Compounds
... ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4], potassium nitrate [KNO3], or sodium nitrate [NaNO3]? 28. A mixture of table salt (NaCl) and water has a total mass of 345 grams. Upon analysis, it was determined that 48 grams of oxygen were present in the sample. How many grams of each of the following MUST also be in ...
... ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4], potassium nitrate [KNO3], or sodium nitrate [NaNO3]? 28. A mixture of table salt (NaCl) and water has a total mass of 345 grams. Upon analysis, it was determined that 48 grams of oxygen were present in the sample. How many grams of each of the following MUST also be in ...
Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Oxidative
... is the major contributor to aging and to degenerative diseases of aging such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, cataracts, immune system decline and brain dysfunction [30]. Free radicals have been implicated in the pathogenesis of at least 50 diseases [31]. Fortunately, free radical formation is con ...
... is the major contributor to aging and to degenerative diseases of aging such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, cataracts, immune system decline and brain dysfunction [30]. Free radicals have been implicated in the pathogenesis of at least 50 diseases [31]. Fortunately, free radical formation is con ...
2010
... 26. A water trough, aqueous sodium hydroxide, burning candle, watch class and a graduated gas jar were used in an experimental set up to determine the percentage of active part of air. Draw a labeled diagram of the set up at the end of the experiment. (3 marks) 27. The atomic numbers of phosphorus, ...
... 26. A water trough, aqueous sodium hydroxide, burning candle, watch class and a graduated gas jar were used in an experimental set up to determine the percentage of active part of air. Draw a labeled diagram of the set up at the end of the experiment. (3 marks) 27. The atomic numbers of phosphorus, ...
Role of Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle
... Cell culture studies show that TNF acts directly on differentiated muscle cells to stimulate cytosolic ROS activity.2 In contrast, oxidant activity is unaffected by exposure to IFN, IL-1, interleukin-6, or c-reactive protein.3,4 TNF administration also stimulates loss of muscle protein, both in cul ...
... Cell culture studies show that TNF acts directly on differentiated muscle cells to stimulate cytosolic ROS activity.2 In contrast, oxidant activity is unaffected by exposure to IFN, IL-1, interleukin-6, or c-reactive protein.3,4 TNF administration also stimulates loss of muscle protein, both in cul ...
rll 24.5 The citric ocid cycle
... The oxaloacetate molecule is now available to start another turn of the cycle by reacting with another molecule of acetyl CoA. This is what happens in the citric acid cycle: 1. Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetatecombine to form citrate. 2. Citric acid eventually loses two carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. The ...
... The oxaloacetate molecule is now available to start another turn of the cycle by reacting with another molecule of acetyl CoA. This is what happens in the citric acid cycle: 1. Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetatecombine to form citrate. 2. Citric acid eventually loses two carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. The ...
Effect of essential and non-essential amino acid addition to a
... ABSTRACT: Pigs fitted with ileal T-cannula in the terminal ileum were used to study the effect of synthetic amino acids (AA) added to a nitrogen-free diet on endogenous losses. We compared the obtained data with data from other research centres in the world that are focusing on these problems. In th ...
... ABSTRACT: Pigs fitted with ileal T-cannula in the terminal ileum were used to study the effect of synthetic amino acids (AA) added to a nitrogen-free diet on endogenous losses. We compared the obtained data with data from other research centres in the world that are focusing on these problems. In th ...
E2 and E11 Acid Deposition Past Paper Questions
... 1CO2(g) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) OR CO2(g) + H2O(l) 2 H (aq) + HCO3 (aq) ...
... 1CO2(g) + H2O(l) H2CO3(aq) OR CO2(g) + H2O(l) 2 H (aq) + HCO3 (aq) ...
Cells and Molecules of Life
... (1) While the H:O ratio in carbohydrates is about 2:1, the H:O ratio in lipids is 18:1. (Read this as: “While the hydrogen to oxygen ratio in carbohydrates is about two to one, the hydrogen to oxygen ratio in lipids is eighteen to one.”) (2) Lipids are insoluble in water, but they are soluble in org ...
... (1) While the H:O ratio in carbohydrates is about 2:1, the H:O ratio in lipids is 18:1. (Read this as: “While the hydrogen to oxygen ratio in carbohydrates is about two to one, the hydrogen to oxygen ratio in lipids is eighteen to one.”) (2) Lipids are insoluble in water, but they are soluble in org ...
Chapter 3 - PKDiet.com
... Yet, chlorophyll is not so unique in its chemical make-up. It is built around a structure known as a porphyrin ring, which occurs in a variety of natural organic molecules. The most interesting group of molecules which contain porphyrin rings are those involved in cellular respiration, or the transp ...
... Yet, chlorophyll is not so unique in its chemical make-up. It is built around a structure known as a porphyrin ring, which occurs in a variety of natural organic molecules. The most interesting group of molecules which contain porphyrin rings are those involved in cellular respiration, or the transp ...
Pyruvate Oxidation
... and then channelled toward fat production or ATP production, depending on the organism’s immediate energy needs ...
... and then channelled toward fat production or ATP production, depending on the organism’s immediate energy needs ...
Bacterial Classification
... – Enzymes are biological catalysts – Catalysts are agents which speed up a reaction – Enzymes are very specific – Enzymes are typically proteins – Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction ...
... – Enzymes are biological catalysts – Catalysts are agents which speed up a reaction – Enzymes are very specific – Enzymes are typically proteins – Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction ...
DNA intro There is a famous quip by Jacques Monod that “what is
... the whole helix a little larger in diameter and changing the relative size of the major and minor groove. Z-DNA on the other hand has a drastically different local geometry – for one thing its helix is left-handed – but still the DNA fulfills the three criteria of having the backbones well-separated ...
... the whole helix a little larger in diameter and changing the relative size of the major and minor groove. Z-DNA on the other hand has a drastically different local geometry – for one thing its helix is left-handed – but still the DNA fulfills the three criteria of having the backbones well-separated ...
Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
... •Solubility of O2 is low in plasma i.e. 10-4 M. •But bound to hemoglobin, [O2] = 0.01 M or that of air •Two alternative O2 transporters are; •Hemocyanin, a Cu containing protein. •Hemoerythrin , a non-heme containing protein. ...
... •Solubility of O2 is low in plasma i.e. 10-4 M. •But bound to hemoglobin, [O2] = 0.01 M or that of air •Two alternative O2 transporters are; •Hemocyanin, a Cu containing protein. •Hemoerythrin , a non-heme containing protein. ...
The representative Elements: Groups 1A – 4A
... paper, plastics, etc.; 2. the source for calcium metal and quicklime: Calcination: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) ...
... paper, plastics, etc.; 2. the source for calcium metal and quicklime: Calcination: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
TIPS for NET-IONIC EQUATIONS A.P. Chemistry (long form)
... 1. dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of barium acetate 2. solutions of sodium phosphate and calcium chloride are mixed 3. hydrogen sulfide gas is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate 4. manganese(II) nitrate solution is mixed with sodium hydroxide solution 5. solutions of zinc sulf ...
... 1. dilute sulfuric acid is added to a solution of barium acetate 2. solutions of sodium phosphate and calcium chloride are mixed 3. hydrogen sulfide gas is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate 4. manganese(II) nitrate solution is mixed with sodium hydroxide solution 5. solutions of zinc sulf ...
Functions
... as bones and teeth. Minerals play a key role in the maintenance of osmotic pressure, and thus regulate the exchange of water and solutes within the animal and human body. Minerals serve as structural constituents of soft tissues. Minerals are essential for the transmission of nerve impulses and musc ...
... as bones and teeth. Minerals play a key role in the maintenance of osmotic pressure, and thus regulate the exchange of water and solutes within the animal and human body. Minerals serve as structural constituents of soft tissues. Minerals are essential for the transmission of nerve impulses and musc ...
the respiratory system
... What is pulmonary respiration? It is the movement of air in and out of the lung passages. This is accomplished by the action of the thorax muscles and diaphragm. What is external respiration? It is the exchange of gases between the air and blood at pulmonary capillaries, happens at the ends of lung ...
... What is pulmonary respiration? It is the movement of air in and out of the lung passages. This is accomplished by the action of the thorax muscles and diaphragm. What is external respiration? It is the exchange of gases between the air and blood at pulmonary capillaries, happens at the ends of lung ...
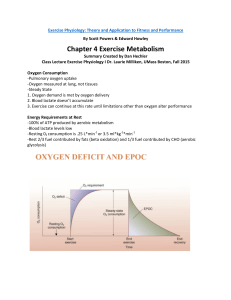
File - twynham a level pe
... lactate threshold and the functions of Excess Postexercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC). ...
... lactate threshold and the functions of Excess Postexercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC). ...
Fate and Transport of Air Pollutants from CAFOs
... Gases are also of concern. These may include odorants, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), ammonia (NH3), methane (CH4) and other trace gas constituents. Some of these persist in the atmosphere for hours or days, and they may be transported hundreds of kilometers (Table 1). Ammonia and sulfur compounds from CAF ...
... Gases are also of concern. These may include odorants, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), ammonia (NH3), methane (CH4) and other trace gas constituents. Some of these persist in the atmosphere for hours or days, and they may be transported hundreds of kilometers (Table 1). Ammonia and sulfur compounds from CAF ...
Protein oxidation and cellular homeostasis: Emphasis
... As mentioned previously there are several mechanisms by which ROS may be generated including aerobic respiration, nitric oxide synthesis, and NADPH oxidase pathways during inflammation. In aerobic respiration, the mitochondrial respiratory chain produces ROS as it transfers electrons during the redu ...
... As mentioned previously there are several mechanisms by which ROS may be generated including aerobic respiration, nitric oxide synthesis, and NADPH oxidase pathways during inflammation. In aerobic respiration, the mitochondrial respiratory chain produces ROS as it transfers electrons during the redu ...
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism
... -Accelerated glycolysis (NADH produced faster than it is shuttled into mitochondria and excess NADH in cytoplasm converts to pyruvic acid to lactic acid -Recruitment of fast-twitch muscle fibers (LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) isozyme in fast fibers ...
... -Accelerated glycolysis (NADH produced faster than it is shuttled into mitochondria and excess NADH in cytoplasm converts to pyruvic acid to lactic acid -Recruitment of fast-twitch muscle fibers (LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) isozyme in fast fibers ...
8. Nitrogen Monoxide and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO and NO2 )
... produce ozone (O3) in the troposphere, affecting, as a greenhouse gas, the Earth’s radiative balance and, by reproducing OH, the oxidization capacity of the atmosphere. NOx thus play a great role in controlling greenhouse gas concentrations (CH4, HCFCs, etc.). Sources of NOx include fossil fuel comb ...
... produce ozone (O3) in the troposphere, affecting, as a greenhouse gas, the Earth’s radiative balance and, by reproducing OH, the oxidization capacity of the atmosphere. NOx thus play a great role in controlling greenhouse gas concentrations (CH4, HCFCs, etc.). Sources of NOx include fossil fuel comb ...
22 - IWS2.collin.edu
... liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure The amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid also depends upon its solubility: Carbon dioxide is the most soluble Oxygen is 1/20th as soluble as carbon dioxide Nitrogen is practically insoluble in plasma ...
... liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure The amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid also depends upon its solubility: Carbon dioxide is the most soluble Oxygen is 1/20th as soluble as carbon dioxide Nitrogen is practically insoluble in plasma ...