* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Price System (Markets)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
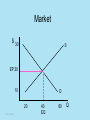
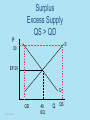
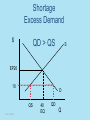
Economics Unit 4, Lesson 1 The Price System (Markets) ©2012, TESCCC Potential Buyers Potential Sellers Markets The interaction of buyers and sellers determines the price and quantity of most goods in a market system. ©2012, TESCCC Buyers and sellers have opposite goals. Buyers want the lowest price. Sellers want the highest price. ©2012, TESCCC Markets Draw Supply & Demand Demand Schedule $ QD 10.00 60 20.00 40 30.00 20 ©2012, TESCCC Supply Schedule $ QS 10.00 20 20.00 40 30.00 60 Market $ 30 S EP 20 10 D 20 ©2012, TESCCC 40 EQ 60 Q With supply and demand both on graph, we now have a market. Market equilibrium – where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal ©2012, TESCCC Based on 2 Assumptions 1. Everything in market has a price. 2. Price is best measure to answer the three basic economic questions. ©2012, TESCCC Prices act as signals. Signals to adjust – Demand – Supply ©2012, TESCCC Disequilibrium QS = QD This creates a shortage or a surplus. ©2012, TESCCC Surplus • A price above equilibrium creates a surplus. • A surplus is when QS is greater than QD. ©2012, TESCCC Surplus Excess Supply QS > QD P S 30 EP 20 D QD ©2012, TESCCC 40 EQ Q QS Shortage • A price below equilibrium created a shortage. • Shortage is when QD is greater than QS. ©2012, TESCCC Shortage Excess Demand $ QD > QS S EP20 10 D QS ©2012, TESCCC 40 EQ QD Q