BIO_103_22_Learning Targets
... b. Red, iron-containing hemoglobin i. is used by almost all vertebrates and many invertebrates and ii. transports oxygen, buffers blood, and transports CO2. 2. Most CO2 in the blood enters red blood cells. 3. Some CO2 combines with hemoglobin. 4. Other CO2 reacts with water, forming carbonic acid, w ...
... b. Red, iron-containing hemoglobin i. is used by almost all vertebrates and many invertebrates and ii. transports oxygen, buffers blood, and transports CO2. 2. Most CO2 in the blood enters red blood cells. 3. Some CO2 combines with hemoglobin. 4. Other CO2 reacts with water, forming carbonic acid, w ...
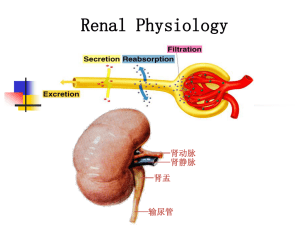
8、kidney organ
... About 65% -70% of the filtered load of sodium and water and a slightly lower percentage of filtered chloride are reabsorbed. Passive water reabsorption by osmosis is coupled mainly to sodium reabsorption. Reabsorption of chloride, urea, and other solutes by passive diffusion Essentially all the ...
... About 65% -70% of the filtered load of sodium and water and a slightly lower percentage of filtered chloride are reabsorbed. Passive water reabsorption by osmosis is coupled mainly to sodium reabsorption. Reabsorption of chloride, urea, and other solutes by passive diffusion Essentially all the ...
Blood - El Camino College
... II. Functions & Properties of Blood A. Transportation 1. Respiratory - RBCs pick up _______ from the lungs and take it to tissue cells for aerobic respiration. ______ from cellular respiration is carried in blood back to lungs for elimination. 2. Nutritive - blood carries digested _______ molecules ...
... II. Functions & Properties of Blood A. Transportation 1. Respiratory - RBCs pick up _______ from the lungs and take it to tissue cells for aerobic respiration. ______ from cellular respiration is carried in blood back to lungs for elimination. 2. Nutritive - blood carries digested _______ molecules ...
Respiratory Lecture Review
... 17. Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across the ALVEOLAR-CAPILLARY MEMBRANE, which consists of two single layers of SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM (one alveolar and one capillary) between which lie epithelial and capillary basement membranes which are often fused to one another. 18. The lungs have a double blo ...
... 17. Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across the ALVEOLAR-CAPILLARY MEMBRANE, which consists of two single layers of SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM (one alveolar and one capillary) between which lie epithelial and capillary basement membranes which are often fused to one another. 18. The lungs have a double blo ...
Chapter 49: Circulatory Systems
... Blood pressure (BP) is determined partly by cardiac output and partly by peripheral resistance due to variable constriction of the arterioles Arteriole smooth muscle also responds to endocrine and neural signals. • The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) innervates most arteri ...
... Blood pressure (BP) is determined partly by cardiac output and partly by peripheral resistance due to variable constriction of the arterioles Arteriole smooth muscle also responds to endocrine and neural signals. • The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) innervates most arteri ...
I. Types of respiration
... 1. Refers to the exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and the blood within the pulmonary capillaries a) Since the alveolus and the capillary are composed of a single layer of cells, diffusion alone accounts for gas exchange b) Carbon dioxide diffuses out because there is a greater concen ...
... 1. Refers to the exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and the blood within the pulmonary capillaries a) Since the alveolus and the capillary are composed of a single layer of cells, diffusion alone accounts for gas exchange b) Carbon dioxide diffuses out because there is a greater concen ...
CHAPTER 47, SECTIONS 1 AND 2 THE CIRCULATORY
... ______________ BLOOD CELLS (RBC), ________________ BLOOD CELLS (WBC), AND ___________________. RED BLOOD CELLS (RBC) ERTHROCYTES 1. RBC are the most ____________________ of the Blood Cells. One microliter of blood contains approx. 5 million RBCs. 2. RBC are _______________________, or shaped so that ...
... ______________ BLOOD CELLS (RBC), ________________ BLOOD CELLS (WBC), AND ___________________. RED BLOOD CELLS (RBC) ERTHROCYTES 1. RBC are the most ____________________ of the Blood Cells. One microliter of blood contains approx. 5 million RBCs. 2. RBC are _______________________, or shaped so that ...
Hemodialysis Study Guide
... Osmotic solution to draw interstitial fluid into vascular compartment for hypotension. Side effects are rare. ...
... Osmotic solution to draw interstitial fluid into vascular compartment for hypotension. Side effects are rare. ...
The Endocrine system
... Adrenal glands Located just above the kidney Secretes many hormones that deal with stress like adrenaline! ...
... Adrenal glands Located just above the kidney Secretes many hormones that deal with stress like adrenaline! ...
Organization of the Human Body
... • connective tissue: Group of cells that are all involved in supporting and binding other tissues of the body; i.e. tendon, cartilage, bone, and blood. • epithelial tissue: Layers of tightly packed cells that line the surfaces of the body. • muscle tissue: Bands of cells that contract and allow move ...
... • connective tissue: Group of cells that are all involved in supporting and binding other tissues of the body; i.e. tendon, cartilage, bone, and blood. • epithelial tissue: Layers of tightly packed cells that line the surfaces of the body. • muscle tissue: Bands of cells that contract and allow move ...
Blood Vessels - Austin Community College
... (exception: in the pulmonary circulation the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated) B. Arterioles These are small arteries that deliver blood to capillaries C. Capillaries These are the blood vessels with the smallest diameter (many are only lar ...
... (exception: in the pulmonary circulation the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated) B. Arterioles These are small arteries that deliver blood to capillaries C. Capillaries These are the blood vessels with the smallest diameter (many are only lar ...
Function of the Respiratory System
... Rate and Depth Stimuli • High concentrations of CO2 and H+ ions stimulate chemoreceptors in the medulla to increase breathing rate. • Low O2 concentration stimulate chemoreceptors in the Aorta and Carotid arteries to stimulate the medulla to increase breathing rate. • Fear and pain increase breathi ...
... Rate and Depth Stimuli • High concentrations of CO2 and H+ ions stimulate chemoreceptors in the medulla to increase breathing rate. • Low O2 concentration stimulate chemoreceptors in the Aorta and Carotid arteries to stimulate the medulla to increase breathing rate. • Fear and pain increase breathi ...
Cos-Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology
... • Bicep- muscle that produces the contour of the front and inner side of the arm; lifts the forearm and flexes the elbow • Deltoid- large, triangular muscle covering the shoulder joint; allows the arm to extend outward and to the side of the body • Tricep- large muscle that covers the entire back of ...
... • Bicep- muscle that produces the contour of the front and inner side of the arm; lifts the forearm and flexes the elbow • Deltoid- large, triangular muscle covering the shoulder joint; allows the arm to extend outward and to the side of the body • Tricep- large muscle that covers the entire back of ...
GAS EXCHANGE SURFACES FOR BIO
... can result in almost all of the property being transferred. By contrast, in the concurrent (or co-current, parallel) exchange system the two fluid flows are in the same direction. As the diagram shows, a concurrent exchange system has a variable gradient over the length of the exchanger and is only ...
... can result in almost all of the property being transferred. By contrast, in the concurrent (or co-current, parallel) exchange system the two fluid flows are in the same direction. As the diagram shows, a concurrent exchange system has a variable gradient over the length of the exchanger and is only ...
document
... – Dendrites – receive impulses from neuron – Axon – send impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, glands, or muscles – Nerves – nerve fibers held together by connective tissue through which impulses are transmitted ...
... – Dendrites – receive impulses from neuron – Axon – send impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, glands, or muscles – Nerves – nerve fibers held together by connective tissue through which impulses are transmitted ...
Grade 11 College Biology – Unit 3
... body. ARTERIES are very elastic vessels that stretch each time the heart pumps blood. CAPILLARIES are tiny blood vessels connecting arteries to veins. It is in the capillaries that the exchange of nutrients, salts, oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs between cells and the blood. VEINS carry blood back ...
... body. ARTERIES are very elastic vessels that stretch each time the heart pumps blood. CAPILLARIES are tiny blood vessels connecting arteries to veins. It is in the capillaries that the exchange of nutrients, salts, oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs between cells and the blood. VEINS carry blood back ...
Student Material - CBSE
... Single celled organisms or primitive multicellular organisms are simple in body organization, as compared to the complex organ systems found in humans, the former are considered as lower organisms. They do not have a proper transport system. Why? Their body surface is in constant contact with their ...
... Single celled organisms or primitive multicellular organisms are simple in body organization, as compared to the complex organ systems found in humans, the former are considered as lower organisms. They do not have a proper transport system. Why? Their body surface is in constant contact with their ...
End of chapter review excretory system
... 4. How is excretory system different from the other three body systems: circulatory, respiratory and digestive systems? ...
... 4. How is excretory system different from the other three body systems: circulatory, respiratory and digestive systems? ...
Chapter 1 Introduction 一、名词解释 1.Human Physiology Physiology
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------11.A patient complains of several days of vomiting and diarrhea and is found to have a reduced effective circulating volume that activates the sympathetic nervous system. In this case, activation of the sympathetic nervou ...
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------11.A patient complains of several days of vomiting and diarrhea and is found to have a reduced effective circulating volume that activates the sympathetic nervous system. In this case, activation of the sympathetic nervou ...
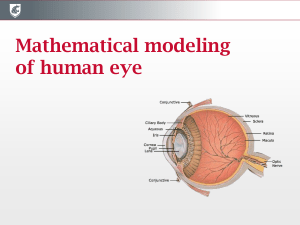
slides - WSU Department of Mathematics
... CDI and waveform parameters • Significant blood velocity derangements in the OA, CRA, and PCAs are associated with diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma • CDI is a consolidated noninvasive technique to measure blood velocity profile in some of the major ocular vessels • Typical waveform parameters util ...
... CDI and waveform parameters • Significant blood velocity derangements in the OA, CRA, and PCAs are associated with diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma • CDI is a consolidated noninvasive technique to measure blood velocity profile in some of the major ocular vessels • Typical waveform parameters util ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.