18. Cardiovascular System: Blood
... begin the production of hemoglobin. The erythroblasts lose their nuclei to become reticulocytes, which enter the blood and become mature erythrocytes. Cells in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow typically phagocytize dead and dying erythrocytes (Fig. 18.8). These cells process hemoglobin, recycle th ...
... begin the production of hemoglobin. The erythroblasts lose their nuclei to become reticulocytes, which enter the blood and become mature erythrocytes. Cells in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow typically phagocytize dead and dying erythrocytes (Fig. 18.8). These cells process hemoglobin, recycle th ...
Chapter 33: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Every breath
... 1. High blood pressure (hypertension): when blood pressure in arteries remains above normal. Causes – stress, excessive salt consumption, cigarette smoking, heredity factors 2. Atherosclerosis: arteries become narrower and inelastic because of deposits of cholesterol & other fatty materials on their ...
... 1. High blood pressure (hypertension): when blood pressure in arteries remains above normal. Causes – stress, excessive salt consumption, cigarette smoking, heredity factors 2. Atherosclerosis: arteries become narrower and inelastic because of deposits of cholesterol & other fatty materials on their ...
Chapter 37
... of pearl inside • Filter feeders that are usually sessile can move w/foot • Incurrent & excurrent siphons to move water into and out of the body for respiration w/gills and for feeding • Mostly separate sexes w/external fertilization Size ranges from 1mm to 1.5 m ...
... of pearl inside • Filter feeders that are usually sessile can move w/foot • Incurrent & excurrent siphons to move water into and out of the body for respiration w/gills and for feeding • Mostly separate sexes w/external fertilization Size ranges from 1mm to 1.5 m ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... Chapter 13 Adapted form Tortora 10th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 405) 1. The cardiovascular system consists of: i. blood ii. heart iii. blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins) 2. Blood is a connective tissue composed of a liquid portion called plasma (the mat ...
... Chapter 13 Adapted form Tortora 10th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 405) 1. The cardiovascular system consists of: i. blood ii. heart iii. blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins) 2. Blood is a connective tissue composed of a liquid portion called plasma (the mat ...
Unit 1 - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... For test be able to analyze: o Calcium homeostasis (page 132) o Body temperature (page 7) o Water regulation (refer to notes) o Control center for sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of PNS o Effectors and response after sympathetic disruption of homeostasis occurs ...
... For test be able to analyze: o Calcium homeostasis (page 132) o Body temperature (page 7) o Water regulation (refer to notes) o Control center for sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of PNS o Effectors and response after sympathetic disruption of homeostasis occurs ...
Name Nick DiMucci
... neonate need so many anti-oxidants? Bilirubin is a byproduct of the normal breakdown of red blood cells. The liver processes bilirubin so that it can be excreted by the body as waste. At birth, a baby's liver is still developing its ability to process bilirubin. Therefore, bilirubin levels are a lit ...
... neonate need so many anti-oxidants? Bilirubin is a byproduct of the normal breakdown of red blood cells. The liver processes bilirubin so that it can be excreted by the body as waste. At birth, a baby's liver is still developing its ability to process bilirubin. Therefore, bilirubin levels are a lit ...
drugs-and-blood-presure-on-the
... This process of converting fat-soluble drugs into water soluble metabolites that can be excreted by the kidney is carried out in the liver. Usually (but not always) the process of metabolism decreases the pharmacological activity of a drug. Even though a metabolite might remain in the body (awaiting ...
... This process of converting fat-soluble drugs into water soluble metabolites that can be excreted by the kidney is carried out in the liver. Usually (but not always) the process of metabolism decreases the pharmacological activity of a drug. Even though a metabolite might remain in the body (awaiting ...
KS4 Blood Vessels
... These vessels link arteries with veins. They are found all over the body and are essential for the exchange of materials between the blood and other body cells. artery ...
... These vessels link arteries with veins. They are found all over the body and are essential for the exchange of materials between the blood and other body cells. artery ...
Lecture #17 - Suraj @ LUMS
... the bile, responsible for the color of feces. • Each second 2 million red blood cells are produced to replace those taken out of circulation. ...
... the bile, responsible for the color of feces. • Each second 2 million red blood cells are produced to replace those taken out of circulation. ...
Excretory System - ImperialSchoolWiki
... Along with all of these organs, frogs also exchange substances just like mammals through their skin. An example of this would be water. The Frogs excretory system starts by liquid wastes traveling from the kidneys to the ureters then to the urinary bladder. The solid wastes however pass into the ...
... Along with all of these organs, frogs also exchange substances just like mammals through their skin. An example of this would be water. The Frogs excretory system starts by liquid wastes traveling from the kidneys to the ureters then to the urinary bladder. The solid wastes however pass into the ...
Circulatory_System_Notes
... o Blood flows from the left atrium into the left ventricle as it relaxes. o The left ventricle then contracts to force blood out to the aorta. o Valves between the atrium and ventricle (AV valve) and between the ventricle and the aorta (semilunar valve) prevent blood from flowing backward. o Oxygena ...
... o Blood flows from the left atrium into the left ventricle as it relaxes. o The left ventricle then contracts to force blood out to the aorta. o Valves between the atrium and ventricle (AV valve) and between the ventricle and the aorta (semilunar valve) prevent blood from flowing backward. o Oxygena ...
tissue fluid
... phagocytosis. Usually first to arrive at the scene and attempt to destroy the pathogen. Phagocytosis – the process by which the phagocytic WBC puts our finger like projections and enclose a pathogen into a vacuole (enclosed space) in their cytoplasm. Then the WBC kills the pathogen. ...
... phagocytosis. Usually first to arrive at the scene and attempt to destroy the pathogen. Phagocytosis – the process by which the phagocytic WBC puts our finger like projections and enclose a pathogen into a vacuole (enclosed space) in their cytoplasm. Then the WBC kills the pathogen. ...
7th Grade Fall Semester Review 2011
... The bodily system consisting of the heart, blood vessels, and blood that circulates blood throughout the body, delivers nutrients and other essential materials to cells, and removes waste products ...
... The bodily system consisting of the heart, blood vessels, and blood that circulates blood throughout the body, delivers nutrients and other essential materials to cells, and removes waste products ...
Circulatory System
... • The circulatory system transport gases (i.e. O2 & CO2) and nutrients ( such as glucose and amino acids) throughout the body cells. • Transport metabolites and hormones. • Remove wastes (i.e. excretory p ...
... • The circulatory system transport gases (i.e. O2 & CO2) and nutrients ( such as glucose and amino acids) throughout the body cells. • Transport metabolites and hormones. • Remove wastes (i.e. excretory p ...
Transport of gases
... Mechanism of gas transport • Primary function is to obtain oxygen for use by body's cells & eliminate carbon dioxide that cells produce. • Includes respiratory airways leading into (& out of) lungs plus the lungs themselves • Pathway of air: nasal cavities (or oral cavity) > pharynx > trachea > pri ...
... Mechanism of gas transport • Primary function is to obtain oxygen for use by body's cells & eliminate carbon dioxide that cells produce. • Includes respiratory airways leading into (& out of) lungs plus the lungs themselves • Pathway of air: nasal cavities (or oral cavity) > pharynx > trachea > pri ...
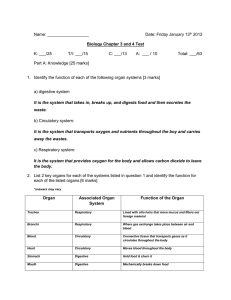
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
Human Body Review - effinghamschools.com
... blood and move through the circulatory system to the body cells. B The nutrients move from the small intestine directly to the liver and then move through the lymphatic system to the body cells. C The small intestine forces the nutrients into the kidneys, where the nutrients are then dissolved in fl ...
... blood and move through the circulatory system to the body cells. B The nutrients move from the small intestine directly to the liver and then move through the lymphatic system to the body cells. C The small intestine forces the nutrients into the kidneys, where the nutrients are then dissolved in fl ...
Lecture 16: The Nephron
... 2. Macula densa cells send a chemical message to afferent arteriole 3. Afferent arteriole releases renin (an enzyme) into the blood 4. Renin converts angiotensinogen in the blood to angiotensin I 5. Angiotensin I encounters “Angiotensin converting enzyme” (ACE), often in the lungs, and is turned ...
... 2. Macula densa cells send a chemical message to afferent arteriole 3. Afferent arteriole releases renin (an enzyme) into the blood 4. Renin converts angiotensinogen in the blood to angiotensin I 5. Angiotensin I encounters “Angiotensin converting enzyme” (ACE), often in the lungs, and is turned ...
Maintaining a Constant Internal Environment
... by a transport epithelium process filtrate to form urine reabsorb solutes and water •sugar, vitamins, and other organic nutrients from the initial filtrate and about 99% of the water reduce 180 L of initial filtrate to about 1.5 L of urine to be voided ...
... by a transport epithelium process filtrate to form urine reabsorb solutes and water •sugar, vitamins, and other organic nutrients from the initial filtrate and about 99% of the water reduce 180 L of initial filtrate to about 1.5 L of urine to be voided ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.