Discussion Exercise 2: Polyprotic Acids Answer key Problem 1
... about half way between 2.2 and 9.9, about 6.1 d. What is the isoelectric point of alanine? The isoelectric point is where the net charge is zero, so the isoelectric point is 6.1. e. Draw the structure of alanine at its isoelectric point. ...
... about half way between 2.2 and 9.9, about 6.1 d. What is the isoelectric point of alanine? The isoelectric point is where the net charge is zero, so the isoelectric point is 6.1. e. Draw the structure of alanine at its isoelectric point. ...
The Hypothesis that the Genetic Code Originated in Coupled
... one configuration, L-amino acids, are incorporated into proteins to provide reproducible structures that catalyze reactions in the cell including synthesis of the L-amino acids themselves as well as numerous other chiral molecules including D-ribose in RNA and D-deoxyribose in DNA. All chirality in ...
... one configuration, L-amino acids, are incorporated into proteins to provide reproducible structures that catalyze reactions in the cell including synthesis of the L-amino acids themselves as well as numerous other chiral molecules including D-ribose in RNA and D-deoxyribose in DNA. All chirality in ...
Instructor Supplement: Ideas for Workshop Extension Activities Core
... their chosen audience in language that audience would be expected to understand. The presentation should use some type of visual support (drawing on the board, physical models, “acting” the concept, etc.), but NOT Powerpoint. Be sure students know that they need to convey why the topic they’re expla ...
... their chosen audience in language that audience would be expected to understand. The presentation should use some type of visual support (drawing on the board, physical models, “acting” the concept, etc.), but NOT Powerpoint. Be sure students know that they need to convey why the topic they’re expla ...
Document
... Mutarotation is transformation of one anomeric form into another. An intermediate form is a chain form of monosaccharide. In D-glucose solution there is more b-D-glucopyranose. All its –OH groups have the most energetically beneficial equatorial position. ...
... Mutarotation is transformation of one anomeric form into another. An intermediate form is a chain form of monosaccharide. In D-glucose solution there is more b-D-glucopyranose. All its –OH groups have the most energetically beneficial equatorial position. ...
Poster
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
Protein_Structure_Final_Powerpoint
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
Intermolecular interaction studies in some amino acids with aqueous
... Thermodynamic properties of amino acids i.e. proteins in electrolyte solution provide information about solute- solvent interactions, those are important in understanding the stability of Proteins. Some of these interactions are found applicable in several biochemical and physiological processses in ...
... Thermodynamic properties of amino acids i.e. proteins in electrolyte solution provide information about solute- solvent interactions, those are important in understanding the stability of Proteins. Some of these interactions are found applicable in several biochemical and physiological processses in ...
Chapter 8
... 1. They serve as building blocks of nucleic acids. 2. ATP plays an important pole in energy transformation. 3. ATP , ADP, and AMP may function as allosteric regulators and participate in regulation of many metabolic pathways. ATP involves in covalent modification of enzymes. ...
... 1. They serve as building blocks of nucleic acids. 2. ATP plays an important pole in energy transformation. 3. ATP , ADP, and AMP may function as allosteric regulators and participate in regulation of many metabolic pathways. ATP involves in covalent modification of enzymes. ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... conversion of their energy into ATP. Two of these enzyme complexes, PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) and alpha-KGDH (alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) are part of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and as such assume a central role for general energy production. Another lipoic acid containing enzyme ...
... conversion of their energy into ATP. Two of these enzyme complexes, PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) and alpha-KGDH (alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) are part of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and as such assume a central role for general energy production. Another lipoic acid containing enzyme ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
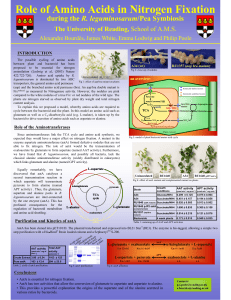
Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
Chapter 14 Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism
... • Patients suffering from diabetes-related ketosis are usually given insulin as a first step in treatment. The insulin restores normal glucose metabolism and reduces the rate of formation of ketone bodies. • Acid-base balance can be restored by the intravenous administration of sodium bicarbonate. ...
... • Patients suffering from diabetes-related ketosis are usually given insulin as a first step in treatment. The insulin restores normal glucose metabolism and reduces the rate of formation of ketone bodies. • Acid-base balance can be restored by the intravenous administration of sodium bicarbonate. ...
Publication: Amino acid profile of organically grown alternative
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
Amino acid profile of organically grown alternative agricultural
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
Model Description Sheet
... RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: An estimated 900,000 people a year develop venous blood clots in the United States and 60,000 to 100,000 die as a result. Anticoagulants are used to prevent and treat thrombosis. New oral anticoagulants (NOAC’s), like apixaban (Eliquis) are designed to specificall ...
... RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: An estimated 900,000 people a year develop venous blood clots in the United States and 60,000 to 100,000 die as a result. Anticoagulants are used to prevent and treat thrombosis. New oral anticoagulants (NOAC’s), like apixaban (Eliquis) are designed to specificall ...
Amino acid contents and biological value of protein in various
... ABSTRACT: Amino acid content before and after heat treatment was assessed in grain of six selected amaranth varieties and four species: Amaranthus cruentus, A. hypochondriacus, A. caudatus and A. hybridus, cultivated in the Czech Republic. High content of Lys and Arg was detected in both heat treate ...
... ABSTRACT: Amino acid content before and after heat treatment was assessed in grain of six selected amaranth varieties and four species: Amaranthus cruentus, A. hypochondriacus, A. caudatus and A. hybridus, cultivated in the Czech Republic. High content of Lys and Arg was detected in both heat treate ...
here - Sites@PSU
... Lactococcus sp. Lactobacillus sp. Leuconostoc sp. Pediococcus sp. Oenococcus sp. Streptococcus sp. Enterococcus sp. Sporolactobacillus sp. Carnobacterium sp. Aerococcus sp. Tetragenococcus sp. Vagococcus sp. Weisella sp. ...
... Lactococcus sp. Lactobacillus sp. Leuconostoc sp. Pediococcus sp. Oenococcus sp. Streptococcus sp. Enterococcus sp. Sporolactobacillus sp. Carnobacterium sp. Aerococcus sp. Tetragenococcus sp. Vagococcus sp. Weisella sp. ...
Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis
... 13. Biosynthesis of fatty acids and eicosanoids Fatty acid synthesis and fatty acid breakdown occur by similar pathways. Describe, very briefly, four ways in which the synthetic and breakdown pathways differ. Ans: Fatty acid synthesis (in any order) (1) employs NADPH as reducing agent; (2) involves ...
... 13. Biosynthesis of fatty acids and eicosanoids Fatty acid synthesis and fatty acid breakdown occur by similar pathways. Describe, very briefly, four ways in which the synthetic and breakdown pathways differ. Ans: Fatty acid synthesis (in any order) (1) employs NADPH as reducing agent; (2) involves ...