Review over DNA, RNA, proteins, viruses, bacteria, DNA technology
... 3.A.1.c.4. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation and termination. The salient features include: iv. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA v. The amin ...
... 3.A.1.c.4. In prokaryotic organisms, transcription is coupled to translation of the message. Translation involves energy and many steps, including initiation, elongation and termination. The salient features include: iv. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA v. The amin ...
MOLLECULAR BIOLOGY COURSE
... (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way ...
... (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way ...
A Primer on Gene Regulation
... (The grouping of genes into operons is common in bacteria but rare in eukaryotes.) The lactose or lac operon contains three genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA but we will only be concerned with the most promoter-proximal gene, lacZ, which encodes β-galactosidase. β-galactosidase is an enzyme that enables E ...
... (The grouping of genes into operons is common in bacteria but rare in eukaryotes.) The lactose or lac operon contains three genes: lacZ, lacY, and lacA but we will only be concerned with the most promoter-proximal gene, lacZ, which encodes β-galactosidase. β-galactosidase is an enzyme that enables E ...
Slides PPT
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
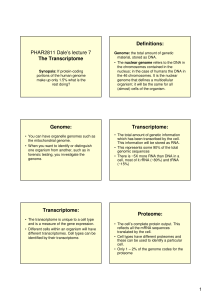
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... • RNA polymerase II which transcribes mRNA. • The primary transcript is a direct copy of the gene. • It includes the introns, 5’ and 3’UTRs but NOT the promoter region • This process is really complicated ...
... • RNA polymerase II which transcribes mRNA. • The primary transcript is a direct copy of the gene. • It includes the introns, 5’ and 3’UTRs but NOT the promoter region • This process is really complicated ...
S4O3 Pretest 2015-2016
... give them information that will help them make a decision as to whether or not they will do fetal testing. 65. Consider the function of homeobox genes, described on page 344. They were first discovered and are best known in fruit flies (Drosophila), though similar genes exist in many other organisms ...
... give them information that will help them make a decision as to whether or not they will do fetal testing. 65. Consider the function of homeobox genes, described on page 344. They were first discovered and are best known in fruit flies (Drosophila), though similar genes exist in many other organisms ...
Mulitplexing primer sets
... need to quantify the DNA the genomic DNA you isolated and then prepare a plate where all of the DNA samples are set to the same concentration. At NGC we set all template DNA to 5ng/ul and then use 4ul (=20ng) per PCR. If you skip this step your data will be difficult to call as some samples will giv ...
... need to quantify the DNA the genomic DNA you isolated and then prepare a plate where all of the DNA samples are set to the same concentration. At NGC we set all template DNA to 5ng/ul and then use 4ul (=20ng) per PCR. If you skip this step your data will be difficult to call as some samples will giv ...
Is there a code for protein–DNA recognition?
... energy sites, those with energies most similar to the preferred sequence, but has a non-specific energy that tends to 3.0, for triplets with predicted energies greater than 1.5. This means that over 90% of the predicted energies are wrong and many of them significantly so, by up to 3.0 units. Is the ...
... energy sites, those with energies most similar to the preferred sequence, but has a non-specific energy that tends to 3.0, for triplets with predicted energies greater than 1.5. This means that over 90% of the predicted energies are wrong and many of them significantly so, by up to 3.0 units. Is the ...
Resolvase OsGEN1 Mediates DNA Repair by
... 2009). The resolution of HJs is crucial for the completion of recombination. In addition, HJs are toxic DNA structures if not processed appropriately because they can interfere with normal chromosome segregation as well as DNA replication. HJs are processed by two major mechanisms. One is through di ...
... 2009). The resolution of HJs is crucial for the completion of recombination. In addition, HJs are toxic DNA structures if not processed appropriately because they can interfere with normal chromosome segregation as well as DNA replication. HJs are processed by two major mechanisms. One is through di ...
DNA analysis summary - Medical Research Council
... condition which may be relevant not only to the individual themselves but also to their immediate family, or future persons). For guidance on how to decide if and when to provide participants with health related feedback, please see the MRC/Wellcome Trust Framework on the feedback of health-related ...
... condition which may be relevant not only to the individual themselves but also to their immediate family, or future persons). For guidance on how to decide if and when to provide participants with health related feedback, please see the MRC/Wellcome Trust Framework on the feedback of health-related ...
Conformation and Rigidity of DNA Microcircles Containing waf1
... regions connecting these and a 30-residue basic C terminus which is known to modulate DNAbinding by the protein. The majority of human tumorigenic mutations occur in the central DNAbinding domain of p53 and may affect contacts between p53 and the DNA target or alter the structure of the DNA-binding ...
... regions connecting these and a 30-residue basic C terminus which is known to modulate DNAbinding by the protein. The majority of human tumorigenic mutations occur in the central DNAbinding domain of p53 and may affect contacts between p53 and the DNA target or alter the structure of the DNA-binding ...
DNA Hybridization: A Decade of Molecular Discourse in Hominoid
... Adding energy in the form of heat breaks these bonds and dissociates the two strands from one another. This is called denaturing the DNA (Tattersall et aI. 1988; Marks et aI. 1988). Poorly-paired DNA strands will dissociate at much lower temperatures than well-paired DNA strands. Thus, the thermal s ...
... Adding energy in the form of heat breaks these bonds and dissociates the two strands from one another. This is called denaturing the DNA (Tattersall et aI. 1988; Marks et aI. 1988). Poorly-paired DNA strands will dissociate at much lower temperatures than well-paired DNA strands. Thus, the thermal s ...
3-4 DNA F11 - De Anza College
... An mRNA binds to the small ribosomal subunit. A special initiator tRNA binds to the start codon, AUG The large ribosomal subunit binds, creating a functional ...
... An mRNA binds to the small ribosomal subunit. A special initiator tRNA binds to the start codon, AUG The large ribosomal subunit binds, creating a functional ...
Lab 2 Sequence
... – Scientists can build designer plasmids that contain specific restriction sites – This allows scientist to cut out and recombine genes to allow for cloning and gene expression. (requires sticky ends) – Sticky ends: want to form hydrogen bonds which scientists use to ligate the DNA together again in ...
... – Scientists can build designer plasmids that contain specific restriction sites – This allows scientist to cut out and recombine genes to allow for cloning and gene expression. (requires sticky ends) – Sticky ends: want to form hydrogen bonds which scientists use to ligate the DNA together again in ...
Coffee, B, Muralidharan, K, Highsmith Jr., WE, Lapunzina, P and Warren, ST: Molecular diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome using quantitative methylation-sensitive polymerase chain reaction; Genetics in Medicine, Vol 8 - No.10 (2006).
... in the promoter of the KCNQ10T1 gene, which is antisense to the KCNQ1 gene. The KCNQ10T1 amplification primers are Lit1FGTTTAATTAGTAGGTGGGGGG and Lit1R-CCTAACAAAATCTTACTAAAAAACTCC. The TaqMan probes target the sequence !6 to !34 relative to transcription initiation of KCNQ10T1 (Genbank AJ006345; pos ...
... in the promoter of the KCNQ10T1 gene, which is antisense to the KCNQ1 gene. The KCNQ10T1 amplification primers are Lit1FGTTTAATTAGTAGGTGGGGGG and Lit1R-CCTAACAAAATCTTACTAAAAAACTCC. The TaqMan probes target the sequence !6 to !34 relative to transcription initiation of KCNQ10T1 (Genbank AJ006345; pos ...
Construction of a Genetic Linkage Map in Man Using Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms.
... relationship of the modification genes. Furthermore, these polymorphisms might not give the expected codominant phenotype, but will be expressed as either true dominants or recessives, depending on whether the gene is structural for a modifying enzyme or regulatory; and if regulatory, whether positi ...
... relationship of the modification genes. Furthermore, these polymorphisms might not give the expected codominant phenotype, but will be expressed as either true dominants or recessives, depending on whether the gene is structural for a modifying enzyme or regulatory; and if regulatory, whether positi ...
Protein–DNA Hydrophobic Recognition in the Minor Groove
... remained in “standard” B configuration. In other words, two schemes are being used to facilitate the recognition: in addition to “digital” H-bond recognition, the “analogue” one helps in fitting to structural constraints in the complexes.12 So, there is no simple code for protein –DNA recognition.13 ...
... remained in “standard” B configuration. In other words, two schemes are being used to facilitate the recognition: in addition to “digital” H-bond recognition, the “analogue” one helps in fitting to structural constraints in the complexes.12 So, there is no simple code for protein –DNA recognition.13 ...
Sterile, 24-well tissue culture plates are filled with melted minimal ... 1.0 ml per well using a repeating syringe. After the...
... can be used immediately or stored for several weeks in plastic bags at 5°C. complementation tests, each well of a plate is inoculated with a drop of spore suspension from an auxotrophic mutant (usually nitM) of a VCG standard strain. A sterile Pasteur pipette is used for inoculations. A drop of spor ...
... can be used immediately or stored for several weeks in plastic bags at 5°C. complementation tests, each well of a plate is inoculated with a drop of spore suspension from an auxotrophic mutant (usually nitM) of a VCG standard strain. A sterile Pasteur pipette is used for inoculations. A drop of spor ...
Cloning methods
... ends, and then purified by preparative gel electrophoresis, in order to remove uncut plasmid, because restriction digestion usually isn’t 100 % complete. The digested plasmid furthermore needs to be dephosphorylated, in order to prevent recircularization of plasmids without insert in the following l ...
... ends, and then purified by preparative gel electrophoresis, in order to remove uncut plasmid, because restriction digestion usually isn’t 100 % complete. The digested plasmid furthermore needs to be dephosphorylated, in order to prevent recircularization of plasmids without insert in the following l ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.