BIO SOL Review 10 - Macromolecules - Enzymes
... d. Enzymes act as catalysts to drive chemical reactions forward. ...
... d. Enzymes act as catalysts to drive chemical reactions forward. ...
Biology Homework - Whitinsville Christian School
... changes, although the sequence of amino acids remains the same. Choose one of them to explain. (Do some research. Contact me ahead of the due date if you are stuck, and I can direct you to some helpful websites.) The white of an egg solidifies when it is heated. The white of an egg thickens when ...
... changes, although the sequence of amino acids remains the same. Choose one of them to explain. (Do some research. Contact me ahead of the due date if you are stuck, and I can direct you to some helpful websites.) The white of an egg solidifies when it is heated. The white of an egg thickens when ...
transcription translation mutation lesson ppt
... Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
... Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
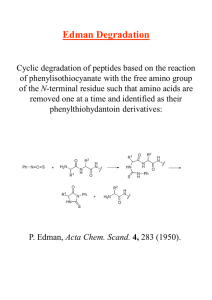
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Rab32 family proteins mediate mitochondria membrane dynamics
... interaction of the secretory pathway with mitochondria. We and others have published that Rab32 has to be in its GTP-bound, active state to allow for mitochondrial fission. Consistent with this, the activity of Rab32 determines apoptosis progression and ER calcium signaling. Expanding on our publish ...
... interaction of the secretory pathway with mitochondria. We and others have published that Rab32 has to be in its GTP-bound, active state to allow for mitochondrial fission. Consistent with this, the activity of Rab32 determines apoptosis progression and ER calcium signaling. Expanding on our publish ...
Quiz #4 1. Which of the following statements is
... Normal-phase chromatography has a polar stationary phase and a non-polar mobile phase, resulting in more hydrophilic molecules eluting later. HPLC does not provide any direct information about the molecular weight or number of charged groups. Therefore, Protein A is more hydrophobic than Protein B. ...
... Normal-phase chromatography has a polar stationary phase and a non-polar mobile phase, resulting in more hydrophilic molecules eluting later. HPLC does not provide any direct information about the molecular weight or number of charged groups. Therefore, Protein A is more hydrophobic than Protein B. ...
Computational protein design
... conformers of each side-chain, called rotamers. Residues that form the boundary between the core and surface require a combination of the core and the surface scoring functions. The algorithm considers both hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids at boundary positions, while core positions are restr ...
... conformers of each side-chain, called rotamers. Residues that form the boundary between the core and surface require a combination of the core and the surface scoring functions. The algorithm considers both hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids at boundary positions, while core positions are restr ...
Protein
... • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to form proteins • Synthesis of protein determined through gene expression • DNA transcription phase – DNA code transferred from the nucleus to the cytosol via messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
... • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds to form proteins • Synthesis of protein determined through gene expression • DNA transcription phase – DNA code transferred from the nucleus to the cytosol via messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
Protein Structure
... • The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. • This final shape is determined and stabilized by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains of the amino acids • These bonding interactions between side chains may cause a number of folds, bends, ...
... • The tertiary structure is the final specific geometric shape that a protein assumes. • This final shape is determined and stabilized by a variety of bonding interactions between the side chains of the amino acids • These bonding interactions between side chains may cause a number of folds, bends, ...
Organic Chemistry
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
Macromolecule Scramble
... o cells, tissue fluid, or in fluids being transported (blood or phloem) metabolic roles Ex: enzymes in all organisms, plasma proteins and antibodies in mammals Fibrous form long fibres mostly consist of repeated sequences of amino acids which are insoluble in water usually have structura ...
... o cells, tissue fluid, or in fluids being transported (blood or phloem) metabolic roles Ex: enzymes in all organisms, plasma proteins and antibodies in mammals Fibrous form long fibres mostly consist of repeated sequences of amino acids which are insoluble in water usually have structura ...
Organic Chemistry - Biology Junction
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
Proteins as drugs
... gene sequences. This is because different proteins can be derived from a single gene and proteins are often modified following their synthesis. • There are roughly 40,000 genes, whereas a typical cell contains hundreds of thousands of different proteins. • knowing the structure of a protein does not ...
... gene sequences. This is because different proteins can be derived from a single gene and proteins are often modified following their synthesis. • There are roughly 40,000 genes, whereas a typical cell contains hundreds of thousands of different proteins. • knowing the structure of a protein does not ...
Organic Chemistry - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
... membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like localized hormones to induce cellular/tissue responses ...
4.7-4.16
... -the golgi receives vesicles from the ER and chemically modifies them -some chemical modifications are used to mark and sort proteins for export out of the cell -one function of the shipping portion of the golgi is to package a finished protein into a vesicle to move to the plasma membrane so it ca ...
... -the golgi receives vesicles from the ER and chemically modifies them -some chemical modifications are used to mark and sort proteins for export out of the cell -one function of the shipping portion of the golgi is to package a finished protein into a vesicle to move to the plasma membrane so it ca ...
Supporting Information File SF5
... ependorf tube and precipitate from the phenol-ethanol supernatants using 1.5ml isopropanol per 1ml reagent. Light vertex, and incubation (10 min., room temp.), and then centrifuged (10,254g, 10 min at 4 °C). In-gel proteolysis Proteins subjected to gel electrophoresis were reduced with 10 mM DTT (60 ...
... ependorf tube and precipitate from the phenol-ethanol supernatants using 1.5ml isopropanol per 1ml reagent. Light vertex, and incubation (10 min., room temp.), and then centrifuged (10,254g, 10 min at 4 °C). In-gel proteolysis Proteins subjected to gel electrophoresis were reduced with 10 mM DTT (60 ...
presentation source
... • Genomic analysis has certainly provided us with much insight into the possible role of particular genes in disease • However proteins are the functional output of the cell and their dynamic nature in specific biological contexts is critical • The expression or function of proteins is modulated at ...
... • Genomic analysis has certainly provided us with much insight into the possible role of particular genes in disease • However proteins are the functional output of the cell and their dynamic nature in specific biological contexts is critical • The expression or function of proteins is modulated at ...
Detecting Protein Function and Protein
... Identify “promiscuous” domains that are present in many proteins and interact with many other domains. Removing the top 5% promiscuous proteins drastically reduces the rate of ...
... Identify “promiscuous” domains that are present in many proteins and interact with many other domains. Removing the top 5% promiscuous proteins drastically reduces the rate of ...
0495116572_102919
... – mRNA codes for amino acid sequence to form protein – mRNA is synthesized in nucleus, then moves to RER in cytoplasmic matrix – Codons - 3-base sequences that code for amino acids – tRNA bring AAs to mRNA on ribosomes 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
... – mRNA codes for amino acid sequence to form protein – mRNA is synthesized in nucleus, then moves to RER in cytoplasmic matrix – Codons - 3-base sequences that code for amino acids – tRNA bring AAs to mRNA on ribosomes 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
poly=many
... As polysaccharides, saccharide means sugar, poly means many. So polysaccharides means many sugars, and ...
... As polysaccharides, saccharide means sugar, poly means many. So polysaccharides means many sugars, and ...
3 - Food Nutrition
... enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract: • First by pepsin, present in the gastric juice; • Then by proteases secreted by the pancreas and by the cells from the intestinal mucosa. • Most of these enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of specific peptide bonds. ...
... enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract: • First by pepsin, present in the gastric juice; • Then by proteases secreted by the pancreas and by the cells from the intestinal mucosa. • Most of these enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of specific peptide bonds. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.