Centre for Reviews and Dissemination
... Spanish database (e-Salud). The resource use assumptions came from a panel of four experts with clinical expertise in pulmonary arterial hypertension management (two pneumologists, one cardiologist, and one hospital pharmacist). All NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) Produced by the Centre f ...
... Spanish database (e-Salud). The resource use assumptions came from a panel of four experts with clinical expertise in pulmonary arterial hypertension management (two pneumologists, one cardiologist, and one hospital pharmacist). All NHS Economic Evaluation Database (NHS EED) Produced by the Centre f ...
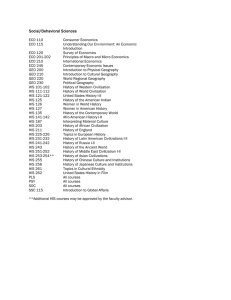
Social and Behavioral Science Electives
... Social/Behavioral Sciences ECO 110 ECO 115 ECO 120 ECO 201-202 ECO 210 ECO 245 GEO 200 GEO 210 GEO 220 GEO 230 HIS 101-102 HIS 111-112 HIS 121-122 HIS 125 HIS 126 HIS 127 HIS 135 HIS 141-142 HIS 187 HIS 203 HIS 211 HIS 225-226 HIS 231-232 HIS 241-242 HIS 243 HIS 251-252 HIS 253-254** HIS 255 HIS 256 ...
... Social/Behavioral Sciences ECO 110 ECO 115 ECO 120 ECO 201-202 ECO 210 ECO 245 GEO 200 GEO 210 GEO 220 GEO 230 HIS 101-102 HIS 111-112 HIS 121-122 HIS 125 HIS 126 HIS 127 HIS 135 HIS 141-142 HIS 187 HIS 203 HIS 211 HIS 225-226 HIS 231-232 HIS 241-242 HIS 243 HIS 251-252 HIS 253-254** HIS 255 HIS 256 ...
Myths and Truths about Advertising
... demand for the advertised product becomes less elastic. Lack of high detail data – need exposure and brand-purchase ...
... demand for the advertised product becomes less elastic. Lack of high detail data – need exposure and brand-purchase ...
سیر مفهومی Resources در متون اقتصاد و مدیریت
... 2. Capital consists of the long-lasting tools people use to produce goods and services. This includes physical capital, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, as well as human capital—the skills and training that workers possess. 3. Land is the physical space on which production takes place, a ...
... 2. Capital consists of the long-lasting tools people use to produce goods and services. This includes physical capital, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, as well as human capital—the skills and training that workers possess. 3. Land is the physical space on which production takes place, a ...
DRAFT On the Cambridge, England, critique of the marginal
... individuals within each class having different functions with regard to spending, saving, investing and producing. The marginal productivity theory was developed partly as a response to these views, but also as part of the development of the subjective theory of value in which utility was the sourc ...
... individuals within each class having different functions with regard to spending, saving, investing and producing. The marginal productivity theory was developed partly as a response to these views, but also as part of the development of the subjective theory of value in which utility was the sourc ...
chapter 3 t_f test answers - Hialeah Senior High School
... 11. The distribution and production of goods and services is determined by individual choice in a command economy. FALSE 12. In a market economy, consumers and producers together determine the prices and quantities of goods and services produced. TRUE 13. When supply does not equal demand, the equil ...
... 11. The distribution and production of goods and services is determined by individual choice in a command economy. FALSE 12. In a market economy, consumers and producers together determine the prices and quantities of goods and services produced. TRUE 13. When supply does not equal demand, the equil ...
1. Consumer Theory (Cont.) 1.5- Consumer Choice 1.6
... good to its price can be given by the slope of the demand curve, since it gives the magnitude of the variation in the quantity demanded that follows a price change. However, that measure is dependent on the units in which quantities and prices are measured. For example, the response of demand of cho ...
... good to its price can be given by the slope of the demand curve, since it gives the magnitude of the variation in the quantity demanded that follows a price change. However, that measure is dependent on the units in which quantities and prices are measured. For example, the response of demand of cho ...
environmental economics
... How markets work The market is the way in which an economic activity is organized between buyers and sellers through their behavior and interaction with one another. Buyers, as a group, determine the overall demand for a particular product at various prices while sellers, as a group, determine the ...
... How markets work The market is the way in which an economic activity is organized between buyers and sellers through their behavior and interaction with one another. Buyers, as a group, determine the overall demand for a particular product at various prices while sellers, as a group, determine the ...
Supply and Demand Extra Practice Answers
... 3d. Beef is an input into the production of vegetable beef soup. Since beef is now more expensive, the cost of producing the soup will rise. The increased costs make soup production less profitable at each price. The supply of vegetable beef soup shifts to the left (less is supplied at each price). ...
... 3d. Beef is an input into the production of vegetable beef soup. Since beef is now more expensive, the cost of producing the soup will rise. The increased costs make soup production less profitable at each price. The supply of vegetable beef soup shifts to the left (less is supplied at each price). ...
Microeconomics
Microeconomics (from Greek prefix mikro- meaning ""small"") is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of limited resources. Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are bought and sold. Microeconomics examines how these decisions and behaviors affect the supply and demand for goods and services, which determines prices, and how prices, in turn, determine the quantity supplied and quantity demanded of goods and services.This is in contrast to macroeconomics, which involves the ""sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment."" Microeconomics also deals with the effects of national economic policies (such as changing taxation levels) on the aforementioned aspects of the economy. Particularly in the wake of the Lucas critique, much of modern macroeconomic theory has been built upon 'microfoundations'—i.e. based upon basic assumptions about micro-level behavior.One of the goals of microeconomics is to analyze market mechanisms that establish relative prices amongst goods and services and allocation of limited resources amongst many alternative uses. Microeconomics also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results, and describes the theoretical conditions needed for perfect competition. Significant fields of study in microeconomics include general equilibrium, markets under asymmetric information, choice under uncertainty and economic applications of game theory. Also considered is the elasticity of products within the market system.