Recombination - Transformation
... The suppression of homologous recombination started outside of the SRY (Sex Reversal of Y) gene and spread to other regions in a rather spontaneous fashion, leading to the loss of genes and chromatin. It has been speculated that the cause of suppression is inversion on the Y-chromosome. When the hom ...
... The suppression of homologous recombination started outside of the SRY (Sex Reversal of Y) gene and spread to other regions in a rather spontaneous fashion, leading to the loss of genes and chromatin. It has been speculated that the cause of suppression is inversion on the Y-chromosome. When the hom ...
Mapping the DNA Damage Response
... Response Case study reveals transcription factor (TF) modules, dynamic TF binding and an expanded role for cell cycle regulators ...
... Response Case study reveals transcription factor (TF) modules, dynamic TF binding and an expanded role for cell cycle regulators ...
Genetics - Doc Ireland
... 2. Separate the Codons 3. Translate the Codons till you reach a “Stop” Codon ...
... 2. Separate the Codons 3. Translate the Codons till you reach a “Stop” Codon ...
notes
... and many nonrecombinant plasmids. Recombinant DNA plasmids Introduce the DNA into bacterial cells that have a mutation in their own lacZ ...
... and many nonrecombinant plasmids. Recombinant DNA plasmids Introduce the DNA into bacterial cells that have a mutation in their own lacZ ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 07. Knudson medium is used for orchid culture. 08. The opine synthesized by Nop. Ti plasmid is acetosyringone. 09. pBR 322 is constructed from pUC. 10. Sodium alginate is used as fusogent. III. Complete the following 11. Hot air oven is used for …………. of glassware. 12. PEG refers to ………… 13. Agrobac ...
... 07. Knudson medium is used for orchid culture. 08. The opine synthesized by Nop. Ti plasmid is acetosyringone. 09. pBR 322 is constructed from pUC. 10. Sodium alginate is used as fusogent. III. Complete the following 11. Hot air oven is used for …………. of glassware. 12. PEG refers to ………… 13. Agrobac ...
Biology B Trimester Review 6-1
... 12. What are gametes? 13. If the “n” number of a cell is 24, what would its diploid number be? 14. Be able to explain the different phases of meiosis. 15. What is crossing over, and when does it take place? 16. Identify another way to increase genetic variation in offspring? 17. Compare and contrast ...
... 12. What are gametes? 13. If the “n” number of a cell is 24, what would its diploid number be? 14. Be able to explain the different phases of meiosis. 15. What is crossing over, and when does it take place? 16. Identify another way to increase genetic variation in offspring? 17. Compare and contrast ...
Stem cell researchers uncover previously unknown patterns in DNA
... influences DNA methylation patterning throughout the genome and that DNA methyltransfereases (the enzymes that methylates DNA) preferentially target nucloesome-bound DNA," said Pellegrini, an associate professor of molecular, cell and developmental biology and an informatics expert. The work was ini ...
... influences DNA methylation patterning throughout the genome and that DNA methyltransfereases (the enzymes that methylates DNA) preferentially target nucloesome-bound DNA," said Pellegrini, an associate professor of molecular, cell and developmental biology and an informatics expert. The work was ini ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
... and blue appear in the linear order of the thread. This will illustrate to students how genes appear stacked on chromosomes. 4. Review with students what each material was used to represent the DNA, genes, and chromosomes (thread, colored sections of thread, and thread on spool). 5. Take time now to ...
... and blue appear in the linear order of the thread. This will illustrate to students how genes appear stacked on chromosomes. 4. Review with students what each material was used to represent the DNA, genes, and chromosomes (thread, colored sections of thread, and thread on spool). 5. Take time now to ...
A new direction in materials assembly: using
... nanoparticles into complex materials with novel functionality. This work has been a joint collaboration with Chad Mirkin, and it began in 2008 with the fabrication of superlattices composed of identical gold particles that could either be fcc or bcc depending on whether the DNA is self-complementary ...
... nanoparticles into complex materials with novel functionality. This work has been a joint collaboration with Chad Mirkin, and it began in 2008 with the fabrication of superlattices composed of identical gold particles that could either be fcc or bcc depending on whether the DNA is self-complementary ...
PS401- Lec. 3
... certain genes and their associated phenotypes due to their being localized in the same chromosome. (Morgan, 1910) Linked: two genes showing less than 50% recombination. ...
... certain genes and their associated phenotypes due to their being localized in the same chromosome. (Morgan, 1910) Linked: two genes showing less than 50% recombination. ...
Paper Plasmid 2 - dublin.k12.ca.us
... WILL CUT THE PLASMID ONCE AND ONLY ONCE. Continue this procedure until all 8 enzymes have been tried. Everyone’s results will be different because of different plasmid sequences. If you have no enzymes that will cut your plasmid only once, thenreconstruct your plasmid. ...
... WILL CUT THE PLASMID ONCE AND ONLY ONCE. Continue this procedure until all 8 enzymes have been tried. Everyone’s results will be different because of different plasmid sequences. If you have no enzymes that will cut your plasmid only once, thenreconstruct your plasmid. ...
Document
... Transformation occurs when bacteria take up DNA from their surroundings. (Think of the R to S transformation that introduced us to the idea of DNA as the genetic material.) You will take advantage of this bacterial property in lab this week. When you mix plasmid DNA with calcium chloridetreated E. c ...
... Transformation occurs when bacteria take up DNA from their surroundings. (Think of the R to S transformation that introduced us to the idea of DNA as the genetic material.) You will take advantage of this bacterial property in lab this week. When you mix plasmid DNA with calcium chloridetreated E. c ...
Genetics Quiz – 18 October 2005
... For the next few questions - A) True / B) False 1. Somatic cells include all body cells with the exception of gamete producing cells True 2. Gametes (sperm or egg) are diploid, that is they have half the number of chromosomes of either parent False 3. mitosis occurs in gametes producing four identic ...
... For the next few questions - A) True / B) False 1. Somatic cells include all body cells with the exception of gamete producing cells True 2. Gametes (sperm or egg) are diploid, that is they have half the number of chromosomes of either parent False 3. mitosis occurs in gametes producing four identic ...
STAAR Review 4
... This chart shows the results of several crosses with whitefeathered chickens and dark-feathered chickens. ...
... This chart shows the results of several crosses with whitefeathered chickens and dark-feathered chickens. ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 3 BIOINFORMATI
... for coding sequences similar to know genes – Start sequences (there is a good chance that each of these will be followed by a coding sequence – Sequences lacking stop codons (a protein coding sequence is normally a very long chain of base triplets containing no stop codon except the one at its end ...
... for coding sequences similar to know genes – Start sequences (there is a good chance that each of these will be followed by a coding sequence – Sequences lacking stop codons (a protein coding sequence is normally a very long chain of base triplets containing no stop codon except the one at its end ...
FALL EOC Questions
... 5. What mRNA sequence and amino acid sequence would the following DNA code for: ATTCCGATCTTT 6. How does each of the following provide evidence for evolution: a.embryology, b. homologous structures, c. vestigial structures, d. similarities in protein sequences, e. fossil record? 7. Explain how the G ...
... 5. What mRNA sequence and amino acid sequence would the following DNA code for: ATTCCGATCTTT 6. How does each of the following provide evidence for evolution: a.embryology, b. homologous structures, c. vestigial structures, d. similarities in protein sequences, e. fossil record? 7. Explain how the G ...
DNA functions worksheet
... 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the structure of chromosomes? ...
... 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the structure of chromosomes? ...
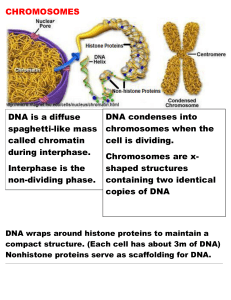
Chromosomes Notes
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Understanding Biotechnology
... • GEO / GMO = creation of a “recombinant DNA modified organism” – It’s the method, can use native or foreign genes ...
... • GEO / GMO = creation of a “recombinant DNA modified organism” – It’s the method, can use native or foreign genes ...
Cloning - Somers Public Schools
... cells from a single cell. 1997 - Ian Wilmut with Dolly, the cloned sheep 1. Remove nucleus from egg cell 2. Fuse de-nucleated cell with a body cell from another adult 3. Cells fuse to become 2N and then divides 4. Implant embryo in reproductive system of foster mother ...
... cells from a single cell. 1997 - Ian Wilmut with Dolly, the cloned sheep 1. Remove nucleus from egg cell 2. Fuse de-nucleated cell with a body cell from another adult 3. Cells fuse to become 2N and then divides 4. Implant embryo in reproductive system of foster mother ...
Lab Techniques
... both cut using the same restriction enzyme. • The single-stranded ends of the fragment are complementary to those of the cut plasmid. • The DNA fragment and the cut plasmid are annealed and then joined by DNA ligase. ...
... both cut using the same restriction enzyme. • The single-stranded ends of the fragment are complementary to those of the cut plasmid. • The DNA fragment and the cut plasmid are annealed and then joined by DNA ligase. ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.