Applied Pediatrics Jose A. Robles, MD Pediatric Neurology HISTORY
... • Definition of Terms: – Obtundation : mild to moderate blunting of alertness, accompanied by a lessened interest in or response to the environment. Patient have an increase in the number of hours of sleep, often with drowsiness in Delirium : characterized by disorientation, irritability, delusions ...
... • Definition of Terms: – Obtundation : mild to moderate blunting of alertness, accompanied by a lessened interest in or response to the environment. Patient have an increase in the number of hours of sleep, often with drowsiness in Delirium : characterized by disorientation, irritability, delusions ...
CHRONIC PAIN
... i. PAIN: (IASP) Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with potential or actual tissue damage ii. PAIN: a conscious experience which may be influenced by alterations in somatosensory processing following injury as well as psychosocial factors. iii. SUFFERING: a state of severe distre ...
... i. PAIN: (IASP) Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with potential or actual tissue damage ii. PAIN: a conscious experience which may be influenced by alterations in somatosensory processing following injury as well as psychosocial factors. iii. SUFFERING: a state of severe distre ...
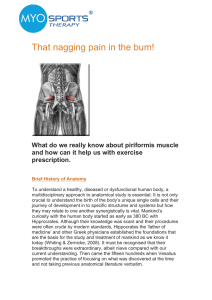
That nagging pain in the bum
... What affect can it have on the sciatic nerve? Cael (2009) observed tightness in piriformis may compress the sciatic nerve, causing radiating pain, weakness, and altered sensation in the lower extremity. This mimics the symptoms of nerve root compression associated with a protruding intervertebral di ...
... What affect can it have on the sciatic nerve? Cael (2009) observed tightness in piriformis may compress the sciatic nerve, causing radiating pain, weakness, and altered sensation in the lower extremity. This mimics the symptoms of nerve root compression associated with a protruding intervertebral di ...
Formation of a full complement of cranial proprioceptors requires
... development was further supported by the expression of the spindle-specific slow-developmental myosin heavy-chain (MyHC) isoform in nuclear bag fibers of the residual spindles of mutants (Fig. 1). Expression of this isoform by intrafusal fibers of spindles is dependent on the presence of Ia afferent ...
... development was further supported by the expression of the spindle-specific slow-developmental myosin heavy-chain (MyHC) isoform in nuclear bag fibers of the residual spindles of mutants (Fig. 1). Expression of this isoform by intrafusal fibers of spindles is dependent on the presence of Ia afferent ...
BIO 210 Course Outline
... 3. Define neurotransmitter, identify several types and describe their effects. 4. Define neuromodulator, identify several types and describe their effects. F. Discuss information processing by neurons. 1. Distinguish between EPSPs and IPSPs 2. Distinguish between temporal and spatial summation. 3. D ...
... 3. Define neurotransmitter, identify several types and describe their effects. 4. Define neuromodulator, identify several types and describe their effects. F. Discuss information processing by neurons. 1. Distinguish between EPSPs and IPSPs 2. Distinguish between temporal and spatial summation. 3. D ...
ZAPORIZHZHIA STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... his/her feelings that arise during irritation of the receptor apparatus. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to certain conditions during the study. The study should be carried out in a quiet atmosphere, in a warm room, with a patient's eyes closed. Irritations should be inscribed on symmetric sect ...
... his/her feelings that arise during irritation of the receptor apparatus. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to certain conditions during the study. The study should be carried out in a quiet atmosphere, in a warm room, with a patient's eyes closed. Irritations should be inscribed on symmetric sect ...
2-L2 new chronic pain
... (Pain wind-up: is a frequency-dependent increase in the excitability (hyperexcitability) of spinal cord neurons, evoked by electrical stimulation of afferent C-fibers. It occurs due to sustained and repeated state of excitation of the projection neurons. Causing the dorsal horn neuron to transmit pr ...
... (Pain wind-up: is a frequency-dependent increase in the excitability (hyperexcitability) of spinal cord neurons, evoked by electrical stimulation of afferent C-fibers. It occurs due to sustained and repeated state of excitation of the projection neurons. Causing the dorsal horn neuron to transmit pr ...
Chapter 35: Kandel - krigolson teaching
... the underlying mechanisms is one of the challenging areas of contemporary research on motor systems. Second, sensory input from a localized source generally produces coordinated reflex responses in several muscles at once, some of which may be distant from the stimulus. Third, supraspinal centers pl ...
... the underlying mechanisms is one of the challenging areas of contemporary research on motor systems. Second, sensory input from a localized source generally produces coordinated reflex responses in several muscles at once, some of which may be distant from the stimulus. Third, supraspinal centers pl ...
Brainstem II - Bellarmine University
... Receives input to mediate visceral and cranial nerve reflexes Projects to parasagittal medial nuclei Pedunculopontine n. ...
... Receives input to mediate visceral and cranial nerve reflexes Projects to parasagittal medial nuclei Pedunculopontine n. ...
COMPRESSION OF THE DEEP PALMAR BRANCH OF THE ULNAR
... The role of this fibrous band as a cause of compression was ...
... The role of this fibrous band as a cause of compression was ...
specification of synaptic connections mediating the simple stretch
... We tested this idea by replacing the single brachial DRG (which normally provides the entire sensory innervation of the forelimb) in developing tadpoles with one or two DRGs transplanted from mid-thoracic levels (Smith and Frank, 1987). Whenever the transplantation was made sufficiently early for th ...
... We tested this idea by replacing the single brachial DRG (which normally provides the entire sensory innervation of the forelimb) in developing tadpoles with one or two DRGs transplanted from mid-thoracic levels (Smith and Frank, 1987). Whenever the transplantation was made sufficiently early for th ...
Motor System & Behavior
... that the body is idle, so that no voluntary movement occurs. Now assume a ball has been spotted, and the motivation to grab the ball is born within the motivation areas of the cortex. The motor has currently no idea of how to actually get the ball, and cannot execute any movement yet because the mot ...
... that the body is idle, so that no voluntary movement occurs. Now assume a ball has been spotted, and the motivation to grab the ball is born within the motivation areas of the cortex. The motor has currently no idea of how to actually get the ball, and cannot execute any movement yet because the mot ...
Morris_2007_Macrosto..
... profusely branched neurites of serotonergic neurons located in the brain form a subepidermal network throughout the body of Macrostomum (Ladurner et al. 1997) and other species (Gustafsson et al. 2002). Mechanosensory and chemosensory neurons are located either in the epidermis or the central nervou ...
... profusely branched neurites of serotonergic neurons located in the brain form a subepidermal network throughout the body of Macrostomum (Ladurner et al. 1997) and other species (Gustafsson et al. 2002). Mechanosensory and chemosensory neurons are located either in the epidermis or the central nervou ...
Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... alters these proportions in humans. ...
... alters these proportions in humans. ...
LESSON PLAN
... Lesson aim: knowing the structure of the spinal cord and the way the nervous system functions based on the reflex arc. Type of lesson: acquiring new information Types of interaction: teacher-students, student-student, group work Targeted aims A1 Using learning by discovery for highlighting the struc ...
... Lesson aim: knowing the structure of the spinal cord and the way the nervous system functions based on the reflex arc. Type of lesson: acquiring new information Types of interaction: teacher-students, student-student, group work Targeted aims A1 Using learning by discovery for highlighting the struc ...
a spiking stretch receptor with central cell bodies in the uropod
... The small tonic unit shows a slight increase in frequency at peak stretch, (c) Later in the same experiment, recruitment of the phasic unit with concurrent inhibition of the tonic unit (from G. ttrigota). ...
... The small tonic unit shows a slight increase in frequency at peak stretch, (c) Later in the same experiment, recruitment of the phasic unit with concurrent inhibition of the tonic unit (from G. ttrigota). ...
Fecal Incontinence/Anal Incontinence What are Fecal incontinence/ Anal Incontinence?
... skeletal muscle and can be strengthened. If the sphincter muscles are injured or weak from any reason, they are not able to fully close, and this may cause stool to leak out. Constipation or having frequent or loose bowel movements. Frequent loose bowel movements can add to the incontinence. Loose s ...
... skeletal muscle and can be strengthened. If the sphincter muscles are injured or weak from any reason, they are not able to fully close, and this may cause stool to leak out. Constipation or having frequent or loose bowel movements. Frequent loose bowel movements can add to the incontinence. Loose s ...
Somatosensory and Pain
... Neuropathic pain Neuropathic pain: BAD PAIN… Nerves can generate pain by firing abnormally and this pain sometimes doesn't go away. Phantom pain is a kind of neuropathic pain which has attracted a lot of attention - but many other millions of people are affected by neuropathic pain who don’t have p ...
... Neuropathic pain Neuropathic pain: BAD PAIN… Nerves can generate pain by firing abnormally and this pain sometimes doesn't go away. Phantom pain is a kind of neuropathic pain which has attracted a lot of attention - but many other millions of people are affected by neuropathic pain who don’t have p ...
Central nervous System Lesions Leading to Disability
... brainstem and spinal systems. Three features of the hierarchy of motor structures are particularly important. Different components of the motor systems contain somatotopic maps. The areas that influence adjacent body parts can be found adjacent to each other in these maps. This somatotopic organizat ...
... brainstem and spinal systems. Three features of the hierarchy of motor structures are particularly important. Different components of the motor systems contain somatotopic maps. The areas that influence adjacent body parts can be found adjacent to each other in these maps. This somatotopic organizat ...
Why are brain pathways
... particular sensory cell is most sensitive - light, touch, sound, etc.) • Law of specific nerve energies (depolarization of neurons in a pathway is interpreted as a particular form of stimulation - pressure to the eyes or direct electrical activation of the visual cortex are both interpreted as a cha ...
... particular sensory cell is most sensitive - light, touch, sound, etc.) • Law of specific nerve energies (depolarization of neurons in a pathway is interpreted as a particular form of stimulation - pressure to the eyes or direct electrical activation of the visual cortex are both interpreted as a cha ...
Neck Pain - Masters of TCM
... Instability (hypermobility) If your neck problem is instability, you may be feeling pain, muscle spasm, and the curious sensation of a wobbly neck. Instability is often caused by a whiplash injury from a car accident. Your head is hurled in one direction, then another, causing the ligaments, muscle ...
... Instability (hypermobility) If your neck problem is instability, you may be feeling pain, muscle spasm, and the curious sensation of a wobbly neck. Instability is often caused by a whiplash injury from a car accident. Your head is hurled in one direction, then another, causing the ligaments, muscle ...
Chapter 18
... a. posterior or dorsal root contains sensory nerve fibers which transmit nerve impulses from the periphery into the spinal cord; it has an enlargement called the posterior or dorsal root ganglion which contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons b. anterior or ventral root contains motor neuron ...
... a. posterior or dorsal root contains sensory nerve fibers which transmit nerve impulses from the periphery into the spinal cord; it has an enlargement called the posterior or dorsal root ganglion which contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons b. anterior or ventral root contains motor neuron ...
Repetitive Strain Injuries - Working
... 6 - Pinching. This may feel as if you had tape attached lengthwise to your fingers, causing a tautness or strain. Again, you feel more, rather than less, sensation than normal. 8 - Reduced Sensation. This is a noticeable sensation that the surface of the skin is less sensitive. It may feel thick or ...
... 6 - Pinching. This may feel as if you had tape attached lengthwise to your fingers, causing a tautness or strain. Again, you feel more, rather than less, sensation than normal. 8 - Reduced Sensation. This is a noticeable sensation that the surface of the skin is less sensitive. It may feel thick or ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.