1. Overview
... • Coordinates can be extracted and viewed • Comparisons of structures allows identification of structural motifs • Proteins with similar functions and sequences = homologs ...
... • Coordinates can be extracted and viewed • Comparisons of structures allows identification of structural motifs • Proteins with similar functions and sequences = homologs ...
Slide 1
... the cysteine chains that are close together to form disulfide bridges. As a result, the hair will remain in the shape that it was held after the perm. This will last until the disulfide bridges naturally break down. If you have very curly hair, the protein in your hair contains a more cysteine than ...
... the cysteine chains that are close together to form disulfide bridges. As a result, the hair will remain in the shape that it was held after the perm. This will last until the disulfide bridges naturally break down. If you have very curly hair, the protein in your hair contains a more cysteine than ...
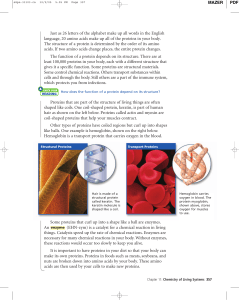
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
Histone Methylation
... by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence – hence the name epi- (Greek: επί- over, above, outer) -genetics. It refers to functionally relevant modifications to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of such modifications are DNA methylation ...
... by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence – hence the name epi- (Greek: επί- over, above, outer) -genetics. It refers to functionally relevant modifications to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of such modifications are DNA methylation ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Part 1 a. What is DNA transcription? Where and why does it occur? In other words - why is it such an important process? Describe the major steps involved in transcription & explain how DNA serves as a “Code” (or template)for the production of the building blocks of an organism. Think helicase to unw ...
... Part 1 a. What is DNA transcription? Where and why does it occur? In other words - why is it such an important process? Describe the major steps involved in transcription & explain how DNA serves as a “Code” (or template)for the production of the building blocks of an organism. Think helicase to unw ...
Who should get the Nobel prize Who are my all
... from dirty hay, crocodiles from rotting logs at the bottom of bodies of water, and so on. After ca. 2000 years this nonsense idea went away! 3: Creationism:…oh god! Still there… 4: Abiogenesis: Biological life arises from inorganic matter through natural processes. What we will discuss today. ...
... from dirty hay, crocodiles from rotting logs at the bottom of bodies of water, and so on. After ca. 2000 years this nonsense idea went away! 3: Creationism:…oh god! Still there… 4: Abiogenesis: Biological life arises from inorganic matter through natural processes. What we will discuss today. ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
DNA replication
... transcribed into mRNA; – (ii) translation, during which mRNA is translated to produce a protein. DNA mRNA protein Other important aspects of regulation: methylation, alternative splicing, etc. ...
... transcribed into mRNA; – (ii) translation, during which mRNA is translated to produce a protein. DNA mRNA protein Other important aspects of regulation: methylation, alternative splicing, etc. ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation Lab
... Each amino acid is matched with one or more 3-letter “words.” The words are analogous to an amino acid. When the words are put together they make a sentence. The sentence is analogous to a protein. So, let’s break the following code. 10. Given the following DNA code, how would this segment be transc ...
... Each amino acid is matched with one or more 3-letter “words.” The words are analogous to an amino acid. When the words are put together they make a sentence. The sentence is analogous to a protein. So, let’s break the following code. 10. Given the following DNA code, how would this segment be transc ...
1.5 Page 4 - csfcbiology
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... control your characteristics? DNA contains instructions for all the proteins your body makes. Proteins, in turn, determine the structure and function of all your cells. What determines a protein’s structure? It begins with the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making ...
... control your characteristics? DNA contains instructions for all the proteins your body makes. Proteins, in turn, determine the structure and function of all your cells. What determines a protein’s structure? It begins with the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making ...
protein synthesis
... Proteins are transferred during their synthesis to the lumen of ER This is aided by a signal sequence at the terminus of the synthesized protein, which binds with a signal recognition particle to a pore protein present in the ER membrane and thus directs the protein to the ER lumen In such cas ...
... Proteins are transferred during their synthesis to the lumen of ER This is aided by a signal sequence at the terminus of the synthesized protein, which binds with a signal recognition particle to a pore protein present in the ER membrane and thus directs the protein to the ER lumen In such cas ...
`RNA world`.
... It has ceded primacy as the repository of genetic information to DNA but it has gained versatility. It is a master architect, forming complex, threedimensional structures, and it can carry out catalysis, a trick it learned long before proteins knew how to be enzymes. In short, life probably evolved ...
... It has ceded primacy as the repository of genetic information to DNA but it has gained versatility. It is a master architect, forming complex, threedimensional structures, and it can carry out catalysis, a trick it learned long before proteins knew how to be enzymes. In short, life probably evolved ...
Discovery of potent inhibitors of the epigenetic cancer target PRMT4
... [5] Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumormicroenvironment. Cell. 2010;141(1):52-67. [6] Majumder S, Liu Y, Ford OH, 3rd, Mohler JL, Whang YE. Involvement of argininemethyltransferase CARM1 in androgen receptor function and prostate cancer cell viability. ...
... [5] Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumormicroenvironment. Cell. 2010;141(1):52-67. [6] Majumder S, Liu Y, Ford OH, 3rd, Mohler JL, Whang YE. Involvement of argininemethyltransferase CARM1 in androgen receptor function and prostate cancer cell viability. ...
DNA/RNA
... directions for one gene and transport it to a ribosome in the cytoplasm where it is translated. – This is so the cell can begin assembling amino acids, the building blocks of proteins – Like it’s name, it is sending a message on how to do the job – This is part of a process called ...
... directions for one gene and transport it to a ribosome in the cytoplasm where it is translated. – This is so the cell can begin assembling amino acids, the building blocks of proteins – Like it’s name, it is sending a message on how to do the job – This is part of a process called ...
Gene Expression
... absolute and relative quantification methods. The former method is distinguished from the later method by reference to a standard curve versus reference to another reference sample. This distinction is misleading and should not be used. Absolute quantification is a myth, because all readings are rel ...
... absolute and relative quantification methods. The former method is distinguished from the later method by reference to a standard curve versus reference to another reference sample. This distinction is misleading and should not be used. Absolute quantification is a myth, because all readings are rel ...
157KB - NZQA
... the function of the final protein. When A is substituted into the DNA sequence instead of T, it still has the right number of bases to produce a final protein. However, a new amino acid is included, and this will affect final protein shape and functioning. Substitution mutation involves the exchange ...
... the function of the final protein. When A is substituted into the DNA sequence instead of T, it still has the right number of bases to produce a final protein. However, a new amino acid is included, and this will affect final protein shape and functioning. Substitution mutation involves the exchange ...
63KB - NZQA
... make a polypeptide / protein. The purpose of translation is explained: to use mRNA to make a polypeptide / protein. So that the protein can be used for cellular functions (or named example given e.g. to make an enzyme). The process of transcription is described: e.g. DNA unwinds and a single mRNA st ...
... make a polypeptide / protein. The purpose of translation is explained: to use mRNA to make a polypeptide / protein. So that the protein can be used for cellular functions (or named example given e.g. to make an enzyme). The process of transcription is described: e.g. DNA unwinds and a single mRNA st ...
protein
... Pure proteins can be used to determine what other proteins or molecules they might interact with. Pure proteins are needed for studies of protein function (e.g. Are there regulatory subunits? Is it phosphorylated? Is the protein regulated by its interactions with other proteins? Etc.) ...
... Pure proteins can be used to determine what other proteins or molecules they might interact with. Pure proteins are needed for studies of protein function (e.g. Are there regulatory subunits? Is it phosphorylated? Is the protein regulated by its interactions with other proteins? Etc.) ...
Genome Anatomy - K
... biology, which means that many of the relevant genes can be recognized because their protein products are known. • Genes whose products have not yet been identified are more likely to be involved in the less well studied areas of cellular activity. ...
... biology, which means that many of the relevant genes can be recognized because their protein products are known. • Genes whose products have not yet been identified are more likely to be involved in the less well studied areas of cellular activity. ...
Isolation and expression of an allergen
... Conserved cysteine residues are identified with an asterisk (*). Sequences were aligned by the CLUSTAL program. Dashes (-) were added to optimize the alignment. ...
... Conserved cysteine residues are identified with an asterisk (*). Sequences were aligned by the CLUSTAL program. Dashes (-) were added to optimize the alignment. ...
experimental design
... generation of first strand cDNA in a 25µl reaction volume. 1µg of RNA (5~10µl), 1µl of oligo(dT)18 (500µg/ml) and 1µl dNTP mix (Invitrogen, Catalog No. 18427) were incubated at 70℃ for 10 min and quick chilled on ice. All other steps were performed according to manufacturer’s instructions except tha ...
... generation of first strand cDNA in a 25µl reaction volume. 1µg of RNA (5~10µl), 1µl of oligo(dT)18 (500µg/ml) and 1µl dNTP mix (Invitrogen, Catalog No. 18427) were incubated at 70℃ for 10 min and quick chilled on ice. All other steps were performed according to manufacturer’s instructions except tha ...
Molecular biology: Gene cloning
... copies not only of itself, but also of the gene that it carries. When the host cell divides, copies of the recombinant DNA molecule are passed to the progeny and further vector replication takes place. After a large number of cell divisions, a colony or clone of identical host cells is produced. Eac ...
... copies not only of itself, but also of the gene that it carries. When the host cell divides, copies of the recombinant DNA molecule are passed to the progeny and further vector replication takes place. After a large number of cell divisions, a colony or clone of identical host cells is produced. Eac ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.