Kein Folientitel
... The first useful feature of pBR 322 is its size. As outlined before, a cloning vector ought to be less than 10 kb, to avoid problems such as DNA breakdown during purification. The size of 4363 bp means that not only the vector itself can be purified with ease, but so can recombinant DNA molecules co ...
... The first useful feature of pBR 322 is its size. As outlined before, a cloning vector ought to be less than 10 kb, to avoid problems such as DNA breakdown during purification. The size of 4363 bp means that not only the vector itself can be purified with ease, but so can recombinant DNA molecules co ...
Reporting Category 2
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA in the nucleus DNA is too big to leave the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus to take the information to the ribosome (in the cytoplasam) The DNA then winds back up Which process is next? ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA in the nucleus DNA is too big to leave the nucleus mRNA then leaves the nucleus to take the information to the ribosome (in the cytoplasam) The DNA then winds back up Which process is next? ...
Dna sequence and Cell Activity
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... associated proteins Many bacteria also have plasmids, smaller circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the chromosome Bacterial cells divide by binary fission, which is preceded by replication of the chromosome ...
... associated proteins Many bacteria also have plasmids, smaller circular DNA molecules that can replicate independently of the chromosome Bacterial cells divide by binary fission, which is preceded by replication of the chromosome ...
Basics of DNA
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...
Cloning and PCR File
... 1. In isolation, an enzyme (called a restriction enzyme) is used to break DNA at a specific base sequence. This is done to isolate a gene. 2. During ligation, the enzyme DNA ligase combines the isolated gene with plasmid DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome ...
... 1. In isolation, an enzyme (called a restriction enzyme) is used to break DNA at a specific base sequence. This is done to isolate a gene. 2. During ligation, the enzyme DNA ligase combines the isolated gene with plasmid DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology & Genomics
... Yeast cells (eukaryotic fungi) used for making recombinant genes ...
... Yeast cells (eukaryotic fungi) used for making recombinant genes ...
Transgenic Organisms
... Transgenic organisms contain genes from another species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human disea ...
... Transgenic organisms contain genes from another species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human disea ...
SNC2D Genes - Malvern Science
... • Humans have 46 chromosomes in each somatic (body) cell (except the gametes = ovum/sperm, which have 23) • Different species may have different numbers of chromosomes ...
... • Humans have 46 chromosomes in each somatic (body) cell (except the gametes = ovum/sperm, which have 23) • Different species may have different numbers of chromosomes ...
2.5 Changes to a cell`s DNA
... operating system. • Can it get altered? If so, what happens when it gets altered? ...
... operating system. • Can it get altered? If so, what happens when it gets altered? ...
Gene Splicing KVQ Warm-up #70-75
... chance events rather than natural selection. • Genetic Drift 72. A natural process in which a nucleic acid molecule (usually DNA but can be RNA) is broken and then joined to a different molecule; a result of crossing over. • Gene Recombination 73. A technology that includes the process of manipulati ...
... chance events rather than natural selection. • Genetic Drift 72. A natural process in which a nucleic acid molecule (usually DNA but can be RNA) is broken and then joined to a different molecule; a result of crossing over. • Gene Recombination 73. A technology that includes the process of manipulati ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Recombinant DNA is taking DNA from one source and inserting it into an organism’s DNA, giving that organism those characteristics. – Ex.= Inserting salmon’s anti-freezing genes into corn to allow it to survive frost. ...
... • Recombinant DNA is taking DNA from one source and inserting it into an organism’s DNA, giving that organism those characteristics. – Ex.= Inserting salmon’s anti-freezing genes into corn to allow it to survive frost. ...
The Masterof
... to take a picture of DNA and Watson and Crick then took the picture (without permission) - Erwin Chargaff explained that DNA contained equal amounts of A and T molecules and G and C molecules stating that A pairs with T and G pairs with ...
... to take a picture of DNA and Watson and Crick then took the picture (without permission) - Erwin Chargaff explained that DNA contained equal amounts of A and T molecules and G and C molecules stating that A pairs with T and G pairs with ...
1 word is genus and
... 59. What is a codon and where is it found? 3 base sequence from DNA to RNA that codes for an amino acid 60. What is an anti-codon? And where is it found? The complementary base sequence for a codon found on the tRNA 61. Name the three types of RNA and function of each. mRNA- messenger rna that bring ...
... 59. What is a codon and where is it found? 3 base sequence from DNA to RNA that codes for an amino acid 60. What is an anti-codon? And where is it found? The complementary base sequence for a codon found on the tRNA 61. Name the three types of RNA and function of each. mRNA- messenger rna that bring ...
slides
... • Given two strings (of same set of characters) find a sequence of reversals of substrings that will transform one to other • Biologist are interested in shortest such sequence • Which makes the algorithm more challenging, and it is one of the most studied problem in algorithmic bioinformatics !!! ...
... • Given two strings (of same set of characters) find a sequence of reversals of substrings that will transform one to other • Biologist are interested in shortest such sequence • Which makes the algorithm more challenging, and it is one of the most studied problem in algorithmic bioinformatics !!! ...
Chapter 13
... Clone: a collection of molecules or cells, all identical to an original molecule or cell • To "clone a gene" is to make many copies of it - for example, in a population of bacteria • Gene can be an exact copy of a natural gene • Gene can be an altered version of a natural gene • Recombinant DNA tech ...
... Clone: a collection of molecules or cells, all identical to an original molecule or cell • To "clone a gene" is to make many copies of it - for example, in a population of bacteria • Gene can be an exact copy of a natural gene • Gene can be an altered version of a natural gene • Recombinant DNA tech ...
Document
... population of an organism or tissue. 6. A restriction site difference that is polymorphic within a population can be used to carry out _____RFLP___________ mapping of neighboring genes. 7. ___histone___________ genes commonly exist in tandem repetitive arrays in eukayote genomes. 8. ____transposase_ ...
... population of an organism or tissue. 6. A restriction site difference that is polymorphic within a population can be used to carry out _____RFLP___________ mapping of neighboring genes. 7. ___histone___________ genes commonly exist in tandem repetitive arrays in eukayote genomes. 8. ____transposase_ ...
34 Lambda Appendix - RIT
... single stranded tails is called COS (cohesive site) and the left and right arms become contiguous and form a single operon, the right hand operon. The central region comprises a second operon, the left hand operon. λ is a temperate phage, meaning that upon entering a cell, the phage may enter either ...
... single stranded tails is called COS (cohesive site) and the left and right arms become contiguous and form a single operon, the right hand operon. The central region comprises a second operon, the left hand operon. λ is a temperate phage, meaning that upon entering a cell, the phage may enter either ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
... All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain instructions that code for the formation of proteins. (LS1.A) ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
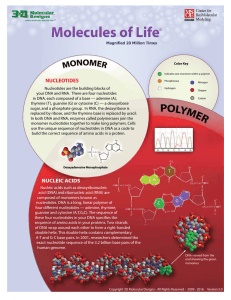
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.