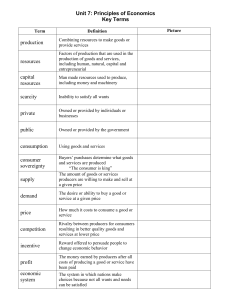
Presentation
... The social science chiefly concerned with the way individuals and societies choose to use their limited resources, which have alternative uses, to produce goods and services, which satisfy needs and wants, for present and future consumption. ...
... The social science chiefly concerned with the way individuals and societies choose to use their limited resources, which have alternative uses, to produce goods and services, which satisfy needs and wants, for present and future consumption. ...
Course Outline
... Prof. Fullerton will provide a mini-course for economics graduate students about how to build and use analytical general equilibrium models. The “log-linearization” method provides a remarkably easy and useful way to analyze topics in applied areas such as public, environmental, development, and tra ...
... Prof. Fullerton will provide a mini-course for economics graduate students about how to build and use analytical general equilibrium models. The “log-linearization” method provides a remarkably easy and useful way to analyze topics in applied areas such as public, environmental, development, and tra ...
Introduction to Economics
... J.S. Mill => He defines Economics as a “Practical science of production and distribution” H.J Davenport => Economics as a subject “Treats phenomena from stand point of price” Adam Smith => He considers Economics as an “Enquiry into the nature of wealth of nations” Alfred Marshal => He considers Econ ...
... J.S. Mill => He defines Economics as a “Practical science of production and distribution” H.J Davenport => Economics as a subject “Treats phenomena from stand point of price” Adam Smith => He considers Economics as an “Enquiry into the nature of wealth of nations” Alfred Marshal => He considers Econ ...
Chapter 1 Basic Economics
... Production – can only take place once all three factors of production are in place Gross Domestic Product – GDP – dollar value of all goods, services and structures produced within a countries’ borders GNP – Gross National Product – everything that a country produces within and outside of its own b ...
... Production – can only take place once all three factors of production are in place Gross Domestic Product – GDP – dollar value of all goods, services and structures produced within a countries’ borders GNP – Gross National Product – everything that a country produces within and outside of its own b ...
Company Name - University of Wisconsin–La Crosse
... The real cost of an item is its opportunity cost: what you must give up in order to get it. ...
... The real cost of an item is its opportunity cost: what you must give up in order to get it. ...
Mock_Economics_AS_Paper.doc
... 4. b) Explain the meaning of the price elasticity supply figure you have calculated. ...
... 4. b) Explain the meaning of the price elasticity supply figure you have calculated. ...
Thinking Like an Economist
... Technological advances in a particular industry can shift the PPF thus increasing the quantity of goods produced with the existing resources. TVs produced ...
... Technological advances in a particular industry can shift the PPF thus increasing the quantity of goods produced with the existing resources. TVs produced ...
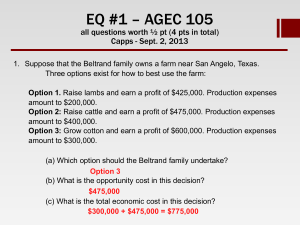
Key - Department of Agricultural Economics
... (c) What is the total economic cost in this decision? ...
... (c) What is the total economic cost in this decision? ...
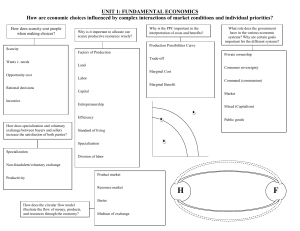
UNIT 1: FUNDAMENTAL ECONOMICS – THE BASICS
... How does scarcity cost people when making choices? ...
... How does scarcity cost people when making choices? ...
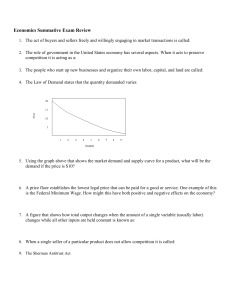
Economics Summative Exam Review
... Too much marketing today focuses on awareness rather than reasons to buy. In the old days, awareness advertising was more effective. There was less competition. All you had to worry about was whether or not people remembered your product. As technology and more kinds of media have come about, it’s n ...
... Too much marketing today focuses on awareness rather than reasons to buy. In the old days, awareness advertising was more effective. There was less competition. All you had to worry about was whether or not people remembered your product. As technology and more kinds of media have come about, it’s n ...
lc_econ_firstlecture
... – Law • promissory deposition torts venues – Economics • supply opportunity cost elasticity consumer surplus demand comparative advantage ...
... – Law • promissory deposition torts venues – Economics • supply opportunity cost elasticity consumer surplus demand comparative advantage ...
Principles of Business, Finance, and Marketing
... • the study of how individuals and groups of individuals strive to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices ...
... • the study of how individuals and groups of individuals strive to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices ...
Introduction to the Economic Problem
... The first job of any discipline is to first define itself and its parameters. How economics is defined at the outset will determine what gets included and what gets excluded from the discussion. Most textbooks use Lord Robbins’s definition: “Economics is the allocation of scarce resources between co ...
... The first job of any discipline is to first define itself and its parameters. How economics is defined at the outset will determine what gets included and what gets excluded from the discussion. Most textbooks use Lord Robbins’s definition: “Economics is the allocation of scarce resources between co ...
Introductiontoeconomics
... produced and consumed because people want to consume far more than an economy can produce. • The law of scarcity states that goods are scarce because there are not enough resources to produce all the goods that people want to consume. All of economics flows from this central fact. ...
... produced and consumed because people want to consume far more than an economy can produce. • The law of scarcity states that goods are scarce because there are not enough resources to produce all the goods that people want to consume. All of economics flows from this central fact. ...
Prof. Ofer Azar received his Ph.D. in economics from Northwestern
... Prof. Ofer Azar received his Ph.D. in economics from Northwestern University and is now an Associate Professor at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. His main research areas include behavioral economics, experimental economics, business strategy, industrial organization, and applied microeconomics. ...
... Prof. Ofer Azar received his Ph.D. in economics from Northwestern University and is now an Associate Professor at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. His main research areas include behavioral economics, experimental economics, business strategy, industrial organization, and applied microeconomics. ...
What is Globalization? - Honorsglobalportfolio
... GLOBAL ECONOMY • Goal: Effective resource mgmt for most efficient production ...
... GLOBAL ECONOMY • Goal: Effective resource mgmt for most efficient production ...
SOC 8311 Basic Social Statistics
... Individuals Maximize Utility Neoclassical economists assume methodological individualism: all economic phenomena can be explained by aggregating over individuals’ behaviors. They de-emphasize institutions – rules & regulations that predate and condition an individual’s actions. Consumers and produc ...
... Individuals Maximize Utility Neoclassical economists assume methodological individualism: all economic phenomena can be explained by aggregating over individuals’ behaviors. They de-emphasize institutions – rules & regulations that predate and condition an individual’s actions. Consumers and produc ...
Econ Unit 1 Study Guide Terms- Write the word, pg number
... 14. What are the benefits of the US free-enterprise system to producers and consumers? 2.2 15. What are the goals of US economic policy? 2.3 16. Why are scarcity and choice basic economic problems? 2.3 17. How do laws against false advertising promote economic equity? And which of the economic goals ...
... 14. What are the benefits of the US free-enterprise system to producers and consumers? 2.2 15. What are the goals of US economic policy? 2.3 16. Why are scarcity and choice basic economic problems? 2.3 17. How do laws against false advertising promote economic equity? And which of the economic goals ...
Economics Courses at MBS
... (Quite Recent) Economics – possibly the only field that can potentially offer a unified framework for thinking systematically about real business decisions. ...
... (Quite Recent) Economics – possibly the only field that can potentially offer a unified framework for thinking systematically about real business decisions. ...
Neoclassical
... Forces of supply and demand interact to achieve optimal outcomes for all Economic decisions are made on the basis of ‘utility maximization’ The economy is a dynamic system with a multitude of individual players, none the less it reaches an equilibrium where these forces are in balance. ...
... Forces of supply and demand interact to achieve optimal outcomes for all Economic decisions are made on the basis of ‘utility maximization’ The economy is a dynamic system with a multitude of individual players, none the less it reaches an equilibrium where these forces are in balance. ...
Exam 1 Topics Guide - Winthrop University
... How was price determined? (1) Church influence in pricing: In early western history, the church had a significant social influence on the business world. If businesses charged more for a product than what the church thought it should, the church looked down upon them. So, churches kept prices down b ...
... How was price determined? (1) Church influence in pricing: In early western history, the church had a significant social influence on the business world. If businesses charged more for a product than what the church thought it should, the church looked down upon them. So, churches kept prices down b ...
Economics
Economics is the social science that seeks to describe the factors which determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek οἰκονομία from οἶκος (oikos, ""house"") and νόμος (nomos, ""custom"" or ""law""), hence ""rules of the house (hold for good management)"". 'Political economy' was the earlier name for the subject, but economists in the late 19th century suggested ""economics"" as a shorter term for ""economic science"" to establish itself as a separate discipline outside of political science and other social sciences.Economics focuses on the behavior and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consistent with this focus, primary textbooks often distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the entire economy (meaning aggregated production, consumption, savings, and investment) and issues affecting it, including unemployment of resources (labor, capital, and land), inflation, economic growth, and the public policies that address these issues (monetary, fiscal, and other policies).Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing ""what is,"" and normative economics, advocating ""what ought to be""; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and behavioral economics; and between mainstream economics (more ""orthodox"" and dealing with the ""rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus"") and heterodox economics (more ""radical"" and dealing with the ""institutions-history-social structure nexus"").Besides the traditional concern in production, distribution, and consumption in an economy, economic analysis may be applied throughout society, as in business, finance, health care, and government. Economic analyses may also be applied to such diverse subjects as crime, education, the family, law, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science, and the environment. Education, for example, requires time, effort, and expenses, plus the foregone income and experience, yet these losses can be weighted against future benefits education may bring to the agent or the economy. At the turn of the 21st century, the expanding domain of economics in the social sciences has been described as economic imperialism.The ultimate goal of economics is to improve the living conditions of people in their everyday life.