Multi-Sensory Neurons
... “real” things. For instance, the ease with which your eye can be deceived is because it only processing representations of things, not the actual things, and likewise, exactly what is actually making a sound and exactly where it is in space are often difficult for hearing – ever tried to find the b ...
... “real” things. For instance, the ease with which your eye can be deceived is because it only processing representations of things, not the actual things, and likewise, exactly what is actually making a sound and exactly where it is in space are often difficult for hearing – ever tried to find the b ...
Slide 1
... Electrical stimulation of A11 depresses nociceptive input to spinal cord dorsal horn neurons ...
... Electrical stimulation of A11 depresses nociceptive input to spinal cord dorsal horn neurons ...
sensory receptors, neuronal circuits for processing information
... These receptors are referred to collectively as low-threshold (or high-sensitivity) mechanoreceptors because even weak mechanical stimulation of the skin induces them to produce action potentials. All low-threshold mechanoreceptors are innervated by relatively large myelinated axons ensuring the rap ...
... These receptors are referred to collectively as low-threshold (or high-sensitivity) mechanoreceptors because even weak mechanical stimulation of the skin induces them to produce action potentials. All low-threshold mechanoreceptors are innervated by relatively large myelinated axons ensuring the rap ...
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord
... Adaptation Adaptation - generator potential or receptor potential decreases in amplitude during a maintained stimulus. Rapidly adapting - e.g. pressure, touch, smell Slowly adapting - e.g. pain, body position ...
... Adaptation Adaptation - generator potential or receptor potential decreases in amplitude during a maintained stimulus. Rapidly adapting - e.g. pressure, touch, smell Slowly adapting - e.g. pain, body position ...
File
... complex processing of information by the brain In a reflex action, sensory neurones detect the stimulus e.g. Heat, and information is passed (via electrical impulses) to the relay neurone. The relay neurone sends the information to the motor neurone, and the motor neurone sends the information (vi ...
... complex processing of information by the brain In a reflex action, sensory neurones detect the stimulus e.g. Heat, and information is passed (via electrical impulses) to the relay neurone. The relay neurone sends the information to the motor neurone, and the motor neurone sends the information (vi ...
The Nervous System
... • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
... • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
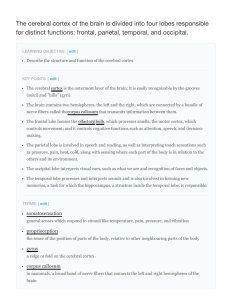
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... piece of nervous system tissue called the cerebral cortex, which is folded into hills called gyri (singular: gyrus) and valleys called sulci (singular: sulcus). The cortex is composed of two hemispheres, right and left, which are separated by a large sulcus. A thick fiber bundle, the corpus callosum ...
... piece of nervous system tissue called the cerebral cortex, which is folded into hills called gyri (singular: gyrus) and valleys called sulci (singular: sulcus). The cortex is composed of two hemispheres, right and left, which are separated by a large sulcus. A thick fiber bundle, the corpus callosum ...
I. Introduction
... b. The two expanded chambers within the vestibule are _______________ ____________________________________________________________ c. The macula is ______________________________________________ d. When the head is upright, the hairs of the macula in the utricle project _______________ and those of ...
... b. The two expanded chambers within the vestibule are _______________ ____________________________________________________________ c. The macula is ______________________________________________ d. When the head is upright, the hairs of the macula in the utricle project _______________ and those of ...
Nervous system - Yr-9-Health
... Myelin – an insulating lining that covers the nerves and increases neural transmission speeds. Multiple Sclerosis is a disease of the myelin sheath that may cause many different symptoms. ...
... Myelin – an insulating lining that covers the nerves and increases neural transmission speeds. Multiple Sclerosis is a disease of the myelin sheath that may cause many different symptoms. ...
What is RF diathermy?
... pulses (controlled by the user) are thought to suppress pain signals to the brain and encourage the body to produce higher levels of its own natural pain killing chemicals called endorphins. It is widely used around the world for a variety of painful conditions by private individuals, professionals ...
... pulses (controlled by the user) are thought to suppress pain signals to the brain and encourage the body to produce higher levels of its own natural pain killing chemicals called endorphins. It is widely used around the world for a variety of painful conditions by private individuals, professionals ...
Types of Receptors
... fluid surrounding the cells to be detected • Olfactory cells undergo adaptation rapidly for ...
... fluid surrounding the cells to be detected • Olfactory cells undergo adaptation rapidly for ...
Outline
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
Outline - MrGalusha.org
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
Slide 1
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
7. The Nervous System Identify the major structures and areas of the
... Identify the major structures and areas of the brain and describe their functions The brain is comprised of three main parts: 1. Forebrain o Cerebral hemispheres § Largest part of brain and maintains muscle tone, coordinates movement and stores memories of skilled movement e.g. walking and dr ...
... Identify the major structures and areas of the brain and describe their functions The brain is comprised of three main parts: 1. Forebrain o Cerebral hemispheres § Largest part of brain and maintains muscle tone, coordinates movement and stores memories of skilled movement e.g. walking and dr ...
ANIMAL RESPONSES TO ENVIRONMENT
... • All the organs and systems of the body work together to create this stable internal condition. • The process of maintaining a constant cell environment in the body is called homeostasis. • The endocrine and nervous systems, as our co-ordinating systems, play a very important part in regulating hom ...
... • All the organs and systems of the body work together to create this stable internal condition. • The process of maintaining a constant cell environment in the body is called homeostasis. • The endocrine and nervous systems, as our co-ordinating systems, play a very important part in regulating hom ...
PPT (20-21)
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
... When the head moves, the fluid sloshes around and bends the hairs. As each hair bends, it makes its nerve cell send a signal, telling the brain about that movement. • When we spin around, the fluid starts spinning, too. That gives us the sensation of spinning. When we stop, the fluid keeps moving (a ...
Chapter 15 Anatomy & Physiology
... • The vibration frequency of the perilymph will be enhanced at a specific resonating region along the basilar membrane: the higher frequencies are closer to the oval window and the lower frequencies are at the further end of the cochlea. • The position oriented movement of basilar membrane moves ha ...
... • The vibration frequency of the perilymph will be enhanced at a specific resonating region along the basilar membrane: the higher frequencies are closer to the oval window and the lower frequencies are at the further end of the cochlea. • The position oriented movement of basilar membrane moves ha ...
Sheet#6 Motor system
... -Both crossed extension reflex and nociceptive reflex sends impulses to more than one muscle (complex muscle). -The smallest body reflex (in the number of neurons) is the muscle stretch reflex, requiring only a sensory and a motor neuron (NO intermediate neurons). - All of these reflexes happen on d ...
... -Both crossed extension reflex and nociceptive reflex sends impulses to more than one muscle (complex muscle). -The smallest body reflex (in the number of neurons) is the muscle stretch reflex, requiring only a sensory and a motor neuron (NO intermediate neurons). - All of these reflexes happen on d ...
Motor Systems - People Server at UNCW
... the patient moves the hand randomly in space or uses the hand as the object itself, such as using the forefinger and middle finger as blades of the scissors. They have additional trouble sequencing the correct series of movements and make errors in orienting their limbs in space consistent with the ...
... the patient moves the hand randomly in space or uses the hand as the object itself, such as using the forefinger and middle finger as blades of the scissors. They have additional trouble sequencing the correct series of movements and make errors in orienting their limbs in space consistent with the ...
BRAIN
... sends memories out to the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary Plays important role in motivation and learning ...
... sends memories out to the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary Plays important role in motivation and learning ...
spinal cord - Dr Magrann
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
Senses - Peoria Public Schools
... • respond to mechanical forces proprioceptors –tensions of muscles and tendons baroreceptors – blood pressure stretch receptors – inflation in lungs Photoreceptors • respond to light ...
... • respond to mechanical forces proprioceptors –tensions of muscles and tendons baroreceptors – blood pressure stretch receptors – inflation in lungs Photoreceptors • respond to light ...
Lecture 1- Electromyography
... →recruitment of MUs →↑number & size of MUAPs. At full contraction separate MUAPs will be indistinguishable resulting in a complete recruitment = interference pattern. ...
... →recruitment of MUs →↑number & size of MUAPs. At full contraction separate MUAPs will be indistinguishable resulting in a complete recruitment = interference pattern. ...
Chapter 20
... nonliving substance called matrix • Loose connective tissue – binding & packaging material, holding other organs & tissues in place • Adipose tissue – contains fat, pads, ...
... nonliving substance called matrix • Loose connective tissue – binding & packaging material, holding other organs & tissues in place • Adipose tissue – contains fat, pads, ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.