Evolution: Natural Selection II
... Natural selection has to act with the trait (body colour) that butterflies clearly need to survive and to reproduce as males or females. In a whiterock island, black butterflies are more easily identified by birds due to their body colour on white-coloured rocks. Therefore they will tend to become c ...
... Natural selection has to act with the trait (body colour) that butterflies clearly need to survive and to reproduce as males or females. In a whiterock island, black butterflies are more easily identified by birds due to their body colour on white-coloured rocks. Therefore they will tend to become c ...
16.1 Darwin`s Voyage of Discovery
... Lamarck’s Evolutionary Hypothesis Jean-Baptiste Lamarck was one of the first scientists to propose hypotheses about how evolution occurred. To explain evolution, Lamarck hypothesized that all organisms have an inborn drive to become more complex and perfect. According to Lamarck, an organism could g ...
... Lamarck’s Evolutionary Hypothesis Jean-Baptiste Lamarck was one of the first scientists to propose hypotheses about how evolution occurred. To explain evolution, Lamarck hypothesized that all organisms have an inborn drive to become more complex and perfect. According to Lamarck, an organism could g ...
No Slide Title
... Variation of Traits Within a Population, cont. • Causes of Variation – Traits vary and can be mapped along a bell curve, which shows that most individuals have average traits, whereas a few individuals have extreme traits. – Variations in genotype arise by mutation (random change in a gene that is p ...
... Variation of Traits Within a Population, cont. • Causes of Variation – Traits vary and can be mapped along a bell curve, which shows that most individuals have average traits, whereas a few individuals have extreme traits. – Variations in genotype arise by mutation (random change in a gene that is p ...
Variation 03.24.04
... that survived showed that: – the larger birds were favored over the smaller ones – birds with larger beaks were favored over those with smaller ones. ...
... that survived showed that: – the larger birds were favored over the smaller ones – birds with larger beaks were favored over those with smaller ones. ...
Darwin and Evolution
... Hardy-Weinberg Principle • Genetic Equilibrium – situation in which allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population remain constant • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occurs during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. • Shows math ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Principle • Genetic Equilibrium – situation in which allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population remain constant • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occurs during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. • Shows math ...
Evolution of Galapagos Island Finches The finches on the
... Q. 3 Using beak size as an example, identify two things that must be true in order for natural selection to be capable of producing the diversity observed. Peter and Rosemary Grant from Princeton University spent twenty years studying the finches in order to test the hypothesis that natural selectio ...
... Q. 3 Using beak size as an example, identify two things that must be true in order for natural selection to be capable of producing the diversity observed. Peter and Rosemary Grant from Princeton University spent twenty years studying the finches in order to test the hypothesis that natural selectio ...
Evolution and Natural Selection (PowerPoint) Madison 2009
... A. When parent lizards learn to catch particular insects, their offspring can inherit their specific insect-catching-skills. B. When parent lizards develop stronger claws through repeated use in catching prey, their offspring can inherit their stronger-claw trait. C. When parent lizards’ claws are u ...
... A. When parent lizards learn to catch particular insects, their offspring can inherit their specific insect-catching-skills. B. When parent lizards develop stronger claws through repeated use in catching prey, their offspring can inherit their stronger-claw trait. C. When parent lizards’ claws are u ...
File
... into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see but bees can’t. Cardinal flower’s pollen structure is just the right length for the hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds. SCENARIO 2: In the ocean surrounding Antarctica, there are fish that survive the cold water by ...
... into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see but bees can’t. Cardinal flower’s pollen structure is just the right length for the hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds. SCENARIO 2: In the ocean surrounding Antarctica, there are fish that survive the cold water by ...
AP Biology Natural Selection Unit 1 HW Sheet
... Natural Selection. If you don’t have 3 questions, write questions to predict how this material can show up on your test. Lesson 3: Population Genetics and Preserving Genetic Diversity Watch the video at https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/crash-coursebiology-science/v/crash-course-biology-11 ...
... Natural Selection. If you don’t have 3 questions, write questions to predict how this material can show up on your test. Lesson 3: Population Genetics and Preserving Genetic Diversity Watch the video at https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/crash-coursebiology-science/v/crash-course-biology-11 ...
What is a population? Review of Genetics Terminology
... Trend toward reducing phenotypic variation and maintenance of the status quo Individuals with the average phenotype (center) are selected Examples: Tuatara reptiles – very little change over long periods of time Birth weight of humans – too small or too large tend to have lower survival rates Se ...
... Trend toward reducing phenotypic variation and maintenance of the status quo Individuals with the average phenotype (center) are selected Examples: Tuatara reptiles – very little change over long periods of time Birth weight of humans – too small or too large tend to have lower survival rates Se ...
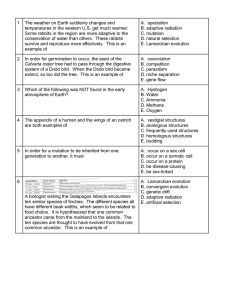
1 The weather on Earth suddenly changes and temperatures in the
... small, isolated island in the Caribbean. Scientists counted the number of turtles and measured the size of each turtle. Fifty years later, a second team of scientists observed the turtles. They again counted and measured the size. What happened to the population ...
... small, isolated island in the Caribbean. Scientists counted the number of turtles and measured the size of each turtle. Fifty years later, a second team of scientists observed the turtles. They again counted and measured the size. What happened to the population ...
Sexual selection: endless forms or tangled bank?
... this point extremely clear, for sexual selection to be ‘wrong’ and not to occur at all (as suggested by Roughgarden et al. 2006), we have to show that one or both of the premises of the syllogism underlying sexual selection are always untrue in natural populations. As such, either there would never ...
... this point extremely clear, for sexual selection to be ‘wrong’ and not to occur at all (as suggested by Roughgarden et al. 2006), we have to show that one or both of the premises of the syllogism underlying sexual selection are always untrue in natural populations. As such, either there would never ...
actionbioscience.org lesson Natural Selection(February 2006)
... 1. Rewriting Darwin and Wallace's Idea in Today’s Terms Darwin and Wallace postulated that natural selection acted on organisms to select the individuals within populations that had the best overall collection of adaptive features suiting their environment, for survival and differential reproduction ...
... 1. Rewriting Darwin and Wallace's Idea in Today’s Terms Darwin and Wallace postulated that natural selection acted on organisms to select the individuals within populations that had the best overall collection of adaptive features suiting their environment, for survival and differential reproduction ...
Darwin - Integrative Biology
... • biological richness of tropical forests: although not evidence of evolution it got Darwin thinking about the huge diversity of living organisms • fossils related to living animals in the same area • oceanic islands species: related to each other and to species on closest mainland • geographic dist ...
... • biological richness of tropical forests: although not evidence of evolution it got Darwin thinking about the huge diversity of living organisms • fossils related to living animals in the same area • oceanic islands species: related to each other and to species on closest mainland • geographic dist ...
Chapter 23 Practice Multiple Choice
... a. sexual dimorphism was developing over time in these species. b. intrasexual selection seems to have occurred. c. the "good genes" hypothesis was refuted by these data. d. stabilizing selection was occurring in these species concerning larynx size. e. selection was acting more directly upon genoty ...
... a. sexual dimorphism was developing over time in these species. b. intrasexual selection seems to have occurred. c. the "good genes" hypothesis was refuted by these data. d. stabilizing selection was occurring in these species concerning larynx size. e. selection was acting more directly upon genoty ...
How Populations Evolve - Mrs. Ford MHS Biology
... each result in microevolution, but only by chance could these events improve a population’s fit to its environment. o Natural selection is a blend of o chance and o sorting. ...
... each result in microevolution, but only by chance could these events improve a population’s fit to its environment. o Natural selection is a blend of o chance and o sorting. ...
RUNAWAY SEXUAL SELECTION LEADS TO GOOD GENES
... the “increment-display” instruction was disabled, preventing organisms from developing displays, and thus eliminating variation in the display. In the “display only” treatment, our second negative control, the “increment-display” instruction was enabled, but mutations causing mating preferences were ...
... the “increment-display” instruction was disabled, preventing organisms from developing displays, and thus eliminating variation in the display. In the “display only” treatment, our second negative control, the “increment-display” instruction was enabled, but mutations causing mating preferences were ...
Popgen_shou_week2
... variation, regeneration by mutation may take a million or more generations (unlikely to occur during the lifespan of the species) • Mutation is almost entirely ineffective in generating useful variation in small populations and probably too slow to help species of ...
... variation, regeneration by mutation may take a million or more generations (unlikely to occur during the lifespan of the species) • Mutation is almost entirely ineffective in generating useful variation in small populations and probably too slow to help species of ...
History of the Theory Notes (15.1)
... Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes in ancestral species. Darwin inferred that if humans could change species by artificial selection, then perhaps the same process could work in nature (natural selection). ...
... Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes in ancestral species. Darwin inferred that if humans could change species by artificial selection, then perhaps the same process could work in nature (natural selection). ...
CHAPTER 22
... ○ The rest are eaten, starved, diseased, unmated, or unable to tolerate physical conditions of the environment, such as salinity or temperature. ...
... ○ The rest are eaten, starved, diseased, unmated, or unable to tolerate physical conditions of the environment, such as salinity or temperature. ...
Darwin Formulates His Theory - Hatboro
... As Darwin contemplated a mechanism for evolutionary change, he began to construct a scientific theory built on observations, inferences, and ideas from his own work and the work of others. From his observations Darwin developed his theory of natural selection. In 1844, Darwin wrote a 200-page essay ...
... As Darwin contemplated a mechanism for evolutionary change, he began to construct a scientific theory built on observations, inferences, and ideas from his own work and the work of others. From his observations Darwin developed his theory of natural selection. In 1844, Darwin wrote a 200-page essay ...
Darwin Formulates His Theory
... As Darwin contemplated a mechanism for evolutionary change, he began to construct a scientific theory built on observations, inferences, and ideas from his own work and the work of others. From his observations Darwin developed his theory of natural selection. In 1844, Darwin wrote a 200-page essay ...
... As Darwin contemplated a mechanism for evolutionary change, he began to construct a scientific theory built on observations, inferences, and ideas from his own work and the work of others. From his observations Darwin developed his theory of natural selection. In 1844, Darwin wrote a 200-page essay ...
File
... • Species tend to be more closely related to other species from the same area than to other species with the same way of life, but living in different areas. • For example, even though some marsupial mammals (those that complete their development in an external pouch) of Australia have look-alikes a ...
... • Species tend to be more closely related to other species from the same area than to other species with the same way of life, but living in different areas. • For example, even though some marsupial mammals (those that complete their development in an external pouch) of Australia have look-alikes a ...
Preventing Sexual Harassment
... – Submission to or rejection of such conduct by an individual is used as the basis for employment or academic decisions affecting such individual – Such conduct has the purpose or effect of unreasonably interfering with an individual’s employment or academic performance or creating an intimidating, ...
... – Submission to or rejection of such conduct by an individual is used as the basis for employment or academic decisions affecting such individual – Such conduct has the purpose or effect of unreasonably interfering with an individual’s employment or academic performance or creating an intimidating, ...
Sexual selection

Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection where typically members of one gender choose mates of the other gender to mate with, called intersexual selection, and where females normally do the choosing, and competition between members of the same gender to sexually reproduce with members of the opposite sex, called intrasexual selection. These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have better reproductive success than others within a population either from being sexier or preferring sexier partners to produce offspring. For instance in the breeding season sexual selection in frogs occurs with the males first gathering at the water's edge and croaking. The females then arrive and choose the males with the deepest croaks and best territories. Generalizing, males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to a group of fertile females. Females have a limited number of offspring they can have and they maximize the return on the energy they invest in reproduction.First articulated by Charles Darwin who described it as driving speciation and that many organisms had evolved features whose function was deleterious to their individual survival, and then developed by Ronald Fisher in the early 20th century. Sexual selection can lead typically males to extreme efforts to demonstrate their fitness to be chosen by females, producing secondary sexual characteristics, such as ornate bird tails like the peacock plumage, or the antlers of deer, or the manes of lions, caused by a positive feedback mechanism known as a Fisherian runaway, where the passing on of the desire for a trait in one sex is as important as having the trait in the other sex in producing the runaway effect. Although the sexy son hypothesis indicates that females would prefer male sons, Fisher's principle explains why the sex ratio is 1:1 almost without exception. Sexual selection is also found in plants and fungi.The maintenance of sexual reproduction in a highly competitive world has long been one of the major mysteries of biology given that asexual reproduction can reproduce much more quickly as 50% of offspring are not males, unable to produce offspring themselves. However, research published in 2015 indicates that sexual selection can explain the persistence of sexual reproduction.