DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
biological sciences 354
... Prerequisites: Students must have Graduate Standing or passed BioSci 325 (P) or BioSci 315 (P) with C or better Course Content: The goal of this course is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of eukaryotic genes. This goal will ...
... Prerequisites: Students must have Graduate Standing or passed BioSci 325 (P) or BioSci 315 (P) with C or better Course Content: The goal of this course is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of eukaryotic genes. This goal will ...
Honors_Genetics_B_Student_Notes
... Termination: stop codon reaches A site, release factor binds to stop codon, polypeptide and ribosome are released ...
... Termination: stop codon reaches A site, release factor binds to stop codon, polypeptide and ribosome are released ...
Cloning Vector
... Restriction sites of the polylinker are not present anywhere else in the plasmid. Cutting plasmids with one of the restriction enzymes that recognize a site in the polylinker does not disrupt any of the essential features of the ...
... Restriction sites of the polylinker are not present anywhere else in the plasmid. Cutting plasmids with one of the restriction enzymes that recognize a site in the polylinker does not disrupt any of the essential features of the ...
10/02 Chromatin and Chromosome structure
... •Either exit current location and move to new location or duplicate self into new location. •Results in insertions in DNA sequences ...
... •Either exit current location and move to new location or duplicate self into new location. •Results in insertions in DNA sequences ...
Name__________________________ Date______ Period
... 11. Where does translation occur in a cell? 12. The cell organelle known as the ___________ is where proteins are made. 13. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by ___________. 14. Transfer RNA (tRNA) has a sequence of three nucleotides called the _____________ that binds to the ________ of mRNA. ...
... 11. Where does translation occur in a cell? 12. The cell organelle known as the ___________ is where proteins are made. 13. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by ___________. 14. Transfer RNA (tRNA) has a sequence of three nucleotides called the _____________ that binds to the ________ of mRNA. ...
DNA Technology
... Steps in Copying DNA • A DNA molecule is placed in a small test tube • +DNA polymerase • +heat to separate into ss • +primers (ss matching DNA pieces to start replication) • +nucleotides ...
... Steps in Copying DNA • A DNA molecule is placed in a small test tube • +DNA polymerase • +heat to separate into ss • +primers (ss matching DNA pieces to start replication) • +nucleotides ...
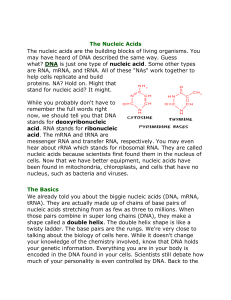
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might that stand for nucleic acid? It might. While you probably don't have to remember the full words right now, we should tell you that DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA stands ...
... are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might that stand for nucleic acid? It might. While you probably don't have to remember the full words right now, we should tell you that DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA stands ...
Macroevolution Part I Phylogenies
... Note the location at which fossils are found is indicative of its age which can be used to recreate phylogenies. ...
... Note the location at which fossils are found is indicative of its age which can be used to recreate phylogenies. ...
DNA makes up chromosomes!
... RNA Editing • RNA Editing – The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. – The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons. – When RNA molecules are formed, introns and exons are copied from DNA. ...
... RNA Editing • RNA Editing – The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. – The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons. – When RNA molecules are formed, introns and exons are copied from DNA. ...
Recombinant reflectin-based camouflage materials
... were synthesized separately for refA, refB and refC modules by MWG-Biotech (High Point, NC). Reflectin block modules sequences were constructed by annealing two synthetic nucleotides for each module as described previously.5 Reflectin block modules containing NheI and SpeI restriction sites were dig ...
... were synthesized separately for refA, refB and refC modules by MWG-Biotech (High Point, NC). Reflectin block modules sequences were constructed by annealing two synthetic nucleotides for each module as described previously.5 Reflectin block modules containing NheI and SpeI restriction sites were dig ...
Laboratory guide - Salisbury NHS Foundation Trust
... and turnaround time of a full gene screen. For example, the cystic fibrosis kit we use screens for mutations which account for over 90% of all CF mutations in populations of NW European origin and 71% of CF mutations worldwide. Targeted screening can also be useful as a pre-screen for founder mutati ...
... and turnaround time of a full gene screen. For example, the cystic fibrosis kit we use screens for mutations which account for over 90% of all CF mutations in populations of NW European origin and 71% of CF mutations worldwide. Targeted screening can also be useful as a pre-screen for founder mutati ...
Summary of sixth lesson
... Scans the entire genome like RAPDs More reliable because it uses longer PCR primers less likely to mismatch • Priming sites are a construct of the sequence in the organism and a piece of synthesized ...
... Scans the entire genome like RAPDs More reliable because it uses longer PCR primers less likely to mismatch • Priming sites are a construct of the sequence in the organism and a piece of synthesized ...
view
... modeled as: ‘mutation in gene X leads to loss of gene product X, which leads to disease A’. A single ‘gene-loss’ model seems pertinent for many diseases (Botstein and Risch, 2003). However, this model cannot fully reconcile with the increasingly appreciated prevalence of complex genotype-to-phenotyp ...
... modeled as: ‘mutation in gene X leads to loss of gene product X, which leads to disease A’. A single ‘gene-loss’ model seems pertinent for many diseases (Botstein and Risch, 2003). However, this model cannot fully reconcile with the increasingly appreciated prevalence of complex genotype-to-phenotyp ...
ppt - Castle High School
... reading frames. When it was first sequenced, only 58 percent coded for proteins with known functions. Since then, the roles of almost all other proteins have been identified. More genes are involved in each function in the larger E. coli. ...
... reading frames. When it was first sequenced, only 58 percent coded for proteins with known functions. Since then, the roles of almost all other proteins have been identified. More genes are involved in each function in the larger E. coli. ...
Is the process of manipulating genes and genomes Biotechnology
... these unions can be sealed with the enzyme DNA ligase -Is DNA that has been artificially made, using DNA from different sources and often different species. An example is the introduction of a human gene into an E coli bacterium ...
... these unions can be sealed with the enzyme DNA ligase -Is DNA that has been artificially made, using DNA from different sources and often different species. An example is the introduction of a human gene into an E coli bacterium ...