Macromolecules
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
Unit 2 Biochemistry Chp 5 Macromolecules Notes
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
... o All amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this context refer only to these groups in the R groups. ...
Lecture Inhibition of Amino Acid Synthesis
... in translation by polymerizing the amino acids in a precise order as defined by the RNA molecule. In total, there are 20 amino acids with a variety of synthetic pathways in the plant. Herbicides that inhibit one of these metabolic pathways prevent the formation of one or more amino acids that may be ...
... in translation by polymerizing the amino acids in a precise order as defined by the RNA molecule. In total, there are 20 amino acids with a variety of synthetic pathways in the plant. Herbicides that inhibit one of these metabolic pathways prevent the formation of one or more amino acids that may be ...
CHAPTER 6
... made by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II) – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CP ...
... made by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS II) – This is a cytosolic enzyme (whereas CPS I is mitochondrial and used for the urea cycle) – Substrates are HCO3-, glutamine (not NH4+), 2 ATP – In mammals, CPS-II can be viewed as the committed step in pyrimidine synthesis – Bacteria have but one CP ...
Canine Osteosarcoma
... reaction of a metal ion from a soluble metal salt with amino acids, with a mole ratio of one mole of metal to one to three (preferably two) moles of amino acids to form coordinate covalent bonds. Amino acids molecular weight must be approximately 150 the chelate molecular weight must not exceed 800. ...
... reaction of a metal ion from a soluble metal salt with amino acids, with a mole ratio of one mole of metal to one to three (preferably two) moles of amino acids to form coordinate covalent bonds. Amino acids molecular weight must be approximately 150 the chelate molecular weight must not exceed 800. ...
Biochemistry Assessment
... are changed by the reactions they catalyze increase the activation energy strengthen the chemical bonds are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH ...
... are changed by the reactions they catalyze increase the activation energy strengthen the chemical bonds are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH ...
acids and bases - Althea`s Academy
... Aprotonic solvents – subs that do not accept proton, do not behave as acids Hydroxide ion (OH-) – a radical composed of a hydrogen atom, an oxygen atom and an electron giving it a neagtive charge Responsible for the chemical properites of alkali Amphoteric subs – subs that may act as acid or base ...
... Aprotonic solvents – subs that do not accept proton, do not behave as acids Hydroxide ion (OH-) – a radical composed of a hydrogen atom, an oxygen atom and an electron giving it a neagtive charge Responsible for the chemical properites of alkali Amphoteric subs – subs that may act as acid or base ...
Identification of amino acid sequence by X
... methods, the most popular ones being Edman degradation, liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS), and cDNA sequencing. Edman degradation was the first approach to be developed. In this method, the single N-terminal residue is chemically labeled, cleaved f ...
... methods, the most popular ones being Edman degradation, liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS), and cDNA sequencing. Edman degradation was the first approach to be developed. In this method, the single N-terminal residue is chemically labeled, cleaved f ...
Gas phase spectroscopy of the penta-peptide
... such as the C@O stretch have frequencies outside the 3100–3800 cm 1 range covered in this experiment. We observe from the experimental IR–UV spectrum that the hydroxyl of the serine residue is H-bonded. This conclusion follows from our previous study of the dipeptide phe-ser (F–S) [18]. In this pept ...
... such as the C@O stretch have frequencies outside the 3100–3800 cm 1 range covered in this experiment. We observe from the experimental IR–UV spectrum that the hydroxyl of the serine residue is H-bonded. This conclusion follows from our previous study of the dipeptide phe-ser (F–S) [18]. In this pept ...
Translation Worksheet
... 7. Explain why shifting the reading frame during a mutation is very dangerous. It can change the amino acids translated/length of the peptide chain. ...
... 7. Explain why shifting the reading frame during a mutation is very dangerous. It can change the amino acids translated/length of the peptide chain. ...
Calculation of hydrophobicities
... total number of amino acid j on the surface of the protein; asa_atjktot – total ASA of the kth atom type in jth amino acid in test tripeptide (e.g. Gly-Ala-Gly for Ala; structure optimized with Bio+).. Critique. This approach, which is –for amino acid based overall hydrophobicity- the one that is us ...
... total number of amino acid j on the surface of the protein; asa_atjktot – total ASA of the kth atom type in jth amino acid in test tripeptide (e.g. Gly-Ala-Gly for Ala; structure optimized with Bio+).. Critique. This approach, which is –for amino acid based overall hydrophobicity- the one that is us ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by addition of metal ions (i.e. Mg2+, is required by many ATP requiring enzy ...
... often participate in substrate binding. • Metal ions of metalloenzymes – cations that are tightly bound to enzyme and participate directly in catalysis (Fe, Zn, Cu, Co). • Metal activated enzymes – require or are stimulated by addition of metal ions (i.e. Mg2+, is required by many ATP requiring enzy ...
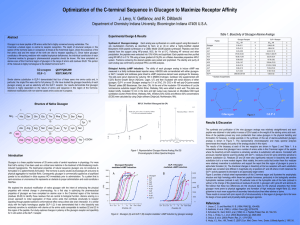
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
... Synthesis of Glucagon Analogs: Each analog was synthesized on a solid support using Boc-based in situ neutralization chemistry as described by Kent, et al. (3) on either a highly-modified Applied Biosystems 430A peptide synthesizer or a CSBio Model CS336 peptide synthesizer. Peptides were then cleav ...
... Synthesis of Glucagon Analogs: Each analog was synthesized on a solid support using Boc-based in situ neutralization chemistry as described by Kent, et al. (3) on either a highly-modified Applied Biosystems 430A peptide synthesizer or a CSBio Model CS336 peptide synthesizer. Peptides were then cleav ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... (b) (i) Chloroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. ...
... (b) (i) Chloroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. ...
- Circle of Docs
... 57. A one-molar solution always contains A. one equivalent weight of the solute in one liter of solution B. one gram-molecular weight of the solute in one liter of solution C. one gram-molecular wieght of the solute in 22.4 liters of solution D. 6.06 x 10 23rd molecules of the solute per 22.4 liter ...
... 57. A one-molar solution always contains A. one equivalent weight of the solute in one liter of solution B. one gram-molecular weight of the solute in one liter of solution C. one gram-molecular wieght of the solute in 22.4 liters of solution D. 6.06 x 10 23rd molecules of the solute per 22.4 liter ...
Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates
... A fat molecule consists of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules joined together. Cut out the glycerol and fatty acid paper model molecules from page 39. You may want to paste the page on lightweight cardboard before cutting out the models. Cut along the solid lines only. Attempt to ...
... A fat molecule consists of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules joined together. Cut out the glycerol and fatty acid paper model molecules from page 39. You may want to paste the page on lightweight cardboard before cutting out the models. Cut along the solid lines only. Attempt to ...
UNIT 2. Structure and function of proteins.
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
Mrs C`s Chem Lecture
... EXAMPLE Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution (water, in living organisms). Glycine Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... EXAMPLE Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution (water, in living organisms). Glycine Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
Study Guide KEY Exam III F 2012
... Primary (1o) structure of proteins is the amino acid sequence. It is maintained by covalent bonds called peptide bonds. Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). ...
... Primary (1o) structure of proteins is the amino acid sequence. It is maintained by covalent bonds called peptide bonds. Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). ...
Mammalian Systematics
... mammals (seals, whales, dolphins, walruses, manatees) and their potential ancestral relationship to land mammals. We will use a protein that all mammals share: the hemoglobin beta protein. Hemoglobin is a good test molecule since it shows both conservation across species (since it performs the essen ...
... mammals (seals, whales, dolphins, walruses, manatees) and their potential ancestral relationship to land mammals. We will use a protein that all mammals share: the hemoglobin beta protein. Hemoglobin is a good test molecule since it shows both conservation across species (since it performs the essen ...