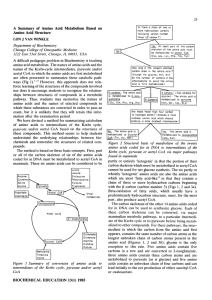
The Producers
... • Facultative CAM photosynthesis ⋅ During heat of day or dry season: stomata close / CAM photosynthesis ⋅ During cooler, humid late day or wet season: stomata open / switch to C3 photosynthesis • “CAM idling” ⋅ During dry season or extended drought, ...
... • Facultative CAM photosynthesis ⋅ During heat of day or dry season: stomata close / CAM photosynthesis ⋅ During cooler, humid late day or wet season: stomata open / switch to C3 photosynthesis • “CAM idling” ⋅ During dry season or extended drought, ...
Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids
... Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Amino acids can be classified as glucogenic or ketogenic based on which of the seven intermediates are produced during their catabolism . A. Glucogenic amino acids Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle. ...
... Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Amino acids can be classified as glucogenic or ketogenic based on which of the seven intermediates are produced during their catabolism . A. Glucogenic amino acids Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle. ...
CHAPTER 1 1.1 Introduction In many developing countries, herbal
... (Kamboj, 2000). This is supported by literature in behavioural and pharmacological sciences with animals and people using a number of different plants for the control of disease symptoms and related illnesses in their environment (Hart, 2004; Cousins and Huffman, 2002). One of such disorder is diabe ...
... (Kamboj, 2000). This is supported by literature in behavioural and pharmacological sciences with animals and people using a number of different plants for the control of disease symptoms and related illnesses in their environment (Hart, 2004; Cousins and Huffman, 2002). One of such disorder is diabe ...
Why a need for Systems Biology
... - Interactomics (studying the interactome, which is the interaction among proteins) -Metabolomics (the study of small-molecule metabolite profiles in cells) - Phenomics (describes the state of an organism as it changes with time) - and so on...... ...
... - Interactomics (studying the interactome, which is the interaction among proteins) -Metabolomics (the study of small-molecule metabolite profiles in cells) - Phenomics (describes the state of an organism as it changes with time) - and so on...... ...
Slides
... At most one reaction R in P has an enzyme, and R is not unique to P The pathway is a biosynthetic pathway missing its final steps The pathway is a catabolic pathway missing its initial steps ...
... At most one reaction R in P has an enzyme, and R is not unique to P The pathway is a biosynthetic pathway missing its final steps The pathway is a catabolic pathway missing its initial steps ...
Chapter 8 - Plant Biology
... containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, as well as smaller amounts of other elements such as sulfur and phosphorus. Water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ion, sulfate (SO42-), and phosphate (PO43-) represent the major basic stocks for the production of all t ...
... containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, as well as smaller amounts of other elements such as sulfur and phosphorus. Water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) ion, sulfate (SO42-), and phosphate (PO43-) represent the major basic stocks for the production of all t ...
Slide 1
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
complete
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
... • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The synthesis of new proteins ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... unsaturated fatty acids. In comparison with the original oil, the new fatty acids have additional double carbon–carbon bonds, replacing what were once single bonds. This process could also be described as _____________. (a) isomerization (b) oxidation (c) reduction (d) protonation ...
... unsaturated fatty acids. In comparison with the original oil, the new fatty acids have additional double carbon–carbon bonds, replacing what were once single bonds. This process could also be described as _____________. (a) isomerization (b) oxidation (c) reduction (d) protonation ...
The Synthesis and Degradation of Nucleotides
... Ribonucleotide Reductase has a unique control mechanism to assure that the deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site ...
... Ribonucleotide Reductase has a unique control mechanism to assure that the deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site ...
22. pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
... nder aerobic conditions, the cells obtain energy from ATP, produced as a result of breakdown of glucose. However, most plant and animal cells are aerobic and hence oxidize their organic fuels (carbohydrates etc.) completely to CO2 and H2O. Under these conditions, the pyruvate formed during glycolysi ...
... nder aerobic conditions, the cells obtain energy from ATP, produced as a result of breakdown of glucose. However, most plant and animal cells are aerobic and hence oxidize their organic fuels (carbohydrates etc.) completely to CO2 and H2O. Under these conditions, the pyruvate formed during glycolysi ...
A summary of amino acid metabolism based on amino acid structure
... Figure 3 Examples of the relationship between amino acid structure and metabolism (a) Tryptophan has at least three hydrocarbon carbons in a row beginning with the f5 carbon (carbon 3) and thus must be converted, at least in part, to acetyl CoA (hydrocarbon carbons are labeled a, b, c, d, e, f, and ...
... Figure 3 Examples of the relationship between amino acid structure and metabolism (a) Tryptophan has at least three hydrocarbon carbons in a row beginning with the f5 carbon (carbon 3) and thus must be converted, at least in part, to acetyl CoA (hydrocarbon carbons are labeled a, b, c, d, e, f, and ...
Inborn errors of Metabolism (IEM)
... • Before screening 25% of diagnoses were post mortem • Crisis often follows D&V, chest infections, etc i.e. prolonged fasting when present with lethargy and decrease conscious level or seizures • Hypoglycaemia severe (→ zero) and no ketones in urine • Neonatal screening now mandated UK-wide • Untre ...
... • Before screening 25% of diagnoses were post mortem • Crisis often follows D&V, chest infections, etc i.e. prolonged fasting when present with lethargy and decrease conscious level or seizures • Hypoglycaemia severe (→ zero) and no ketones in urine • Neonatal screening now mandated UK-wide • Untre ...
Important metabolic pathways in poultry embryos prior to hatch
... important mainly because of its relatively large size and glycogen storage capacity. Even though the pectoral muscle contains less glycogen per unit of mass than the liver, it accounts for the greatest quantity of total glycogen stored in the body (John et al., 1988; Christensen et al., 2001; Uni et ...
... important mainly because of its relatively large size and glycogen storage capacity. Even though the pectoral muscle contains less glycogen per unit of mass than the liver, it accounts for the greatest quantity of total glycogen stored in the body (John et al., 1988; Christensen et al., 2001; Uni et ...
EFFECTS OF ACUTE ETHIONINE-INDUCED
... Ethionine, the ethyl analogue of methionine, has been used for many years as a tool to perturb hepatic metabolism. Ethionine, itself being an amino acid, is handled in much the same way as many other amino acids. It can be incorporated into protein (Wilson et al., 1981), deaminated with subsequent m ...
... Ethionine, the ethyl analogue of methionine, has been used for many years as a tool to perturb hepatic metabolism. Ethionine, itself being an amino acid, is handled in much the same way as many other amino acids. It can be incorporated into protein (Wilson et al., 1981), deaminated with subsequent m ...
Metabolism of Nucleotides
... 2. Essential carriers of chemical energy, especially ATP 3. Components of the cofactors NAD+, FAD, and coenzyme A ...
... 2. Essential carriers of chemical energy, especially ATP 3. Components of the cofactors NAD+, FAD, and coenzyme A ...
Regulation of Hepatic Triacylglycerol Synthesis and Lipoprotein
... [ 181 through its action on carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Lack of insulin has also been reported to decrease the activity of glycerophosphate acyltransferase, particularly that in the mitochondria1 fraction [ 191. These changes promote the partitioning of fatty acids into poxidation and ketogenesi ...
... [ 181 through its action on carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Lack of insulin has also been reported to decrease the activity of glycerophosphate acyltransferase, particularly that in the mitochondria1 fraction [ 191. These changes promote the partitioning of fatty acids into poxidation and ketogenesi ...
Unit F214 - Communication, homeostasis and energy - High
... OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria for the new GCE specifications and to bridge the gap between new specification release and availability of exemplar candidate work. This content has been produced by senior OCR examiners, with ...
... OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the assessment criteria for the new GCE specifications and to bridge the gap between new specification release and availability of exemplar candidate work. This content has been produced by senior OCR examiners, with ...
lect4
... Excess or insufficient dietary amino acid intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
... Excess or insufficient dietary amino acid intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT)
... The class I facilitative transporters contain GLUT1– 4, and these have been comprehensively characterised in terms of structure, function and tissue distribution. GLUT1 is expressed particularly in the brain (including the blood – brain barrier) and erthyrocytes. Moderate levels of expression are al ...
... The class I facilitative transporters contain GLUT1– 4, and these have been comprehensively characterised in terms of structure, function and tissue distribution. GLUT1 is expressed particularly in the brain (including the blood – brain barrier) and erthyrocytes. Moderate levels of expression are al ...
GLUCOKINASE ACTIVATORS: A GLUCOSE SENSOR ROLE IN PANCREATIC ISLETS AND HEPATOCYTE
... GKAs are, small molecules with a considerable variety of chemical structures that mostly adhere to a common pharmacophore model with related structural moties. The model consists of a center of a carbon or an aromatic ring with three attachments to it. Two of these are hydrophobic, and at least one ...
... GKAs are, small molecules with a considerable variety of chemical structures that mostly adhere to a common pharmacophore model with related structural moties. The model consists of a center of a carbon or an aromatic ring with three attachments to it. Two of these are hydrophobic, and at least one ...
Zygorrhynchus moelleri
... Cells of the fungus Zygorrhynchus moelleri, when starved for 24 hr. in phosphate buffer and then supplied with glucose, show a lag period of 2-3 hr. before the rates of respiration and glucose utilization become constant a t their maximum values (Moses, 1954, 1955a). There is no appreciable lag with ...
... Cells of the fungus Zygorrhynchus moelleri, when starved for 24 hr. in phosphate buffer and then supplied with glucose, show a lag period of 2-3 hr. before the rates of respiration and glucose utilization become constant a t their maximum values (Moses, 1954, 1955a). There is no appreciable lag with ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑