LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... automatic mechanical process from the time of birth until death. Most of the time respiration is an unconscious act of exchanging oxygen between the environment around us and the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. Our environmental air contains about 21 percent oxygen, 78 percent nitrogen, 0.4 percent ...
... automatic mechanical process from the time of birth until death. Most of the time respiration is an unconscious act of exchanging oxygen between the environment around us and the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. Our environmental air contains about 21 percent oxygen, 78 percent nitrogen, 0.4 percent ...
Metal Complex in the Blood - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... Our bodies consist of cells that are organized into many specialized organs and tissues to perform a variety of functions. Our stomachs digest food so that the nutrients contained in the food can be distributed to the rest of the body. Our lungs take in the oxygen needed by the body from the air and ...
... Our bodies consist of cells that are organized into many specialized organs and tissues to perform a variety of functions. Our stomachs digest food so that the nutrients contained in the food can be distributed to the rest of the body. Our lungs take in the oxygen needed by the body from the air and ...
1. An inner engine keeps us alive
... provided by the breakdown of foods. Hence, in order to stay alive, grow and perform many necessary functions, we, the humans, require constant supply of foodstuff. The breakdown of food and conversion to energy is called metabolism. The word comes from Greek meta and ballein, meaning “to throw”. So, ...
... provided by the breakdown of foods. Hence, in order to stay alive, grow and perform many necessary functions, we, the humans, require constant supply of foodstuff. The breakdown of food and conversion to energy is called metabolism. The word comes from Greek meta and ballein, meaning “to throw”. So, ...
Possible Roles of Plant Sulfurtransferases in Detoxification of
... homology [14,16]. Therefore, it has been suggested that the inactive rhodanese domain could be involved in signaling [12] but more experimental evidence is needed. Sulfurtransferases or Str-like proteins have been identified in different subcellular compartments. In rats, 3-mercaptopyruvate Str was ...
... homology [14,16]. Therefore, it has been suggested that the inactive rhodanese domain could be involved in signaling [12] but more experimental evidence is needed. Sulfurtransferases or Str-like proteins have been identified in different subcellular compartments. In rats, 3-mercaptopyruvate Str was ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... When an organic compound is oxidized. Complete combustion results in carbon dioxide and water. • e.g. C2H5OH + 3O2 Æ 2CO2 + 3H2O 4. Esterification reactions A carboxylic acid is combined with an alcohol to produce an ester and water. Reactions are usually aided by the addition of a small amount of a ...
... When an organic compound is oxidized. Complete combustion results in carbon dioxide and water. • e.g. C2H5OH + 3O2 Æ 2CO2 + 3H2O 4. Esterification reactions A carboxylic acid is combined with an alcohol to produce an ester and water. Reactions are usually aided by the addition of a small amount of a ...
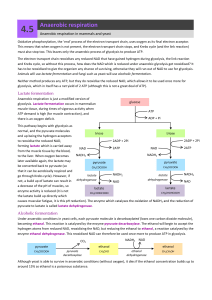
Anaerobic respiration
... Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which allows it to be used once more for glycolysis, which in itself has a net yield of 2 ATP (although this is not a great deal of A ...
... Animals will use lactate fermentation and fungi such as yeast will use alcoholic fermentation. Neither method produces any ATP, but they do reoxidise the reduced NAD, which allows it to be used once more for glycolysis, which in itself has a net yield of 2 ATP (although this is not a great deal of A ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... 2) A) Which of the following metals does not react with aqueous Ni (NO3)2? Why? ...
... 2) A) Which of the following metals does not react with aqueous Ni (NO3)2? Why? ...
Document
... Magnesium has to be heated before it will start to react with oxygen in the air, but once it starts reacting it produces lots of heat and a bright white light (another form of energy). When the reaction is over a white powdery substance has replaced the shiny, malleable metal. This white ...
... Magnesium has to be heated before it will start to react with oxygen in the air, but once it starts reacting it produces lots of heat and a bright white light (another form of energy). When the reaction is over a white powdery substance has replaced the shiny, malleable metal. This white ...
Document
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
4.2 Respiration – Page 1 S. Preston 1 From the
... (oxidative decarboxylation); the acetyl then combines with co-enzyme A. The link reaction takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. 6. Each acetyl co-enzyme A enters the Krebs cycle, the coenzyme A is regenerated and the acetate fragment is picked up by a 4C acid, to produce a 6C acid. 7. The ...
... (oxidative decarboxylation); the acetyl then combines with co-enzyme A. The link reaction takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. 6. Each acetyl co-enzyme A enters the Krebs cycle, the coenzyme A is regenerated and the acetate fragment is picked up by a 4C acid, to produce a 6C acid. 7. The ...
Mechanisms of hormonal regulation and pathologies of protein
... SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID SYNTHESIS •Plants and microorganisms can make all 20 amino acids •Humans can make only 11 of the 20 amino acids (“nonessential” amino acids) •Nonessential amino acids for mammals are usually derived from intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle •The others ar ...
... SPECIFIC WAYS OF AMINO ACID SYNTHESIS •Plants and microorganisms can make all 20 amino acids •Humans can make only 11 of the 20 amino acids (“nonessential” amino acids) •Nonessential amino acids for mammals are usually derived from intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle •The others ar ...
29
... With the procedure, usually between 1 to 4 units of a person's own blood (autologos) are withdrawn, the plasma is removed and immediately reinfused, and the packed red cells are placed in frozen storage. To prevent a dramatic reduction in blood cell concentration, each unit of blood is withdrawn ove ...
... With the procedure, usually between 1 to 4 units of a person's own blood (autologos) are withdrawn, the plasma is removed and immediately reinfused, and the packed red cells are placed in frozen storage. To prevent a dramatic reduction in blood cell concentration, each unit of blood is withdrawn ove ...
1 Assignment 5 Hydrogen – The Unique Element
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
1 Assignment 4 Hydrogen – The Unique Element
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
... Both molecular and saline hydrides are quite reactive. Group 1 and 2 hydrides react vigorously with water to produce hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide. This means that they can be used as drying agents for solvents – the most commonly used in this regard is CaH2. p-Block molecular hydrides have dif ...
2009
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name ...
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name ...
Formulation - Good Hope School
... Zn/ Mg is more reactive than iron [0.5] and will be corroded instead of Fe/ will prevent rusting of iron by sacrificial protection [0.5]. (b) The frames of greenhouses are often made of aluminium. Although they are not painted, they last for many years. Aluminium frame ...
... Zn/ Mg is more reactive than iron [0.5] and will be corroded instead of Fe/ will prevent rusting of iron by sacrificial protection [0.5]. (b) The frames of greenhouses are often made of aluminium. Although they are not painted, they last for many years. Aluminium frame ...
RxnTypesPrednotesIIAP
... written as H-OH. In an acid-base neutralization reaction, the acid is the source of the hydrogen ion while the base is the source of the hydroxide ion in the formation of the water molecule. In the synthesis reaction of an acid anhydride with a basic anhydride, only a salt is formed because the two ...
... written as H-OH. In an acid-base neutralization reaction, the acid is the source of the hydrogen ion while the base is the source of the hydroxide ion in the formation of the water molecule. In the synthesis reaction of an acid anhydride with a basic anhydride, only a salt is formed because the two ...
Hormonal Regulation of Moss Protonema Development and the
... The genomic clone shows the canonical autoinhibitory region and the four EF hands (Mitra & Johri, 2000). The deduced amino acid sequence shows extensive homology with other CDPKs namely, 73% identity with the Fragaria CDPK and 71 % homology with COPK isoform-7 of Arabidopsis. The homology to the liv ...
... The genomic clone shows the canonical autoinhibitory region and the four EF hands (Mitra & Johri, 2000). The deduced amino acid sequence shows extensive homology with other CDPKs namely, 73% identity with the Fragaria CDPK and 71 % homology with COPK isoform-7 of Arabidopsis. The homology to the liv ...
Autophosphorylation Activity of the Arabidopsis Ethylene Receptor
... proteins are also involved in more complex signaling pathways, termed phosphorelays. In these pathways the receptors are often hybrid proteins containing a receiver domain at the carboxyl terminus of their kinase domain. After autophosphorylation of the histidine residue in the kinase domain, the ph ...
... proteins are also involved in more complex signaling pathways, termed phosphorelays. In these pathways the receptors are often hybrid proteins containing a receiver domain at the carboxyl terminus of their kinase domain. After autophosphorylation of the histidine residue in the kinase domain, the ph ...
Day 13 Main Group Pt 1
... There are important differences between hydrogen and the alkali metals within the +1 oxidation state. The alkali metals utilize the +1 oxidation state in all of their common ionic salts and thus exhibit ionic character. Hydrogen in the +1 oxidation state is generally covalent. For example, hydrogen ...
... There are important differences between hydrogen and the alkali metals within the +1 oxidation state. The alkali metals utilize the +1 oxidation state in all of their common ionic salts and thus exhibit ionic character. Hydrogen in the +1 oxidation state is generally covalent. For example, hydrogen ...
Document
... In tissues: oxygen is down, pH is down, and CO2 is up. This is the tense state. The tense state (T) can also represent the deoxy state. In the first box, representing lungs: oxygen is being taken up by the hemoglobin molecule; H+ (protons) are released, along with CO2 is released. The His and Asp am ...
... In tissues: oxygen is down, pH is down, and CO2 is up. This is the tense state. The tense state (T) can also represent the deoxy state. In the first box, representing lungs: oxygen is being taken up by the hemoglobin molecule; H+ (protons) are released, along with CO2 is released. The His and Asp am ...
INDUCIBLE INOS)
... iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) play a significant role in controlling vascular pressure, neurotransmission, microorganism inhibitor, tumor cells and homeostatic system. The high level of Nitric Oxide (NO) influences pathophysiological processes including shock on the blood-pressure circulati ...
... iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) play a significant role in controlling vascular pressure, neurotransmission, microorganism inhibitor, tumor cells and homeostatic system. The high level of Nitric Oxide (NO) influences pathophysiological processes including shock on the blood-pressure circulati ...
biology exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a) a membrane transport protein b) a concentration gradient c) energy d) a membrane transport protein and a concentration gradient 26. Which of the following transport processes require(s) energy? a) facilitated diffusion b) osmosis c) endocytosis d) facilitated diffusion and osmosis e) facilitated ...
... a) a membrane transport protein b) a concentration gradient c) energy d) a membrane transport protein and a concentration gradient 26. Which of the following transport processes require(s) energy? a) facilitated diffusion b) osmosis c) endocytosis d) facilitated diffusion and osmosis e) facilitated ...