pole. Magnetism is the force that pulls the opposite poles of two magnets together or pushes the same poles of two magnets apart. ...
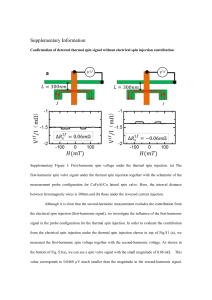
Supplementary Information (doc 560K)
... bottom contact pads. Here, we assume that the thermal conductivities of Cu, CFA, Si, and SiO2 are 400, 29.8, 130 and 1.4 Wm−1 K−1, respectively. Supplementary figures 3(a) and 3(b) show the three dimensional color plots of the simulated temperature for lateral and vertical profiles, respectively. As ...
... bottom contact pads. Here, we assume that the thermal conductivities of Cu, CFA, Si, and SiO2 are 400, 29.8, 130 and 1.4 Wm−1 K−1, respectively. Supplementary figures 3(a) and 3(b) show the three dimensional color plots of the simulated temperature for lateral and vertical profiles, respectively. As ...
Hyperfine Splitting and Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism of Ni at Multimegabar Pressure
... quite weakly, in agreement with the experimental observation of a ferromagnetic state in Ni at multimegabar pressure and at room temperature. Experiments were performed at the nuclear resonance beam line [23] ID18 at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility. The storage ring was operated in the 1 ...
... quite weakly, in agreement with the experimental observation of a ferromagnetic state in Ni at multimegabar pressure and at room temperature. Experiments were performed at the nuclear resonance beam line [23] ID18 at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility. The storage ring was operated in the 1 ...
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a
... The split ring in the electric motor also known as a commutator reverses the direction of current flowing through the coil after every half rotation of the coil. Due to this the coil continues to rotate in the same direction. 14. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil. The different way ...
... The split ring in the electric motor also known as a commutator reverses the direction of current flowing through the coil after every half rotation of the coil. Due to this the coil continues to rotate in the same direction. 14. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil. The different way ...
Magnetism - APlusPhysics
... 1. Forces on moving charges in magnetic fields a. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B, and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. b. Deduce the direction of a magnetic field from information about the forces experienced by charged particles moving ...
... 1. Forces on moving charges in magnetic fields a. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B, and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. b. Deduce the direction of a magnetic field from information about the forces experienced by charged particles moving ...
Chapter 28. Magnetic Field
... (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is known that the external electric field is zero everywhere, can you conclude that the external magnetic field is also zero? Expl ...
... (a) If it is known that the external magnetic field is zero everywhere in this region, can you conclude that the external electric field is also zero? Explain. (b) If it is known that the external electric field is zero everywhere, can you conclude that the external magnetic field is also zero? Expl ...
A magnet - Warren County Schools
... Greeks used a stone substance called “magnetite.” It was discovered near Magnesta so called it magnetite.They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
... Greeks used a stone substance called “magnetite.” It was discovered near Magnesta so called it magnetite.They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.