Economics Unit 1 PPT
... • Illustrates the impact of scarcity on an economy by showing the max number of goods and services that can be produced using limited resources. (Based on assumption) ...
... • Illustrates the impact of scarcity on an economy by showing the max number of goods and services that can be produced using limited resources. (Based on assumption) ...
Economics PowerPoint
... Wants and needs are met by obtaining goods and services Goods – are tangible, can be seen/touched Services – are intangible, cannot be seen/touched ...
... Wants and needs are met by obtaining goods and services Goods – are tangible, can be seen/touched Services – are intangible, cannot be seen/touched ...
Ecological Economics * Environmental Challenges
... The universe is understood as a machine (clockwork), completely causal and deterministic ...
... The universe is understood as a machine (clockwork), completely causal and deterministic ...
Homework C due 8th May51.5 KB
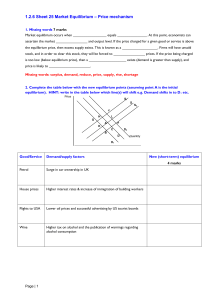
... 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is ...
... 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is ...
economics unit #1 study guide
... productive resources and unlimited wants result in scarcity, opportunity costs, and tradeoffs for individuals, businesses, and governments. a. Define scarcity as a basic condition that exists when unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources. b. Define and give examples of productive resource ...
... productive resources and unlimited wants result in scarcity, opportunity costs, and tradeoffs for individuals, businesses, and governments. a. Define scarcity as a basic condition that exists when unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources. b. Define and give examples of productive resource ...
Paper
... links to the society, (b) the methodology is mainly rationalistic and not evolutionary and (c) the analysis is capital-oriented and not human-centred and (d) they are lacking awareness of economic and societal history. Influencial economists are aware of the societal implications of their theories, ...
... links to the society, (b) the methodology is mainly rationalistic and not evolutionary and (c) the analysis is capital-oriented and not human-centred and (d) they are lacking awareness of economic and societal history. Influencial economists are aware of the societal implications of their theories, ...
Chapter 5 US Economy system
... • Productivity= a measure of the efficiency with which goods and services can be produced • Can be increased through technology and specialization {focus on a certain thing} ...
... • Productivity= a measure of the efficiency with which goods and services can be produced • Can be increased through technology and specialization {focus on a certain thing} ...
Key - KSU Web Home
... Consider the costs of complying with bureaucratic regulations to economic decision makers in Singapore, South Africa, and Venezuela. According to the results of the “Ease of Doing Business” study, of these three countries, such costs are: B. lowest in Singapore and highest in Venezuela. ...
... Consider the costs of complying with bureaucratic regulations to economic decision makers in Singapore, South Africa, and Venezuela. According to the results of the “Ease of Doing Business” study, of these three countries, such costs are: B. lowest in Singapore and highest in Venezuela. ...
Part 2: Thinking like an Economist
... graph showing the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and technology. ...
... graph showing the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and technology. ...
History of Economics
... The Socialist Calculation Debate • Socialists had to come up with a different basis for their thought since Marshall destroyed the foundation of Marx’s theory. • Enrico Barone replaced the invisible hand with the ministry of planning. • He proposed the establishment of a planned society in which ma ...
... The Socialist Calculation Debate • Socialists had to come up with a different basis for their thought since Marshall destroyed the foundation of Marx’s theory. • Enrico Barone replaced the invisible hand with the ministry of planning. • He proposed the establishment of a planned society in which ma ...
The German Economy
... – Reduction of marginal tax rates • The amount of tax paid for earnings above a certain level • For the median-income German in 1950, with an annual income of a little less than DM2,400, the marginal tax rate was 18 percent. That same person, had he earned the reichsmark equivalent in 1948, would ha ...
... – Reduction of marginal tax rates • The amount of tax paid for earnings above a certain level • For the median-income German in 1950, with an annual income of a little less than DM2,400, the marginal tax rate was 18 percent. That same person, had he earned the reichsmark equivalent in 1948, would ha ...
IMBA Managerial Economics Lecture One Fall 2014
... scarce resources to manage more effectively resources – financial, human, physical management of customers, suppliers, competitors, internal organization organizations – business, nonprofit, household ...
... scarce resources to manage more effectively resources – financial, human, physical management of customers, suppliers, competitors, internal organization organizations – business, nonprofit, household ...
다운로드 - Daum
... Mankiw says, “Teaching economics is a double blessing.” Ten principles: Underpinning ideas in economics ...
... Mankiw says, “Teaching economics is a double blessing.” Ten principles: Underpinning ideas in economics ...
Hastings1-Introducti..
... Economics is a social science that deals with how consumers , producers and societies choose among the alternative uses of scarce resources in the process of producing, consuming and exchanging good and services. (Penson et al.) Economics is the social science that studies the production, distri ...
... Economics is a social science that deals with how consumers , producers and societies choose among the alternative uses of scarce resources in the process of producing, consuming and exchanging good and services. (Penson et al.) Economics is the social science that studies the production, distri ...
Problem Areas in AP Economics Real Interest rate
... Economics is the study of limited resources and unlimited needs and wants Scarcity leads to making choices Opportunity Cost is what is sacrificed when one choice is made over the “next best alternative” Every decision has an opportunity cost ...
... Economics is the study of limited resources and unlimited needs and wants Scarcity leads to making choices Opportunity Cost is what is sacrificed when one choice is made over the “next best alternative” Every decision has an opportunity cost ...
here - WordPress.com
... Q3. Fill in the gaps in the paragraph below using the word bank. The paragraph describes how a market economy allocates resources. allocative efficiency - prices - supply - demand - profitable - consumer sovereignty - firms - equilibrium demand - supply - supply A market economy uses _______________ ...
... Q3. Fill in the gaps in the paragraph below using the word bank. The paragraph describes how a market economy allocates resources. allocative efficiency - prices - supply - demand - profitable - consumer sovereignty - firms - equilibrium demand - supply - supply A market economy uses _______________ ...
Martin Fajkus Faculty of applied informatics Tomas Bata University
... A: Small motivation How to fence a garden ...
... A: Small motivation How to fence a garden ...
Unit 1 recap
... The first is a SLIDE on the curve: this is when you decide to produce more of one and less of another. You move along the curve as you decide what your society needs. The second type is a SHIFT of the curve: this is when the curve changes places on the graph because of an increase or decrease of ...
... The first is a SLIDE on the curve: this is when you decide to produce more of one and less of another. You move along the curve as you decide what your society needs. The second type is a SHIFT of the curve: this is when the curve changes places on the graph because of an increase or decrease of ...
Lecture-Chapter 1, Keat and Young
... distributing, and consuming material goods and services in a world of scarce resources.” Managerial economics is defined to be “the use of economic analysis in the determination of business policy.” Economics is really just a framework for making decisions, and the application of economic analysis u ...
... distributing, and consuming material goods and services in a world of scarce resources.” Managerial economics is defined to be “the use of economic analysis in the determination of business policy.” Economics is really just a framework for making decisions, and the application of economic analysis u ...
economics
... – If he quits his present position, he has to give up $90 thousand of annual salary. Even though this is not actually spent, it should be counted as part of cost ...
... – If he quits his present position, he has to give up $90 thousand of annual salary. Even though this is not actually spent, it should be counted as part of cost ...
Opportunity cost (기회비용)
... Mankiw says, “Teaching economics is a double blessing.” Ten principles: Underpinning ideas in economics ...
... Mankiw says, “Teaching economics is a double blessing.” Ten principles: Underpinning ideas in economics ...
continued - Human Kinetics
... expenditures) + capital formation (services from domestic labor – costs of environmental degradation – depreciation of natural capital) ...
... expenditures) + capital formation (services from domestic labor – costs of environmental degradation – depreciation of natural capital) ...
History of economic thought Short characteristic of economics
... • Pure market economy: • Decision of any economic subject depends on their will, skills and possibilities. • Government does not intervene in economy (does not offer some goods and so on), only provides legal structure. ...
... • Pure market economy: • Decision of any economic subject depends on their will, skills and possibilities. • Government does not intervene in economy (does not offer some goods and so on), only provides legal structure. ...
History of economic thought Short characteristic of economics
... market economy works and to identify where government may need to intervene to correct specific aspect of market failure. (Lipsey and Chrystal, 2007) • Which economic system is the best one? • Market system: self-organization, efficient organization, based not on benevolence but on selfinterest. Sel ...
... market economy works and to identify where government may need to intervene to correct specific aspect of market failure. (Lipsey and Chrystal, 2007) • Which economic system is the best one? • Market system: self-organization, efficient organization, based not on benevolence but on selfinterest. Sel ...
Economics
Economics is the social science that seeks to describe the factors which determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek οἰκονομία from οἶκος (oikos, ""house"") and νόμος (nomos, ""custom"" or ""law""), hence ""rules of the house (hold for good management)"". 'Political economy' was the earlier name for the subject, but economists in the late 19th century suggested ""economics"" as a shorter term for ""economic science"" to establish itself as a separate discipline outside of political science and other social sciences.Economics focuses on the behavior and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consistent with this focus, primary textbooks often distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the entire economy (meaning aggregated production, consumption, savings, and investment) and issues affecting it, including unemployment of resources (labor, capital, and land), inflation, economic growth, and the public policies that address these issues (monetary, fiscal, and other policies).Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing ""what is,"" and normative economics, advocating ""what ought to be""; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and behavioral economics; and between mainstream economics (more ""orthodox"" and dealing with the ""rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus"") and heterodox economics (more ""radical"" and dealing with the ""institutions-history-social structure nexus"").Besides the traditional concern in production, distribution, and consumption in an economy, economic analysis may be applied throughout society, as in business, finance, health care, and government. Economic analyses may also be applied to such diverse subjects as crime, education, the family, law, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science, and the environment. Education, for example, requires time, effort, and expenses, plus the foregone income and experience, yet these losses can be weighted against future benefits education may bring to the agent or the economy. At the turn of the 21st century, the expanding domain of economics in the social sciences has been described as economic imperialism.The ultimate goal of economics is to improve the living conditions of people in their everyday life.