![Basic region of residues 228-231 of protein kinase CK1[alpha] is](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015745345_1-81da768c37e720623b4b1898472e2f2e-300x300.png)
Basic region of residues 228-231 of protein kinase CK1[alpha] is
... in these assays was produced by 35S labeling through an in vitro transcription-translation system or by allowing CK1a to autophosphorylate with 32P. Alternatively, the presence of active CK1a bound to axin on the sepharose beads can be assayed by determining its capacity to phosphorylate a specific ...
... in these assays was produced by 35S labeling through an in vitro transcription-translation system or by allowing CK1a to autophosphorylate with 32P. Alternatively, the presence of active CK1a bound to axin on the sepharose beads can be assayed by determining its capacity to phosphorylate a specific ...
biochemical, biophysical and electrophysiological characterisation
... The eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel Na v is an integral membrane protein that transports sodium across the cell membrane. While the Na v has a four-domain structure with six α-helical transmembrane segments in each domain, the first bacterial homologue, which was identified in 2001 in Bacill ...
... The eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel Na v is an integral membrane protein that transports sodium across the cell membrane. While the Na v has a four-domain structure with six α-helical transmembrane segments in each domain, the first bacterial homologue, which was identified in 2001 in Bacill ...
Lecture 1 - "Hudel" Luecke
... An alpha-helix is a tight helix formed out of the polypeptide chain. The polypeptide main chain makes up the central structure, and the side chains extend out and away from the helix. The CO group of one amino acid (n) is hydrogen bonded to the NH group of the amino acid four residues away (n +4). I ...
... An alpha-helix is a tight helix formed out of the polypeptide chain. The polypeptide main chain makes up the central structure, and the side chains extend out and away from the helix. The CO group of one amino acid (n) is hydrogen bonded to the NH group of the amino acid four residues away (n +4). I ...
Unit 14 – Biomolecules
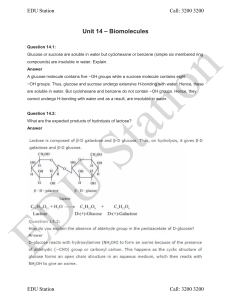
... What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type. Answer ...
... What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type. Answer ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... predicts specificity-determining positions (SDPs) that by definition are positions of multiple alignment which are conserved within subfamilies consisting of the proteins with the same specificity, but differ between these subfamilies. The major advantage of this approach stems from the fact that in ...
... predicts specificity-determining positions (SDPs) that by definition are positions of multiple alignment which are conserved within subfamilies consisting of the proteins with the same specificity, but differ between these subfamilies. The major advantage of this approach stems from the fact that in ...
as PDF
... Proteomics is loosely defined as the description of sets of proteins from any biological source, which have in most cases been identified by using mass spectrometry. However, only the mere identity of proteins present in a certain sample does not give any information about the dynamics of the proteo ...
... Proteomics is loosely defined as the description of sets of proteins from any biological source, which have in most cases been identified by using mass spectrometry. However, only the mere identity of proteins present in a certain sample does not give any information about the dynamics of the proteo ...
Isoelectric point prediction from the amino acid sequence of a protein
... commonly found for these side chains when they are part of a protein. The pKA values for these side chains may be quite different for the free amino acid in solution. pKA values also depend on ...
... commonly found for these side chains when they are part of a protein. The pKA values for these side chains may be quite different for the free amino acid in solution. pKA values also depend on ...
Signals and Structural Features Involved in Integral Membrane
... protein, nor full-length histone H1, can target an integral protein to the inner nuclear membrane although they can target cytosolic proteins to the nucleus. The addition of an NLS to a protein normally located in the ...
... protein, nor full-length histone H1, can target an integral protein to the inner nuclear membrane although they can target cytosolic proteins to the nucleus. The addition of an NLS to a protein normally located in the ...
Model Description Sheet
... fertility problems, Type 2 diabetes, and stroke. Over- and under-eating are related to brain chemistry. A 38 amino acid peptide hormone in the hypothalamus, called pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP), may be linked to eating disorders. PACAP binds to PACAP type 1 receptor (PAC1R), ...
... fertility problems, Type 2 diabetes, and stroke. Over- and under-eating are related to brain chemistry. A 38 amino acid peptide hormone in the hypothalamus, called pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP), may be linked to eating disorders. PACAP binds to PACAP type 1 receptor (PAC1R), ...
Protein kinases of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium
... • the tyrosine kinases (TyrK). ePKs that did not clearly fit into any of these groups were placed into the OPK ("other protein kinases") group. The primary structure of all enzymes in these groups conform to the model described by Hanks, in which the catalytic domain is subdivided into eleven subdom ...
... • the tyrosine kinases (TyrK). ePKs that did not clearly fit into any of these groups were placed into the OPK ("other protein kinases") group. The primary structure of all enzymes in these groups conform to the model described by Hanks, in which the catalytic domain is subdivided into eleven subdom ...
“The function and synthesis of ribosomes.” Nature Reviews Mol Cell
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
The Organellar Genome and Metabolic Potential
... and they contain an electron transport chain with Complexes I through IV as well as an ATPase (Complex V). In the evolution of mitochondria, hydrogenosomes and mitosomes from an a-proteobacterium, a large number of genes and proteins have been lost, gained from various sources, or retargeted to othe ...
... and they contain an electron transport chain with Complexes I through IV as well as an ATPase (Complex V). In the evolution of mitochondria, hydrogenosomes and mitosomes from an a-proteobacterium, a large number of genes and proteins have been lost, gained from various sources, or retargeted to othe ...
Utilization of fats and amino acids as fuels
... many acetyl CoAs, NADHs and FADHs would be produced? ...
... many acetyl CoAs, NADHs and FADHs would be produced? ...
LS1a Fall 2014 Lab 6: Ribosomal Protein Translation (PyMOL lab #3)
... This final scene rotates the large subunit into a particular orientation in which you can see the PTC (the spherically-represented amino-acids) through the thistle of the 23S ribosomal RNA. This “tunnel” though the large subunit that connects the PTC to the environment outside the ribosome is called ...
... This final scene rotates the large subunit into a particular orientation in which you can see the PTC (the spherically-represented amino-acids) through the thistle of the 23S ribosomal RNA. This “tunnel” though the large subunit that connects the PTC to the environment outside the ribosome is called ...
PDF
... secondary endocytobiosis resulted in a complex cellular structure and metabolism compared to algae with primary plastids. Methodology/Principal Findings. The whole genome sequence of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum has recently been completed. We identified and annotated genes for enzymes invol ...
... secondary endocytobiosis resulted in a complex cellular structure and metabolism compared to algae with primary plastids. Methodology/Principal Findings. The whole genome sequence of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum has recently been completed. We identified and annotated genes for enzymes invol ...
the function and synthesis of ribosomes
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
Redox regulation of cysteine
... balance of constituents that are needed to work together. There are times, however, when that balance must shift, such as when kinase activity in a cell is increased to support specific functions. Because prolonged increases in kinase activity would likely lead to cellular dysfunction, this increase ...
... balance of constituents that are needed to work together. There are times, however, when that balance must shift, such as when kinase activity in a cell is increased to support specific functions. Because prolonged increases in kinase activity would likely lead to cellular dysfunction, this increase ...
MILK - Soegijapranata Catholic University
... (A) Uniform liquid. However, the liquid is turbid and thus cannot be homogeneous. (B) Spherical droplets, consisting of fat. These globules float in a liquid (plasma). (C) The plasma contains proteinaceous particles, which are casein micelles. The remaining liquid (serum) is still opalescent, so it ...
... (A) Uniform liquid. However, the liquid is turbid and thus cannot be homogeneous. (B) Spherical droplets, consisting of fat. These globules float in a liquid (plasma). (C) The plasma contains proteinaceous particles, which are casein micelles. The remaining liquid (serum) is still opalescent, so it ...
Protein proteinase inhibitors from avian egg whites
... The reactive site is a single special peptide bond in each inhibitor molecule or domain which serves the cognate enzyme as a high-affinity substrate. A six- or sevenamino acid residue sequence is involved in the complex formation between inhibitor and enzyme. The hydrolysis of the reactive-site pept ...
... The reactive site is a single special peptide bond in each inhibitor molecule or domain which serves the cognate enzyme as a high-affinity substrate. A six- or sevenamino acid residue sequence is involved in the complex formation between inhibitor and enzyme. The hydrolysis of the reactive-site pept ...
Colicins produced by the Escherichia fergusonii strains closely
... cea of pColE1-EF43, resulting in a one-amino acid change (A71T) in colicin E1 protein (Fig. 1). pColE1-EF3 imm and kil gene sequences were identical to those of pColE1-EF43. Consistent with this ¢nding, E. coli strain TOP10FP with pDS455 was immune to colicin E1 produced by EF3 strain and vice versa ...
... cea of pColE1-EF43, resulting in a one-amino acid change (A71T) in colicin E1 protein (Fig. 1). pColE1-EF3 imm and kil gene sequences were identical to those of pColE1-EF43. Consistent with this ¢nding, E. coli strain TOP10FP with pDS455 was immune to colicin E1 produced by EF3 strain and vice versa ...
gender determines the igf-i sensitivity of muscle protein anabolism
... concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay in plasma obtained at the beginning and the completion of the study. Plasma corticosterone concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay in plasma obtained at the beginning of the study to confirm the success of adrenalectomy. Measurement of skelet ...
... concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay in plasma obtained at the beginning and the completion of the study. Plasma corticosterone concentrations were measured by radioimmunoassay in plasma obtained at the beginning of the study to confirm the success of adrenalectomy. Measurement of skelet ...
Dynamic Model of the Process of Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotic Cells
... process (will be described later). During initiation, the Scanning Complex sc leaves the 5’ terminal cap and moves along the 5’ Untranslated Region (UTR) until the AUG codon is encountered. This UTR might be unstructured in which sc migrates along easily without encountering hinders or energy barrie ...
... process (will be described later). During initiation, the Scanning Complex sc leaves the 5’ terminal cap and moves along the 5’ Untranslated Region (UTR) until the AUG codon is encountered. This UTR might be unstructured in which sc migrates along easily without encountering hinders or energy barrie ...
Filip Jagodzinski - WWU Computer Science Faculty Web Pages
... Advisor: Ileana Streinu M.S., Computer Science – Villanova University Advisor: Frank Klassner B.S., Biomedical Engineering, Imaging – Columbia University ...
... Advisor: Ileana Streinu M.S., Computer Science – Villanova University Advisor: Frank Klassner B.S., Biomedical Engineering, Imaging – Columbia University ...
Specific Interaction of the PDZ Domain Protein PICK1 with the
... PDZ domain-containing proteins are shown. The putative carboxylate-binding loop, as described by Doyle et al. (29), is also indicated. Sources of sequences were hROS1 (42), mPSD95 (43), dCAN (27), dDSH (44), hNOS (45), and hZO1 (46). B, comparison of the amino acid sequences of mouse PICK1 and C. el ...
... PDZ domain-containing proteins are shown. The putative carboxylate-binding loop, as described by Doyle et al. (29), is also indicated. Sources of sequences were hROS1 (42), mPSD95 (43), dCAN (27), dDSH (44), hNOS (45), and hZO1 (46). B, comparison of the amino acid sequences of mouse PICK1 and C. el ...
Molecular mechanisms of complement evasion: learning from
... escape the innate immune response, including the expression of an extracellular capsule and ‘hiding’ within host cells, either in a vacuole or in the cytoplasm. Over the past few years it has become clear that, in addition, bacteria can escape recognition by the complement system through the actions ...
... escape the innate immune response, including the expression of an extracellular capsule and ‘hiding’ within host cells, either in a vacuole or in the cytoplasm. Over the past few years it has become clear that, in addition, bacteria can escape recognition by the complement system through the actions ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.