File - Groby Bio Page
... from respiring cells respectively; transport of digested food from the intestine to cells (1): transport of nitrogenous wastes from tissues to excretory organs (1); transport of : hormones (1); platelets (for clotting) (1) and antibodies (1);immune response (1); maintaining constant body temperature ...
... from respiring cells respectively; transport of digested food from the intestine to cells (1): transport of nitrogenous wastes from tissues to excretory organs (1); transport of : hormones (1); platelets (for clotting) (1) and antibodies (1);immune response (1); maintaining constant body temperature ...
Notes: Body Systems
... The skin uses UV light from the sun to make what vitamin? _____________________________ ...
... The skin uses UV light from the sun to make what vitamin? _____________________________ ...
Organization of the Body and General Systems
... 4. Ind. Muscles and groups, responsible for movement, etc. 5. Nose Alveoli, exchange of gases 6. Bones, support/protect/make blood 7. Node/spleen/tonsilsprotection,return of fluids 8. Skin/Hairmake Vit. D/prevent desiccation 9. MouthAnus, nutrients and water to the body ...
... 4. Ind. Muscles and groups, responsible for movement, etc. 5. Nose Alveoli, exchange of gases 6. Bones, support/protect/make blood 7. Node/spleen/tonsilsprotection,return of fluids 8. Skin/Hairmake Vit. D/prevent desiccation 9. MouthAnus, nutrients and water to the body ...
Blood Pressure and New Beginnings
... There’s a reason why high blood pressure is called “the silent killer.” What is blood pressure Your blood circulates throughout your body, being pushed through your arteries and veins by the contraction, or pumping of your heart. Blood moves through your lungs where it picks up oxygen and then is ci ...
... There’s a reason why high blood pressure is called “the silent killer.” What is blood pressure Your blood circulates throughout your body, being pushed through your arteries and veins by the contraction, or pumping of your heart. Blood moves through your lungs where it picks up oxygen and then is ci ...
Circulation
... Made in BONE MARROW Fight infection by causing an immune response. Known as phagocytes because they ...
... Made in BONE MARROW Fight infection by causing an immune response. Known as phagocytes because they ...
Heart Health - Wellness For All Seasons
... Heart Health: Keep Your Ticker in Tip-top Condition Did you know this about your amazing heart? • The human heart weighs between 7-15 ounces and measures about the size of your fist. • It functions as a pump, moving blood through thousands of miles of blood vessels, veins and arteries, pumping more ...
... Heart Health: Keep Your Ticker in Tip-top Condition Did you know this about your amazing heart? • The human heart weighs between 7-15 ounces and measures about the size of your fist. • It functions as a pump, moving blood through thousands of miles of blood vessels, veins and arteries, pumping more ...
Flamingo Final copy
... 3. Air enters lungs through trachea, bronchi break off of trachea 4. Bronchioles then branch off the two bronchi 5. At the tip of the thousands of each bronchiole are alveoli ...
... 3. Air enters lungs through trachea, bronchi break off of trachea 4. Bronchioles then branch off the two bronchi 5. At the tip of the thousands of each bronchiole are alveoli ...
Intro to animal structure and function powerpoint
... • Adjusting metabolic heat production (shivering) • Circulatory adaptations ...
... • Adjusting metabolic heat production (shivering) • Circulatory adaptations ...
Chapter 3 Notes - the NBTSC Community Site!
... - lymphatic vessels pick up most fats from the intestine and then transport them to the blood. - to make sure you have efficient circulation of fluid to all your cells, you need an ample fluid intake. This means drinking sufficient water to replace what is lost each day. Key point – Blood and lymph ...
... - lymphatic vessels pick up most fats from the intestine and then transport them to the blood. - to make sure you have efficient circulation of fluid to all your cells, you need an ample fluid intake. This means drinking sufficient water to replace what is lost each day. Key point – Blood and lymph ...
Animal Physiology an..
... Whilst there are no specific osmoregulatory organs in higher plants the stomata are important in regulating water loss through evapotranspiration and on the cellular level the vacuole is crucial in regulating the concentration of solutes in the cytoplasm. Strong winds, low humidity and high temperat ...
... Whilst there are no specific osmoregulatory organs in higher plants the stomata are important in regulating water loss through evapotranspiration and on the cellular level the vacuole is crucial in regulating the concentration of solutes in the cytoplasm. Strong winds, low humidity and high temperat ...
Human Systems Digestive Circulatory and Respiratory
... • Villi are thin for easy absorption & has an abundance of capillaries and lymph vessels. • All absorbed molecules are taken to body cells by the circulatory system • Nutrient molecule can be used for energy (glucose) or as a component to build a larger molecule (amino acids). – The process of build ...
... • Villi are thin for easy absorption & has an abundance of capillaries and lymph vessels. • All absorbed molecules are taken to body cells by the circulatory system • Nutrient molecule can be used for energy (glucose) or as a component to build a larger molecule (amino acids). – The process of build ...
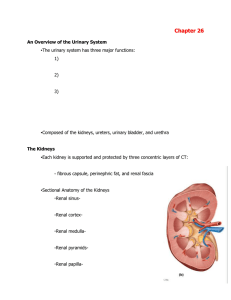
SChapter26
... -Renin is an enzyme released by the JGA when (1) blood pressure declines at the glomerulus, (2) juxtaglomerular cells are stimulated by sympathetic innervation, and (3) there is a decline in the osmotic concentration of the tubular fluid at the macula densa. *see figure 26-11 to refamiliarize yourse ...
... -Renin is an enzyme released by the JGA when (1) blood pressure declines at the glomerulus, (2) juxtaglomerular cells are stimulated by sympathetic innervation, and (3) there is a decline in the osmotic concentration of the tubular fluid at the macula densa. *see figure 26-11 to refamiliarize yourse ...
Ch 22-23
... Organ—contains different types of tissues each performing a function to aid in the overall action of the organ ...
... Organ—contains different types of tissues each performing a function to aid in the overall action of the organ ...
Human Body Introduction - Living Environment H: 8(A,C)
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
Rat Body Systems INTEGUMENTARY (Outer body covering) Skin
... TYMPANIC MEMBRANE (eardrum) inside head; 3 small bones in inner ear EYES see color/good DEPTH PERCEPTION (eyes on front of head) ENDOCRINE: The endocrine system in mammals is the most complex. The THYROID GLAND regulates metabolism, but many others such as the PITUITARY, ADRENAL, and PARATHYROID GLA ...
... TYMPANIC MEMBRANE (eardrum) inside head; 3 small bones in inner ear EYES see color/good DEPTH PERCEPTION (eyes on front of head) ENDOCRINE: The endocrine system in mammals is the most complex. The THYROID GLAND regulates metabolism, but many others such as the PITUITARY, ADRENAL, and PARATHYROID GLA ...
Body Systems
... • An organ system of glands in the body that secrete hormones that help to regulate the body. ▫ Hormone – a chemical messenger released into the bloodstream to create a response in the body; ...
... • An organ system of glands in the body that secrete hormones that help to regulate the body. ▫ Hormone – a chemical messenger released into the bloodstream to create a response in the body; ...
Review Guide for Anatomy and Physiology – Respiratory System
... For this class, think of partial pressure in terms of concentration. If a gas has higher partial pressure in a location, it means there is more of that gas (higher concentration) ...
... For this class, think of partial pressure in terms of concentration. If a gas has higher partial pressure in a location, it means there is more of that gas (higher concentration) ...
H+ Secretion
... Fate of H+ in the Urine • The amount of acid secreted depends upon the subsequent events in the tubular urine. • The maximal H+ gradient against which the transport mechanisms can secrete in humans corresponds to a urine pH of about 4.5, ie, an H+ concentration in the urine that is 1000 times the c ...
... Fate of H+ in the Urine • The amount of acid secreted depends upon the subsequent events in the tubular urine. • The maximal H+ gradient against which the transport mechanisms can secrete in humans corresponds to a urine pH of about 4.5, ie, an H+ concentration in the urine that is 1000 times the c ...
Tissues in the lungs
... The fluid that leaves the blood consists of plasma with dissolved nutrients and oxygen. All the blood cells and plasma proteins remain in the blood as these are too large to pass through the gaps. This fluid that leaves the capillary is known as the tissue fluid. This bathes the tissue cells allowin ...
... The fluid that leaves the blood consists of plasma with dissolved nutrients and oxygen. All the blood cells and plasma proteins remain in the blood as these are too large to pass through the gaps. This fluid that leaves the capillary is known as the tissue fluid. This bathes the tissue cells allowin ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.