A Stable Serine Protease, Wrightin, from the Latex of the Plant
... and 25% glycerol was loaded on each gel and electrophoresed at a constant current of 2 mA per rod for 4 h. After the run, tube gels were fixed in fixing solution (30 mL methanol, 70 mL of distilled water, 3.45 g of sulfosalicylic acid, and 11.5 g of trichloroacetic acid in 100 mL of distilled water) ...
... and 25% glycerol was loaded on each gel and electrophoresed at a constant current of 2 mA per rod for 4 h. After the run, tube gels were fixed in fixing solution (30 mL methanol, 70 mL of distilled water, 3.45 g of sulfosalicylic acid, and 11.5 g of trichloroacetic acid in 100 mL of distilled water) ...
pH-induced conformational changes in human ABO(H) blood group
... H-antigen acceptor (Alfaro et al. 2008). Accordingly, with the exception of GTA, which has recently been shown to form the closed state most readily even in the absence of the acceptor fucose moiety (Johal et al. 2012; Alfaro et al. 2008), the C-terminal loop is not ordered in any of the structures ...
... H-antigen acceptor (Alfaro et al. 2008). Accordingly, with the exception of GTA, which has recently been shown to form the closed state most readily even in the absence of the acceptor fucose moiety (Johal et al. 2012; Alfaro et al. 2008), the C-terminal loop is not ordered in any of the structures ...
Purified dextransucrase from Pediococcus pentosaceus CRAG3 as
... Glucansucrases (GSs) are large size extracellular enzymes that catalyse the synthesis of different types of α-glucans such as dextran, mutan, alternan and reuteran using sucrose as a substrate. Depending upon the nature of synthesized product they are categorize as dextransucrase (EC 2.4.1.5), alter ...
... Glucansucrases (GSs) are large size extracellular enzymes that catalyse the synthesis of different types of α-glucans such as dextran, mutan, alternan and reuteran using sucrose as a substrate. Depending upon the nature of synthesized product they are categorize as dextransucrase (EC 2.4.1.5), alter ...
Document
... exposure to cockroach allergens has been linked to increased asthma morbidity in the United States, especially among lower socioeconomic groups.1 Reports in the literature suggest that enzymatic activity might be an important contributor to allergenicity, especially for mite allergens with cysteine ...
... exposure to cockroach allergens has been linked to increased asthma morbidity in the United States, especially among lower socioeconomic groups.1 Reports in the literature suggest that enzymatic activity might be an important contributor to allergenicity, especially for mite allergens with cysteine ...
Use of a Sec signal peptide library from Bacillus subtilis for the
... acids in length on average [12]. These SPs show a highly conserved three-domain structure: (1) a positively charged N-region, with a high preference for lysine residues at P2 and P3 [12, 13], (2) the longest region, termed H-region, consists of hydrophobic amino acids, and (3) a C-domain, which cont ...
... acids in length on average [12]. These SPs show a highly conserved three-domain structure: (1) a positively charged N-region, with a high preference for lysine residues at P2 and P3 [12, 13], (2) the longest region, termed H-region, consists of hydrophobic amino acids, and (3) a C-domain, which cont ...
Full Text - J
... should be stored in a high salt-concentration solution, and should not be frozen or freeze-dried. Thus we stored the purified toxins in a solution with a high salt concentration such as 0.8 M NaCl and 5 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) at 4°C. Under this condition, 90% of the hemolytic activity of C. ra ...
... should be stored in a high salt-concentration solution, and should not be frozen or freeze-dried. Thus we stored the purified toxins in a solution with a high salt concentration such as 0.8 M NaCl and 5 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) at 4°C. Under this condition, 90% of the hemolytic activity of C. ra ...
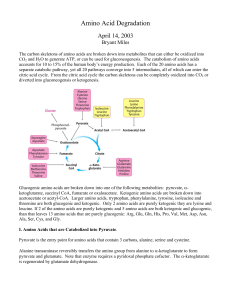
Amino Acid Degradation
... First leucine is transaminatedby branched amino acid aminotransferase to form α-ketoisocaproate which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to form isovaleryl CoA by the branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex we just discussed. In the next step isovaleryl CoA is dehydrogenated to form βmethylc ...
... First leucine is transaminatedby branched amino acid aminotransferase to form α-ketoisocaproate which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to form isovaleryl CoA by the branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex we just discussed. In the next step isovaleryl CoA is dehydrogenated to form βmethylc ...
Chapter 14 Preparing Semisynthetic and Fully Synthetic Histones
... Chemical ligation is an excellent way to prepare the homogenous samples of precisely modified histone proteins that are necessary to characterize the molecular functions of these modifications within the structured nucleosome core (5). Native chemical ligation (NCL) is the chemoselective condensatio ...
... Chemical ligation is an excellent way to prepare the homogenous samples of precisely modified histone proteins that are necessary to characterize the molecular functions of these modifications within the structured nucleosome core (5). Native chemical ligation (NCL) is the chemoselective condensatio ...
... Rabies virus has a bullet-shaped morphology (Fig.1A) and the virions consist of a nucleocapsid core sUlTounded by a host-derived lipid envelope. The nucleocapsid core contains all the elements necessary for viral transcription (Kawai, 1977). These include the single-stranded, negative sense RNA geno ...
36. Amino Acids and Carbohydrates in Sediments and Interstitial
... matter (e.g., Hamilton and Hedges, 1988; Burdige and Martens, 1988). In the Peru upwelling area, for example, up to 70% of the total nitrogen in surface sediments is accounted for by amino acids (Henrichs et al., 1984). A consensus is that these compounds and other labile constituents of seston, e.g ...
... matter (e.g., Hamilton and Hedges, 1988; Burdige and Martens, 1988). In the Peru upwelling area, for example, up to 70% of the total nitrogen in surface sediments is accounted for by amino acids (Henrichs et al., 1984). A consensus is that these compounds and other labile constituents of seston, e.g ...
Organic_2_6.1ed_2012_10th_module_biochem_and_polymers
... Based on the pKa values given, draw the dominant form of each of the following amino acids at pH 3, at pH 7, and at pH 13. Also, calculate the pI for each. a) Glycine: pKa values of 2.3 (for the -COOH) and 9.6 (for the - NH3+). pH 3 pH 7 pH 13 pI ...
... Based on the pKa values given, draw the dominant form of each of the following amino acids at pH 3, at pH 7, and at pH 13. Also, calculate the pI for each. a) Glycine: pKa values of 2.3 (for the -COOH) and 9.6 (for the - NH3+). pH 3 pH 7 pH 13 pI ...
Role of Dietary Soy Protein in Obesity
... Soybeans provide one of the most abundant plant sources of dietary protein. The protein content of soybeans varies from 36% to 56% [24-27]. Protein content of soybean from different areas are quantitatively different with those grown in the southern United States having high concentration of crude p ...
... Soybeans provide one of the most abundant plant sources of dietary protein. The protein content of soybeans varies from 36% to 56% [24-27]. Protein content of soybean from different areas are quantitatively different with those grown in the southern United States having high concentration of crude p ...
Studies on legume receptors for Nod and Myc symbiotic signals
... japonicus became a model plant used to study these symbioses. It forms determinate nodules with Mesorhizobium loti. As for M. truncatula a set of symbiotic genes has also been identified for L. japonicus (Sato and Tabata, 2006; Madsen et al., 2010). For non-symbiotic studies (plant development, inte ...
... japonicus became a model plant used to study these symbioses. It forms determinate nodules with Mesorhizobium loti. As for M. truncatula a set of symbiotic genes has also been identified for L. japonicus (Sato and Tabata, 2006; Madsen et al., 2010). For non-symbiotic studies (plant development, inte ...
1-3 flagellum - Instituto de Higiene
... transporter isoform in L. enriettii are all present in the flagellar membrane, while they occur at low or undetectable levels on the pellicular plasma membrane. In addition, earlier biochemical studies [9] detected specific proteins on SDS-polyacrylamide gels using a membrane fraction from purified ...
... transporter isoform in L. enriettii are all present in the flagellar membrane, while they occur at low or undetectable levels on the pellicular plasma membrane. In addition, earlier biochemical studies [9] detected specific proteins on SDS-polyacrylamide gels using a membrane fraction from purified ...
Abiotic stress in plants: Late Embryogenesis Abundant proteins Imen Amara
... survival or death of the affected plants (Ahuja I 2010; Xiong et al. 2002; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki and Shinozaki 2006). In Arabidopsis gene networks of stress-inducible genes have been identified and have been classified into two groups: regulatory and functional genes (Cramer et al. 2011; Shinozaki and ...
... survival or death of the affected plants (Ahuja I 2010; Xiong et al. 2002; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki and Shinozaki 2006). In Arabidopsis gene networks of stress-inducible genes have been identified and have been classified into two groups: regulatory and functional genes (Cramer et al. 2011; Shinozaki and ...
The Cutting Edge of Affinity Electrophoresis Technology
... the electrophoretic patterns of biological macromolecules that result from interactions or complex-formation processes that induce changes in the size or total charge of the molecules. Nucleic acid fragments can be characterized through their affinity to other molecules, for example transcriptional ...
... the electrophoretic patterns of biological macromolecules that result from interactions or complex-formation processes that induce changes in the size or total charge of the molecules. Nucleic acid fragments can be characterized through their affinity to other molecules, for example transcriptional ...
SAbDab: the structural antibody database | Nucleic Acids Research
... pairings, antigen details and, where available, antibody–antigen binding affinity. The user can select structures, according to these attributes as well as structural properties such as complementarity determining region loop conformation and variable domain orientation. Individual structures, datas ...
... pairings, antigen details and, where available, antibody–antigen binding affinity. The user can select structures, according to these attributes as well as structural properties such as complementarity determining region loop conformation and variable domain orientation. Individual structures, datas ...
Efficiency and Diversity of Protein Localization by Random Signal Sequences.
... during the process of secretion. A large body of biochemical and genetic data indicates that the signal peptide is the primary determinant for segregation of proteins into the secretory pathway (5, 8, 11, 20, 32). Two complementary genetic approaches have been used to identify the elements within si ...
... during the process of secretion. A large body of biochemical and genetic data indicates that the signal peptide is the primary determinant for segregation of proteins into the secretory pathway (5, 8, 11, 20, 32). Two complementary genetic approaches have been used to identify the elements within si ...
Structure and mechanism of ATP-dependent phospholipid transporters
... Fig. 1. General structure of ABC transporters and P-type ATPases. (A) Secondary structure of ABC transporters. The ABC transporter exists both as a monomer full transporter and as a dimer consisting of two half transporters. In either case, this type of transporter contains two transmembrane domains ...
... Fig. 1. General structure of ABC transporters and P-type ATPases. (A) Secondary structure of ABC transporters. The ABC transporter exists both as a monomer full transporter and as a dimer consisting of two half transporters. In either case, this type of transporter contains two transmembrane domains ...
PeptidePicker: a Tool for Determining Most Appropriate Peptides for
... database27 with scores given for the likelihood of observing a given peptide.28 The score also takes into consideration the suitability of an MRM transition, based on the frequency and intensity of the observed fragment ions of the specific peptide. The software checks selected peptides for uniquene ...
... database27 with scores given for the likelihood of observing a given peptide.28 The score also takes into consideration the suitability of an MRM transition, based on the frequency and intensity of the observed fragment ions of the specific peptide. The software checks selected peptides for uniquene ...
The Role of Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase in Plant Mitochondria
... nucleoside triphosphate pools. It has become recognized that as well as having the kinase activity, NDPK proteins have additional or different roles. This study concerns an NDPK isoform located in plant mitochondria that supports the eversurprising functions of the protein. There is increasing evide ...
... nucleoside triphosphate pools. It has become recognized that as well as having the kinase activity, NDPK proteins have additional or different roles. This study concerns an NDPK isoform located in plant mitochondria that supports the eversurprising functions of the protein. There is increasing evide ...
Article - Andrej Sali
... et al., 2006; Selmer et al., 2006; Schuwirth et al., 2005). In addition, structures of programmed bacterial ribosomes have defined a path for the translocation of mRNA and tRNAs through the intersubunit space (Yusupova et al., 2001, 2006; Korostelev et al., 2006; Selmer et al., 2006; Berk et al., 20 ...
... et al., 2006; Selmer et al., 2006; Schuwirth et al., 2005). In addition, structures of programmed bacterial ribosomes have defined a path for the translocation of mRNA and tRNAs through the intersubunit space (Yusupova et al., 2001, 2006; Korostelev et al., 2006; Selmer et al., 2006; Berk et al., 20 ...
The paradox of elongation factor 4: highly conserved, yet of no
... requires the binding of GTP or its non-hydrolysable analogue GDPNP [77,78]. Initially, binding of EF4•GTP stabilizes the ratcheted state of the ribosome, which is associated with the transfer of two tRNAs from the classical E/E, P/P state to the hybrid P/E, A/P state. The factor is then able to furt ...
... requires the binding of GTP or its non-hydrolysable analogue GDPNP [77,78]. Initially, binding of EF4•GTP stabilizes the ratcheted state of the ribosome, which is associated with the transfer of two tRNAs from the classical E/E, P/P state to the hybrid P/E, A/P state. The factor is then able to furt ...
Early days of tRNA research: Discovery, function, purification and
... to obtain overlaps between the oligonucleotide fragments present in a complete digest; and finally (iii) assembly of the fragments into a unique sequence. Sequence analysis of oligonucleotide fragments present in digests of tRNA requires that they be separated from each other. The use of DEAE-cellulo ...
... to obtain overlaps between the oligonucleotide fragments present in a complete digest; and finally (iii) assembly of the fragments into a unique sequence. Sequence analysis of oligonucleotide fragments present in digests of tRNA requires that they be separated from each other. The use of DEAE-cellulo ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.