Carrier Proteins - HCC Learning Web
... Cell-cell recognition- the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. – Cell-cell recognition is the basis for the rejection of foreign cells by the immune system. Cells recognize other cells by binding to surface molecules, often carbohydrates, on the plasma membran ...
... Cell-cell recognition- the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another. – Cell-cell recognition is the basis for the rejection of foreign cells by the immune system. Cells recognize other cells by binding to surface molecules, often carbohydrates, on the plasma membran ...
Effect of nitrogen fertilization on metabolisms of essential and non
... highest N dose (treatment N2) reduced the content of Ser and alanine compared with the other two treatments and also decreased the content of aspartic acid compared with the unfertilised control. Treatment N1 had the lowest content of proline (2008), while in 2009 this AA was significantly reduced ...
... highest N dose (treatment N2) reduced the content of Ser and alanine compared with the other two treatments and also decreased the content of aspartic acid compared with the unfertilised control. Treatment N1 had the lowest content of proline (2008), while in 2009 this AA was significantly reduced ...
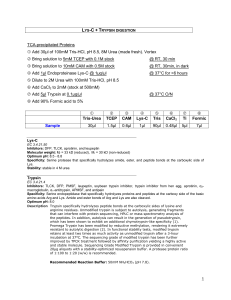
TRYPSIN / LYS
... arginine residues. Unmodified trypsin is subject to autolysis, generating fragments that can interfere with protein sequencing, HPLC or mass spectrometry analysis of the peptides. In addition, autolysis can result in the generation of pseudotrypsin, which has been shown to exhibit an additional chym ...
... arginine residues. Unmodified trypsin is subject to autolysis, generating fragments that can interfere with protein sequencing, HPLC or mass spectrometry analysis of the peptides. In addition, autolysis can result in the generation of pseudotrypsin, which has been shown to exhibit an additional chym ...
Gene Section IGF1 (Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (Somatomedin C))
... Exons 1 and 2 determine the class of the protein and functionally represent the signal peptide for cellular localization post-translation. Exons 3 and 4 will primarily encode the IGF-1 mature peptide; ultimately becoming the receptor binding ligand. Exons 5 and 6 will primarily represent the E domai ...
... Exons 1 and 2 determine the class of the protein and functionally represent the signal peptide for cellular localization post-translation. Exons 3 and 4 will primarily encode the IGF-1 mature peptide; ultimately becoming the receptor binding ligand. Exons 5 and 6 will primarily represent the E domai ...
A1987K192000001
... six-week fast. Furthermore, in prolonged starvation, plasma alanine levels fell to a greater extent than all other amino acids, and the hypoalaninemia, rather than a change in splanchnic fractional extraction of alanine, accounted for the marked reduction in splanchnic alanine uptake observed during ...
... six-week fast. Furthermore, in prolonged starvation, plasma alanine levels fell to a greater extent than all other amino acids, and the hypoalaninemia, rather than a change in splanchnic fractional extraction of alanine, accounted for the marked reduction in splanchnic alanine uptake observed during ...
Nutritional Requirements and Biosynthetic
... vitamin supplement and a selection of nucleic acid derivatives. The strain of S. oncopelti used for the work described in the present paper did not require haematin in either peptone or the defined media. Studies of the catabolic metabolism of S . oncopelti were recently described by Clausen (1955) ...
... vitamin supplement and a selection of nucleic acid derivatives. The strain of S. oncopelti used for the work described in the present paper did not require haematin in either peptone or the defined media. Studies of the catabolic metabolism of S . oncopelti were recently described by Clausen (1955) ...
Zhang, Zhiyong: An Overview of Protein Structure Prediction: From Homology to Ab Initio
... protein representation; 3) Efficient and reliable algorithms to search the conformational space to minimize the energy function. The conformations that minimize the energy function are taken to be the structures that the protein is likely to adopt at native conditions. The folding of the protein se ...
... protein representation; 3) Efficient and reliable algorithms to search the conformational space to minimize the energy function. The conformations that minimize the energy function are taken to be the structures that the protein is likely to adopt at native conditions. The folding of the protein se ...
Document
... message that will be translated to form a protein. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
... message that will be translated to form a protein. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
Amino Acid Analysis Recommendations
... (standard addition method) with reference compounds to define these parameters in the relevant biological matrix. Exact retention times and response factors for each amino acid have to be determined at two wavelengths (λ= 570 nm and λ= 440 nm). Signal ratios at these wavelengths have to be determine ...
... (standard addition method) with reference compounds to define these parameters in the relevant biological matrix. Exact retention times and response factors for each amino acid have to be determined at two wavelengths (λ= 570 nm and λ= 440 nm). Signal ratios at these wavelengths have to be determine ...
Lecture_14.pps
... USUAL TURNOVER • Most glycans are extracellular or on cell surface • Membrane recycling • Receptor and non-receptor mediated endocytosis ...
... USUAL TURNOVER • Most glycans are extracellular or on cell surface • Membrane recycling • Receptor and non-receptor mediated endocytosis ...
extraction of keratin protein from chicken feather
... accomplished by breaking the disulfide bonds of the keratin. The β-keratins from feather have β-pleated sheets twisted together, and then stabilized and hardened by disulfide bonds. So by breaking these disulfide bonds in feathers, the strength of the keratin in the chicken feathers can be reduced t ...
... accomplished by breaking the disulfide bonds of the keratin. The β-keratins from feather have β-pleated sheets twisted together, and then stabilized and hardened by disulfide bonds. So by breaking these disulfide bonds in feathers, the strength of the keratin in the chicken feathers can be reduced t ...
Regulation of Protein Degradation
... have very limited cleavage site specificities and produce detectable protein products. Although several of the proteasome cleaving activities can be related to the four classes of proteinase through the use of class-specific inhibitors and peptide substrates, none of the proteasome subunits shares a ...
... have very limited cleavage site specificities and produce detectable protein products. Although several of the proteasome cleaving activities can be related to the four classes of proteinase through the use of class-specific inhibitors and peptide substrates, none of the proteasome subunits shares a ...
Pavel Doležal
... inhabit oxygen-poor environments, do not possess mitochondria as we know them. These organisms were then called “amitochondriates”. More recent studies of evolution and cell biology of “amitochondriate” protists, however, challenged their amitochondriate status, at least in the case of those organis ...
... inhabit oxygen-poor environments, do not possess mitochondria as we know them. These organisms were then called “amitochondriates”. More recent studies of evolution and cell biology of “amitochondriate” protists, however, challenged their amitochondriate status, at least in the case of those organis ...
Maize streak virus coat protein binds single
... Expression of proteins in E. coli has proven useful for functional studies of many plant virus proteins. We therefore expressed both full-length and truncated MSV CPs in the pET expression system. The expressed wt and truncated proteins had the expected molecular masses as calculated by computer ana ...
... Expression of proteins in E. coli has proven useful for functional studies of many plant virus proteins. We therefore expressed both full-length and truncated MSV CPs in the pET expression system. The expressed wt and truncated proteins had the expected molecular masses as calculated by computer ana ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide
... nucleic acids Know how excess glucose is stored Know dipeptide, tripeptide, polypeptide, disaccharide, polysaccharide Know the functional groups of amino acids Know peptide bonds Know what a glycerol and fatty acid are Know dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis Know condensation reaction Know monomer ...
... nucleic acids Know how excess glucose is stored Know dipeptide, tripeptide, polypeptide, disaccharide, polysaccharide Know the functional groups of amino acids Know peptide bonds Know what a glycerol and fatty acid are Know dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis Know condensation reaction Know monomer ...
Pavel Doležal
... inhabit oxygen-poor environments, do not possess mitochondria as we know them. These organisms were then called “amitochondriates”. More recent studies of evolution and cell biology of “amitochondriate” protists, however, challenged their amitochondriate status, at least in the case of those organis ...
... inhabit oxygen-poor environments, do not possess mitochondria as we know them. These organisms were then called “amitochondriates”. More recent studies of evolution and cell biology of “amitochondriate” protists, however, challenged their amitochondriate status, at least in the case of those organis ...
Chimeric phosphorylation indicator
... tages as phosphorylation-speci?c antibodies, including it is applicable to examining endogenous proteins in intact non transfected tissues, but has poor time resolution and dif?culty in generating a continuous time course. Another mode of energy transfer is bioluminescence resonance energy trans ...
... tages as phosphorylation-speci?c antibodies, including it is applicable to examining endogenous proteins in intact non transfected tissues, but has poor time resolution and dif?culty in generating a continuous time course. Another mode of energy transfer is bioluminescence resonance energy trans ...
Whey Protein: A Functional Food
... Lactoferrin’s antioxidant and antimicrobial effects have already been touched on briefly. Due to its ability to chelate iron, organisms requiring this metal to replicate would seem to be particularly vulnerable to lactoferrin’s effects. Lactoferrin also demonstrates an ability to stimulate immune ...
... Lactoferrin’s antioxidant and antimicrobial effects have already been touched on briefly. Due to its ability to chelate iron, organisms requiring this metal to replicate would seem to be particularly vulnerable to lactoferrin’s effects. Lactoferrin also demonstrates an ability to stimulate immune ...
Conservation and relative importance of residues across protein
... rim or the rest of the protein surface. With the division into core and rim residues one can ask the question of whether as two groups these residues have different contributions to binding energy, and consequently have different evolutionary pressure for their conservation. The degree of conservati ...
... rim or the rest of the protein surface. With the division into core and rim residues one can ask the question of whether as two groups these residues have different contributions to binding energy, and consequently have different evolutionary pressure for their conservation. The degree of conservati ...
Iron-Binding Activity of FutA1 Subunit of an ABC
... or futC, which encode inner membrane-bound or membraneassociated subunits, respectively, showed poor growth in ironfree BG-11 medium and low activity of ferric iron transport. The double mutant lacking both futA1 and futA2, which encode periplasmic binding proteins, showed the same phenotype as Dfut ...
... or futC, which encode inner membrane-bound or membraneassociated subunits, respectively, showed poor growth in ironfree BG-11 medium and low activity of ferric iron transport. The double mutant lacking both futA1 and futA2, which encode periplasmic binding proteins, showed the same phenotype as Dfut ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.