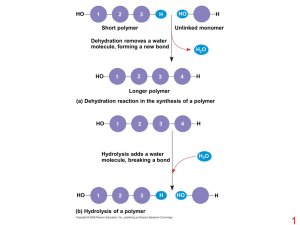
Cell Biology Workshop I
... b. What will the effect of this change be on the overall charge of the modified protein? A neutral serine side group is converted into a negatively charged phosphoserine group. The overall protein will be more negatively charged. ...
... b. What will the effect of this change be on the overall charge of the modified protein? A neutral serine side group is converted into a negatively charged phosphoserine group. The overall protein will be more negatively charged. ...
How many nucleotides are in 12 mRNA codons?
... A particular DNA sequence reads TCGAGGTCACCG. A mutation occurs in which the first "A" in the sequence is deleted. What will happen to the protein produced? A ...
... A particular DNA sequence reads TCGAGGTCACCG. A mutation occurs in which the first "A" in the sequence is deleted. What will happen to the protein produced? A ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of a SNORK
... Use your text book and notes along with your model to complete the following: 2pts each 1) Where in the cell is the DNA located? _________________________ 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? _________ ...
... Use your text book and notes along with your model to complete the following: 2pts each 1) Where in the cell is the DNA located? _________________________ 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? _________ ...
How does DNA copy itself?
... • Translation: putting together amino acids in the right order to make proteins – This is done on ribosomes – Think using the recipe to make tacos ...
... • Translation: putting together amino acids in the right order to make proteins – This is done on ribosomes – Think using the recipe to make tacos ...
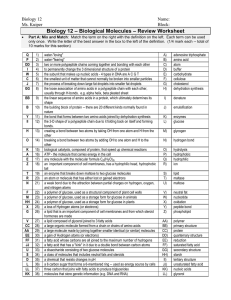
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... an enzyme that breaks down maltose to two glucose molecules an atom or molecule that has either lost or gained electrons a weak bond due to the attraction between partial charges on hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polyme ...
... an enzyme that breaks down maltose to two glucose molecules an atom or molecule that has either lost or gained electrons a weak bond due to the attraction between partial charges on hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polyme ...
Mass Spectrometry of Peptides
... T. S. Nuhse, A. Stensballe, O. Jensen, and S. Peck. “Largescale Analysis of in Vivo Phosphorylated Membrane Proteins by Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry” Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, ...
... T. S. Nuhse, A. Stensballe, O. Jensen, and S. Peck. “Largescale Analysis of in Vivo Phosphorylated Membrane Proteins by Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry” Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, ...
Amino Acid Analysis - Donald Danforth Plant Science Center
... AccQ•Tag™ Ultra Chemistries used in the UPLC Amino Acid Analysis Solution are a comprehensive and fully tested set of reagents, columns, and eluents optimized for use with the ACQUITY UPLC® System. With the system’s superior resolution of all amino acids, you will confidently achieve peak identifica ...
... AccQ•Tag™ Ultra Chemistries used in the UPLC Amino Acid Analysis Solution are a comprehensive and fully tested set of reagents, columns, and eluents optimized for use with the ACQUITY UPLC® System. With the system’s superior resolution of all amino acids, you will confidently achieve peak identifica ...
chapter 3 - rci.rutgers.edu
... produce other amino acids (p. 57) and alter the properties of a protein. A Ramachandran Plot (p. 39) is a theoretical tool for analyzing the structure of proteins. It is a little hard to understand from the description in the book. You look at the alpha carbon. There is a plane of reference between ...
... produce other amino acids (p. 57) and alter the properties of a protein. A Ramachandran Plot (p. 39) is a theoretical tool for analyzing the structure of proteins. It is a little hard to understand from the description in the book. You look at the alpha carbon. There is a plane of reference between ...
Amino acids introduction
... The amino acid sequence (also called primary structure) of a protein is the order of the amino acids in the protein chain. The sequence is always read from the N-terminus to the Cterminus of the protein. ...
... The amino acid sequence (also called primary structure) of a protein is the order of the amino acids in the protein chain. The sequence is always read from the N-terminus to the Cterminus of the protein. ...
Amino Acids and Proteins: →Protein Functions: enzymes, transport
... →Can have cis or trans form, but trans is the most stable conformation, so find trans peptide bonds in proteins. Exception: Pro-because the NH group is attached in a ring structure, cis and trans have about equal energy. Therefore, whether it is cis or trans at the Pro position depends on the overa ...
... →Can have cis or trans form, but trans is the most stable conformation, so find trans peptide bonds in proteins. Exception: Pro-because the NH group is attached in a ring structure, cis and trans have about equal energy. Therefore, whether it is cis or trans at the Pro position depends on the overa ...
REVIEW Protein Synthesis with Analogies
... A Protein Fairytale Once upon a time there were two fraternal twin brothers, Donald N Armstrong and Ronald N. Armstrong. Donald was the smarter of the two and he was a successful inventor with many patents. Although Ronald was not as smart at his brother, he was extremely loyal. One day Donald came ...
... A Protein Fairytale Once upon a time there were two fraternal twin brothers, Donald N Armstrong and Ronald N. Armstrong. Donald was the smarter of the two and he was a successful inventor with many patents. Although Ronald was not as smart at his brother, he was extremely loyal. One day Donald came ...
Biochemistry (Macromolecules)
... Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – This part acts as the acid because it can give off the hydrogen. 2. Amine end (NH2) – The end can act as a base by accepting a third hydrogen. 3. Alpha (α) Carbon – This is the central Carbon tha ...
... Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – This part acts as the acid because it can give off the hydrogen. 2. Amine end (NH2) – The end can act as a base by accepting a third hydrogen. 3. Alpha (α) Carbon – This is the central Carbon tha ...
Multiple Sclerosis and Epstein‐Barr Virus Infection An Epitope
... Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. Although the precise etiology of MS is unknown, data from epidemiological, genetic and twin studies suggest that MS develops in genetically ...
... Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. Although the precise etiology of MS is unknown, data from epidemiological, genetic and twin studies suggest that MS develops in genetically ...
Peptides and Proteins
... By the same way, the dipeptide can then forms a second peptide bond with a third amino acid to give Tripeptide Repetition of this process generates a polypeptide or protein of specific amino acid sequence. ...
... By the same way, the dipeptide can then forms a second peptide bond with a third amino acid to give Tripeptide Repetition of this process generates a polypeptide or protein of specific amino acid sequence. ...
Lipids,proteins, and nucleic acids
... * Carboxyl group (“head”) has properties of an acid. * Hydrocarbon chain – long carbon skeleton. Non-polar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and not water soluble. ...
... * Carboxyl group (“head”) has properties of an acid. * Hydrocarbon chain – long carbon skeleton. Non-polar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and not water soluble. ...
Lipids,proteins, and nucleic acids
... * Carboxyl group (“head”) has properties of an acid. * Hydrocarbon chain – long carbon skeleton. Non-polar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and not water soluble. ...
... * Carboxyl group (“head”) has properties of an acid. * Hydrocarbon chain – long carbon skeleton. Non-polar C-H bonds make the chain hydrophobic and not water soluble. ...
10.3 Protein Synthesis
... • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • There a ...
... • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • There a ...
Macromolecules Part 2
... Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – This part acts as the acid because it can give off the Hydrogen. 2. Amine end (NH2) – The end can act as a base by accepting a third Hydrogen. 3. Alpha (α) Carbon – This is the central Carbon tha ...
... Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – This part acts as the acid because it can give off the Hydrogen. 2. Amine end (NH2) – The end can act as a base by accepting a third Hydrogen. 3. Alpha (α) Carbon – This is the central Carbon tha ...