Eutrophication Subcommittee Conference Call
... indicators. Bob Steneck mentioned that he thought the overall arching goal of the indicators was to assess the ecosystem. Christine Tilburg agreed that in general the ESIP indicators are meant to represent the ecosystem in terms of the focus area. However, previous conference calls for the Fisheries ...
... indicators. Bob Steneck mentioned that he thought the overall arching goal of the indicators was to assess the ecosystem. Christine Tilburg agreed that in general the ESIP indicators are meant to represent the ecosystem in terms of the focus area. However, previous conference calls for the Fisheries ...
Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement and Problem Solving
... Molecules have a lot of space between them Free to move Compressible: forcing gas into a small container No fixed volume: volume of the container No fixed shape: take the shape of container Examples: Helium and Nitrogen ...
... Molecules have a lot of space between them Free to move Compressible: forcing gas into a small container No fixed volume: volume of the container No fixed shape: take the shape of container Examples: Helium and Nitrogen ...
E:\My Documents\snc1d\feb12notes.wpd
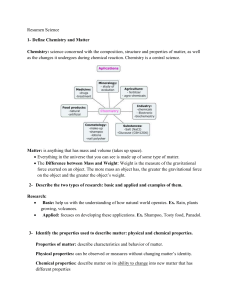
... Pure substances: uniform and consistent properties in different samples. Mixtures: may or may not be uniform, but properties are variable. Explanation In a pure substance, only one type of particle is present. - every sample is uniform throughout and each is the same as any other. In a mixture, ther ...
... Pure substances: uniform and consistent properties in different samples. Mixtures: may or may not be uniform, but properties are variable. Explanation In a pure substance, only one type of particle is present. - every sample is uniform throughout and each is the same as any other. In a mixture, ther ...
Service Order
... or extract from the Contractor’s proposal document(s) that may be inserted in, appended or embedded in the publication or release of the contract under FOIA or the Government’s Transparency Agenda. To the extent that it is necessary for HMRC to include any parts of the Contractor’s proposal or the c ...
... or extract from the Contractor’s proposal document(s) that may be inserted in, appended or embedded in the publication or release of the contract under FOIA or the Government’s Transparency Agenda. To the extent that it is necessary for HMRC to include any parts of the Contractor’s proposal or the c ...
Chapter 2
... Condensation cont. • This is an example of water and condensation but other substance act in the same way. ...
... Condensation cont. • This is an example of water and condensation but other substance act in the same way. ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
CO 2(g) - cloudfront.net
... • Energy symbols used above the arrow for decomposition reactions. ∆ = heat. hv = light. shock = mechanical. elec = electrical. ...
... • Energy symbols used above the arrow for decomposition reactions. ∆ = heat. hv = light. shock = mechanical. elec = electrical. ...
Section 2 Chemical Formulas and Equations
... When carbon burns, it reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. Figure 5 shows how to write an equation to describe this reaction. The starting materials in a chemical reaction are reactants. The substances formed from a reaction are products. In this example, carbon and oxygen are reactants. Carbo ...
... When carbon burns, it reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. Figure 5 shows how to write an equation to describe this reaction. The starting materials in a chemical reaction are reactants. The substances formed from a reaction are products. In this example, carbon and oxygen are reactants. Carbo ...
I Examen I Trim Science
... Chemical properties of matter: 1. Flammability: ability of a substance to burn. Ex. Wood, fuel (ash, smoke has no flammability) 2. Reactivity: ability to combine and form new substances. Ex. Iron reacts with oxygen and forms rust 3. Oxidation: ability to react with oxygen and form rust. Ex. Iron 4. ...
... Chemical properties of matter: 1. Flammability: ability of a substance to burn. Ex. Wood, fuel (ash, smoke has no flammability) 2. Reactivity: ability to combine and form new substances. Ex. Iron reacts with oxygen and forms rust 3. Oxidation: ability to react with oxygen and form rust. Ex. Iron 4. ...
File - Mr. L`s Room
... 2. Precipitate formation---solid forms from combining liquids 3. Oxidation---metal exposed to air and moisture; new substance forms During/after the change the particles are rearranged forming a brand new substance 14. Why are volume, mass, and length not properties. Give an example. Volume, mass, a ...
... 2. Precipitate formation---solid forms from combining liquids 3. Oxidation---metal exposed to air and moisture; new substance forms During/after the change the particles are rearranged forming a brand new substance 14. Why are volume, mass, and length not properties. Give an example. Volume, mass, a ...
Chemical Reactions
... Rules for Writing and Balancing Equations 1. Determine the correct formulas for all 4. Balance the elements one at a time by the reactants and products. using coefficients. When no coefficient is written, it is assumed to be 1. Begin by 2. Write the skeleton equation by placing the formulas for the ...
... Rules for Writing and Balancing Equations 1. Determine the correct formulas for all 4. Balance the elements one at a time by the reactants and products. using coefficients. When no coefficient is written, it is assumed to be 1. Begin by 2. Write the skeleton equation by placing the formulas for the ...
Presentation
... Process used to drive vapor from liquid by heating Great for separating two or more liquids which have different boiling points. ...
... Process used to drive vapor from liquid by heating Great for separating two or more liquids which have different boiling points. ...
Chemistry: Introduction to Chemical Reactions Guided Inquiry What
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
5.12 Lab Design and Safety
... Obtain chemical types, concentrations, quantities, and storage needs for each laboratory space early in design phase to inform building planning and related requirements. Coordinate with Design Manager. Provide adequate chemical storage that physically separates incompatible chemicals/gases. Do not ...
... Obtain chemical types, concentrations, quantities, and storage needs for each laboratory space early in design phase to inform building planning and related requirements. Coordinate with Design Manager. Provide adequate chemical storage that physically separates incompatible chemicals/gases. Do not ...
Compound vs Element chart
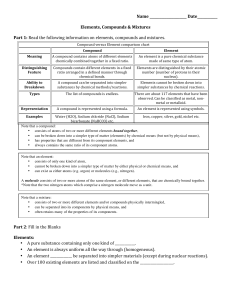
... • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consi ...
... • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consi ...
Section 4-1 - North Mac Schools
... beetle Fish share the pond while their leaves, on long flexible stems, float on the with turtles and other surface. animals. Many of them feed on insects at the water’s edge. Trout The bottom of the pond is inhabited by decomposers and Hydra other organisms that feed on particles drifting down from ...
... beetle Fish share the pond while their leaves, on long flexible stems, float on the with turtles and other surface. animals. Many of them feed on insects at the water’s edge. Trout The bottom of the pond is inhabited by decomposers and Hydra other organisms that feed on particles drifting down from ...
Chapter 9 Balancing Equations
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into new substances. • A chemical equation uses symbols to represent a chemical reaction. • A reactant or reagent is a substance used to begin a chemical reaction. • A product is a substance that forms during chemical r ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which one or more substances are changed into new substances. • A chemical equation uses symbols to represent a chemical reaction. • A reactant or reagent is a substance used to begin a chemical reaction. • A product is a substance that forms during chemical r ...
Populations and Communities Section 2 Predator
... • In parasitism, one organism feeds on another organism called a host. • The host is almost always larger than the parasite and is usually harmed but not killed. • Parasites often live on or in their host. Therefore, the parasite depends on its host not only for food but for a place to live as well. ...
... • In parasitism, one organism feeds on another organism called a host. • The host is almost always larger than the parasite and is usually harmed but not killed. • Parasites often live on or in their host. Therefore, the parasite depends on its host not only for food but for a place to live as well. ...
Presentation
... Process used to drive vapor from liquid by heating Great for separating two or more liquids which have different boiling points. ...
... Process used to drive vapor from liquid by heating Great for separating two or more liquids which have different boiling points. ...
Unit 1 Matter Day 32 2016 Counting Atoms
... same mass after the reaction as you do before the reaction. This means… *The # and type of atoms are the same in the reactants and products (just in different ...
... same mass after the reaction as you do before the reaction. This means… *The # and type of atoms are the same in the reactants and products (just in different ...
Chapter 14 Online activities
... 1. How does a “limiting factor” directly or indirectly affect a population in an area? GRAPH A 2a. Which limiting factor is described in Graph A? 2b. Describe what happens to the organisms because of this limiting factor. ...
... 1. How does a “limiting factor” directly or indirectly affect a population in an area? GRAPH A 2a. Which limiting factor is described in Graph A? 2b. Describe what happens to the organisms because of this limiting factor. ...
Document
... 1. Color the carbon atoms black, the oxygen atoms red, and leave the hydrogen atoms white. 2. Use scissors to carefully cut out the atoms. o Build the reactants: 3. On a sheet of paper, place the atoms together to make the molecules of the reactants on the left side of the chemical equation for the ...
... 1. Color the carbon atoms black, the oxygen atoms red, and leave the hydrogen atoms white. 2. Use scissors to carefully cut out the atoms. o Build the reactants: 3. On a sheet of paper, place the atoms together to make the molecules of the reactants on the left side of the chemical equation for the ...
Properties and Changes of Matter
... physical blend of two or more pure substances. can be separated by a physical change The two categories of mixtures are homogeneous and heterogeneous. ...
... physical blend of two or more pure substances. can be separated by a physical change The two categories of mixtures are homogeneous and heterogeneous. ...
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES - can observe w/o changing the
... CHEMICAL CHANGES – alter the substance’s identity at an atomic level. Can’t be reversed with a physical change. Examples: burning, dissolving something in an acid, letting iron rust, letting silver tarnish, mixing vinegar and baking soda, cooking an egg Also called a CHEMICAL REACTION (5 signs to wa ...
... CHEMICAL CHANGES – alter the substance’s identity at an atomic level. Can’t be reversed with a physical change. Examples: burning, dissolving something in an acid, letting iron rust, letting silver tarnish, mixing vinegar and baking soda, cooking an egg Also called a CHEMICAL REACTION (5 signs to wa ...
Safety data sheet
A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is an important component of product stewardship and occupational safety and health. It is intended to provide workers and emergency personnel with procedures for handling or working with that substance in a safe manner, and includes information such as physical data (melting point, boiling point, flash point, etc.), toxicity, health effects, first aid, reactivity, storage, disposal, protective equipment, and spill-handling procedures. SDS formats can vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements.SDSs are a widely used system for cataloging information on chemicals, chemical compounds, and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product. These data sheets can be found anywhere where chemicals are being used.There is also a duty to properly label substances on the basis of physico-chemical, health and/or environmental risk. Labels can include hazard symbols such as the European Union standard black diagonal cross on an orange background, used to denote a harmful substance.A SDS for a substance is not primarily intended for use by the general consumer, focusing instead on the hazards of working with the material in an occupational setting.In some jurisdictions, the SDS is required to state the chemical's risks, safety, and effect on the environment.It is important to use an SDS specific to both country and supplier, as the same product (e.g. paints sold under identical brand names by the same company) can have different formulations in different countries. The formulation and hazard of a product using a generic name (e.g. sugar soap) may vary between manufacturers in the same country.