1. Products of Amino Acid Transamination Name
... Answer The second amino group introduced into urea is transferred from aspartate. This amino acid is generated in large quantities by transamination between oxaloacetate and glutamate (and many other amino acids), catalyzed by aspartate aminotransferase. Approximately one half of all the amino group ...
... Answer The second amino group introduced into urea is transferred from aspartate. This amino acid is generated in large quantities by transamination between oxaloacetate and glutamate (and many other amino acids), catalyzed by aspartate aminotransferase. Approximately one half of all the amino group ...
Biochemistry Study Guide NITROGEN METABOLISM
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
No Slide Title
... • The positive heterotropic activator, N-acetylglutamate, is required for activity. • Brings one C atom and one N atom into the urea cycle as a carbamoyl group. • Catalyzes the critical step in removing NH4+ from the blood. ...
... • The positive heterotropic activator, N-acetylglutamate, is required for activity. • Brings one C atom and one N atom into the urea cycle as a carbamoyl group. • Catalyzes the critical step in removing NH4+ from the blood. ...
Nucleotides
... sites (known as the substrate specificity sites) on the enzyme regulates substrate specificity, causing an increase in the conversion of different species of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides as they are required for DNA synthesis. E.g., deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) binding at the spec ...
... sites (known as the substrate specificity sites) on the enzyme regulates substrate specificity, causing an increase in the conversion of different species of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides as they are required for DNA synthesis. E.g., deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) binding at the spec ...
The First Class Program
... or a more rigid region of the protein such as a turn or a helix. Increased flexibility is reported to lead to improved affinity, however, rigid structures can provide good epitopes more resistant to detergent denaturation. Additionally, sequences containing aromatic residues rather than highly polar ...
... or a more rigid region of the protein such as a turn or a helix. Increased flexibility is reported to lead to improved affinity, however, rigid structures can provide good epitopes more resistant to detergent denaturation. Additionally, sequences containing aromatic residues rather than highly polar ...
Synthesis of Oligonucleotides
... isopropylphenoxyacetyl for dG and acetyl for dC can be removed by treatment with 0.05 M potassium carbonate in methanol at room temperature within a few hours. When nucleosides are prepared for incorporation into oligonucleotides, it is usual to protect nucleobase exocyclic amino groups first. There ...
... isopropylphenoxyacetyl for dG and acetyl for dC can be removed by treatment with 0.05 M potassium carbonate in methanol at room temperature within a few hours. When nucleosides are prepared for incorporation into oligonucleotides, it is usual to protect nucleobase exocyclic amino groups first. There ...
Protein synthesis in the Liver and the Urea Cycle
... muscle proteins are being broken down with the amino acid carbon skeletons providing the energy. Thus the amount of ammonia that must be excreted increases. Defects in the urea cycle. Absence of any of the enzymes involved in urea synthesis is not compatible with life. Deficiencies in any one of the ...
... muscle proteins are being broken down with the amino acid carbon skeletons providing the energy. Thus the amount of ammonia that must be excreted increases. Defects in the urea cycle. Absence of any of the enzymes involved in urea synthesis is not compatible with life. Deficiencies in any one of the ...
Human Metabolism Compared to Other Species
... We are more closely related to eukaryotes than bacteria. ...
... We are more closely related to eukaryotes than bacteria. ...
L- Amino Acid Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
... FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures ...
... FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures ...
The Roles of Amino Acids in Milk Yield and Components
... corresponding keto-acid is provided in the diet. Racemic mixtures of D and L-isomers of AAs can provide an effective source of supplemental AA to balance rations. The ketoacid produced following action of D-oxidase has no racemic center and so it can be reaminated to yield the L-isomer. Therefore, k ...
... corresponding keto-acid is provided in the diet. Racemic mixtures of D and L-isomers of AAs can provide an effective source of supplemental AA to balance rations. The ketoacid produced following action of D-oxidase has no racemic center and so it can be reaminated to yield the L-isomer. Therefore, k ...
Document
... aromatic groups in the ring, have interesting molecular recognition properties.1 Because they are macrocycles, these hosts have built into them a measure of preorganization that enhances their affinity for guest molecules of the appropriate size and shape.2 The hydrophobicity and π-stacking interact ...
... aromatic groups in the ring, have interesting molecular recognition properties.1 Because they are macrocycles, these hosts have built into them a measure of preorganization that enhances their affinity for guest molecules of the appropriate size and shape.2 The hydrophobicity and π-stacking interact ...
DNA / RNA
... taken to the ribosome where it serves as the directions to form a sequence of amino acids which form proteins. - Ribosome is made out of protein and rRNA ...
... taken to the ribosome where it serves as the directions to form a sequence of amino acids which form proteins. - Ribosome is made out of protein and rRNA ...
Chapters 14 and 15 Outline
... Standard solution – a solution that contains the precisely known concentration of a solute. Primary standard – is a highly purified solid compound used to check the concentration of the known solution in a titration. ...
... Standard solution – a solution that contains the precisely known concentration of a solute. Primary standard – is a highly purified solid compound used to check the concentration of the known solution in a titration. ...
CHAPTER 6 Gene Expression: Translation
... edited by Yue-Wen Wang Ph. D. Dept. of Agronomy,台大農藝系 NTU 遺傳學 601 20000 ...
... edited by Yue-Wen Wang Ph. D. Dept. of Agronomy,台大農藝系 NTU 遺傳學 601 20000 ...
Biochemistry - Austin Community College
... Lipids • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • Utilized for energy storage, membranes, insulation, protection • Greasy or oily substances • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water - insoluble in water • Lipids are hydroph ...
... Lipids • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • Utilized for energy storage, membranes, insulation, protection • Greasy or oily substances • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water - insoluble in water • Lipids are hydroph ...
The First Steps of Chemical Evolution towards the
... protein-governed world, whereas later on RNA and DNA, which could remain stable within the protected cells of this Gprotein worldF even in an otherwise hostile environment of a salty ocean, could have gradually been used to build new, faster, and more efficient mechanisms, to find better ways of rep ...
... protein-governed world, whereas later on RNA and DNA, which could remain stable within the protected cells of this Gprotein worldF even in an otherwise hostile environment of a salty ocean, could have gradually been used to build new, faster, and more efficient mechanisms, to find better ways of rep ...
Slide
... – Large side chains take up more space than small ones – Hydrophobic side chains want to be near one another – Hydrophilic side chains form hydrogen bonds to one another and to water molecules – Negatively charged (acidic) side chains want to be near positively charged (basic) side chains ...
... – Large side chains take up more space than small ones – Hydrophobic side chains want to be near one another – Hydrophilic side chains form hydrogen bonds to one another and to water molecules – Negatively charged (acidic) side chains want to be near positively charged (basic) side chains ...
protein
... • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups • Amino acids differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups ...
... • Amino acids are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups • Amino acids differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups ...
Effect of nitrogen fertilization on metabolisms of essential and non
... to cadmium, copper, and zinc (Hamer 1986). At the same time these proteins are cystein-rich proteins. This is again connected with the plant’s demand for available amino acids which are necessary for the production of proteins forming the aleurone layer (Chittenden et al. 1978). In terms of essentia ...
... to cadmium, copper, and zinc (Hamer 1986). At the same time these proteins are cystein-rich proteins. This is again connected with the plant’s demand for available amino acids which are necessary for the production of proteins forming the aleurone layer (Chittenden et al. 1978). In terms of essentia ...
Overview of Absorptive/Post-Absorptive States
... portal circulation. Peripheral tissues continue to take up glucose at first until plasma glucose levels dip below about 80 mg/dl at which point hepatocytes begin to catabolize their glycogen stores (glyco ...
... portal circulation. Peripheral tissues continue to take up glucose at first until plasma glucose levels dip below about 80 mg/dl at which point hepatocytes begin to catabolize their glycogen stores (glyco ...
4-Catabolism of Purine Nucleotides
... limit [>7mg/dl (men) & >6mg/dl (women)], it crystallizes in the soft tissues and joints inflammatory reaction (Gouty arthritis) ...
... limit [>7mg/dl (men) & >6mg/dl (women)], it crystallizes in the soft tissues and joints inflammatory reaction (Gouty arthritis) ...
and Trp cage
... Exendin peptide from gila monster venom Trp cage synthetic peptide similar in sequence and structure to Exendin GLP-1 increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion, decreases glucose-dependent glucagon secretion, and and decelerates gastric emptying. ...
... Exendin peptide from gila monster venom Trp cage synthetic peptide similar in sequence and structure to Exendin GLP-1 increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion, decreases glucose-dependent glucagon secretion, and and decelerates gastric emptying. ...
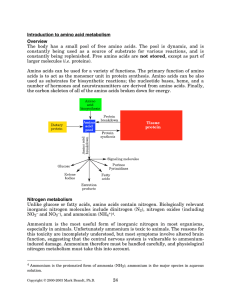
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... Plants can use either ammonium or nitrogen oxides (especially nitrate) as sources of usable nitrogen. Nitrate is formed by microorganisms that can use ammonium as an energy source, and is thus the lowest energy form of nitrogen. On the other hand, nitrate and other nitrogen oxides are major componen ...
... Plants can use either ammonium or nitrogen oxides (especially nitrate) as sources of usable nitrogen. Nitrate is formed by microorganisms that can use ammonium as an energy source, and is thus the lowest energy form of nitrogen. On the other hand, nitrate and other nitrogen oxides are major componen ...
Protein digestion and amino acid absorption along
... acids. This phenomenon was recently confirmed by Murai et a/. (1984). The free amino acid fraction was highest in carp intestinal content 3 h after a meal, but 6 h after feeding (Dabrowski, 1983a) it had decreased to less than the level found in the present trial 2.5 h after feeding. However, water ...
... acids. This phenomenon was recently confirmed by Murai et a/. (1984). The free amino acid fraction was highest in carp intestinal content 3 h after a meal, but 6 h after feeding (Dabrowski, 1983a) it had decreased to less than the level found in the present trial 2.5 h after feeding. However, water ...