How Exercise Changes Fat and Muscle Cells
... methylation, in which methyl groups, a cluster of carbon and hydrogen atoms, attach to the outside of a gene and make it easier or harder for that gene to receive and respond to messages from the body. In this way, the behavior of the gene is changed, but not the fundamental structure of the gene it ...
... methylation, in which methyl groups, a cluster of carbon and hydrogen atoms, attach to the outside of a gene and make it easier or harder for that gene to receive and respond to messages from the body. In this way, the behavior of the gene is changed, but not the fundamental structure of the gene it ...
B2 Topic 1 The Components of Life
... What are stem cells, how can they be used and where do we find them? ...
... What are stem cells, how can they be used and where do we find them? ...
File
... E. The stage when the cell prepares to divide F. Rod shaped structure of condensed chromatin that contains DNA G. Regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo H. Material in cells that contain DNA and carries genetic information I. The stage when the nucleus divides ...
... E. The stage when the cell prepares to divide F. Rod shaped structure of condensed chromatin that contains DNA G. Regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo H. Material in cells that contain DNA and carries genetic information I. The stage when the nucleus divides ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... that allow cells to become specialists at making the particular proteins associated with their functions ...
... that allow cells to become specialists at making the particular proteins associated with their functions ...
The Cell Cycle and Mitosis: An Intro
... In the last stage of mitosis, telophase, the cell divides the cytoplasm into two portions. The final separation of the cytoplasm into two distinct cells is called cytokinesis. ...
... In the last stage of mitosis, telophase, the cell divides the cytoplasm into two portions. The final separation of the cytoplasm into two distinct cells is called cytokinesis. ...
curriculum vitae
... Buzgo M., Greplova J., Soural M., Bezdekova D. , Lukasova V. , Mickova A. , Lytvynets A. , Hlavac J. , Electrospun PVAPEG-biotin Immunonanofibers with Controlled Decay (Poster at Nancon, 2012) Bezděková D., Buzgo M., Lukášová V.: Plasmatic modification of PVA nanofibers to enhance adhesion and proli ...
... Buzgo M., Greplova J., Soural M., Bezdekova D. , Lukasova V. , Mickova A. , Lytvynets A. , Hlavac J. , Electrospun PVAPEG-biotin Immunonanofibers with Controlled Decay (Poster at Nancon, 2012) Bezděková D., Buzgo M., Lukášová V.: Plasmatic modification of PVA nanofibers to enhance adhesion and proli ...
DNA-Genetics Assessment Guide
... Correctly fill in the Punnett square and predict percentages of possible phenotypes and genotypes Create a Punnett square and correctly predict the possible offspring Correctly answer multiple choice questions ...
... Correctly fill in the Punnett square and predict percentages of possible phenotypes and genotypes Create a Punnett square and correctly predict the possible offspring Correctly answer multiple choice questions ...
Stem cell derived retinal pigment epithelial cells have similar water
... imbalance between the photoreceptor cells and blood flow. In normal conditions, this ionic gradient leads to passive fluid absorption by RPE cells, likely through water channel, called aquaporins. Aquaporin gene expression or protein dysfunction is affected in several common ...
... imbalance between the photoreceptor cells and blood flow. In normal conditions, this ionic gradient leads to passive fluid absorption by RPE cells, likely through water channel, called aquaporins. Aquaporin gene expression or protein dysfunction is affected in several common ...
Supplementary Information (doc 54K)
... 18IM cells produce elevated levels of puryvate As we have mentioned already, a significant set of genes that are involved in glycolysis and red-ox reactions were differentially expressed in 18IM cells compared to REFs (Table S1). Biochemical assays were performed to measure the concentration of lact ...
... 18IM cells produce elevated levels of puryvate As we have mentioned already, a significant set of genes that are involved in glycolysis and red-ox reactions were differentially expressed in 18IM cells compared to REFs (Table S1). Biochemical assays were performed to measure the concentration of lact ...
Maurie Perl 212-365-7443 [email protected] Joint Research
... both the study of neural-physiology as well as the development of treatments for nervous system disorders. We feel that examination of disease relevant cell-types made from patient-specific stem cells represents an important step in the ever evolving process of drug discovery and have identified thi ...
... both the study of neural-physiology as well as the development of treatments for nervous system disorders. We feel that examination of disease relevant cell-types made from patient-specific stem cells represents an important step in the ever evolving process of drug discovery and have identified thi ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... In multicellular organisms individual cells grow and then divide via a process called mitosis, thereby allowing the organism to grow. The organism begins as a single cell (fertilized egg) that divides successively to produce many cells, with each parent cell passing identical genetic material (two v ...
... In multicellular organisms individual cells grow and then divide via a process called mitosis, thereby allowing the organism to grow. The organism begins as a single cell (fertilized egg) that divides successively to produce many cells, with each parent cell passing identical genetic material (two v ...
PPT2
... Problems with Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in order for genes to be ...
... Problems with Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in order for genes to be ...
Scope and Application of Stem Cell Research in Livestock
... ES cells from cloned bovine embryos with marker staining pattern similar to bovine blastocysts Yadav et al 2005 Bovine ICM derived cells express the Oct4 ortholog ...
... ES cells from cloned bovine embryos with marker staining pattern similar to bovine blastocysts Yadav et al 2005 Bovine ICM derived cells express the Oct4 ortholog ...
Stem Cell and Cloning Glossary
... Assisted reproductive technology: Fertility treatments that involve a laboratory handling eggs or embryos, such as in vitro fertilization. Blastocyst: Early stage of embryo, approximately 5-7 days after conception (50-250 cells.) Cloning: Creation of an animal or person that derives its genes from a ...
... Assisted reproductive technology: Fertility treatments that involve a laboratory handling eggs or embryos, such as in vitro fertilization. Blastocyst: Early stage of embryo, approximately 5-7 days after conception (50-250 cells.) Cloning: Creation of an animal or person that derives its genes from a ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) ISSN: 2278-3008.
... ESC pluripotency. They regulate common downstream genes that encourage pluripotency and self-renewal, whilst inhibiting differentiation processes [27]. Oct4 is found fundamental for pluripotency, self-renewal and embryogenesis[27].During the early stages of embryonic development,an essential role is ...
... ESC pluripotency. They regulate common downstream genes that encourage pluripotency and self-renewal, whilst inhibiting differentiation processes [27]. Oct4 is found fundamental for pluripotency, self-renewal and embryogenesis[27].During the early stages of embryonic development,an essential role is ...
Stem Cells
... What are stem cells? Stem cells (Master cell): A cells that have the ability to continuously divide and differentiate (develop) into various other kind(s) of cells/tissues. In other word an undifferentiated cell of a multicellular organism which is capable of giving rise to indefinitely more cells ...
... What are stem cells? Stem cells (Master cell): A cells that have the ability to continuously divide and differentiate (develop) into various other kind(s) of cells/tissues. In other word an undifferentiated cell of a multicellular organism which is capable of giving rise to indefinitely more cells ...
13-3 Cell Transformation
... Transforming Plant Cells Bacterial plasmids can be used to transform plant cells. Agrobacterium tumefaciens Type of bacteria that inserts a plasmid into plant cells and grows tumors. The tumor-producing gene can be removed and replaced with recombinant DNA. If transformation is successfu ...
... Transforming Plant Cells Bacterial plasmids can be used to transform plant cells. Agrobacterium tumefaciens Type of bacteria that inserts a plasmid into plant cells and grows tumors. The tumor-producing gene can be removed and replaced with recombinant DNA. If transformation is successfu ...
Study Guide for Heredity Test
... Incomplete Dominance- A condition that results when genes produce a trait somewhere in between the traits of the parents – two different color eyes – skin color on a mixed race child. Somatic cell - is almost any cell forming the body of an organism other than a gamete. Gametes- Sex cells; egg and s ...
... Incomplete Dominance- A condition that results when genes produce a trait somewhere in between the traits of the parents – two different color eyes – skin color on a mixed race child. Somatic cell - is almost any cell forming the body of an organism other than a gamete. Gametes- Sex cells; egg and s ...
Module 1 poster
... Diseases interfere with the body’s major functions and may lead to death. We focus on some of the problems associated with ageing and diseases from the point of view of what is happening at the cell level and try to address what has been done to help cells function ...
... Diseases interfere with the body’s major functions and may lead to death. We focus on some of the problems associated with ageing and diseases from the point of view of what is happening at the cell level and try to address what has been done to help cells function ...
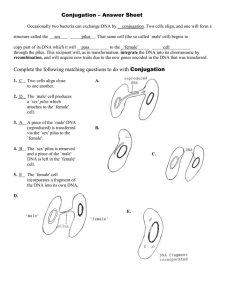
Conjugation Answer Sheet
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
DNA and Cell Division - Student Note
... structure of DNA allows it to carry the genetic information for all different organisms DNA is a molecule arranged in a double helix with two backbones linked by bases order of the bases determines the genetic code ...
... structure of DNA allows it to carry the genetic information for all different organisms DNA is a molecule arranged in a double helix with two backbones linked by bases order of the bases determines the genetic code ...
Slide 1
... - no specific time (unless you insist), you can come anytime - to make sure I’ll have time, please, write me or call me in advance ...
... - no specific time (unless you insist), you can come anytime - to make sure I’ll have time, please, write me or call me in advance ...
Genetics (Quick Questions) 1. How many chromosomes are there in
... 10. A: Mitosis makes identical copies of cells, meiosis doesn’t. B: Mitosis involved 1 division of the cell, meiosis involves 2 divisions. C: Mitosis makes cells containing 46 chromosomes, meiosis makes cells containing 23 chromosomes. 11. It is how we write the genetic make up of the chromosome pai ...
... 10. A: Mitosis makes identical copies of cells, meiosis doesn’t. B: Mitosis involved 1 division of the cell, meiosis involves 2 divisions. C: Mitosis makes cells containing 46 chromosomes, meiosis makes cells containing 23 chromosomes. 11. It is how we write the genetic make up of the chromosome pai ...
Use of Human Embryos: Research
... • The hope is that tissues derived from stem cells will provide a limitless supply of material to treat currently-incurable diseases and injuries. • All ES cell research (UK) uses cells derived from in vitro fertilisation (IVF) embryos donated by couples for research when they are not needed for inf ...
... • The hope is that tissues derived from stem cells will provide a limitless supply of material to treat currently-incurable diseases and injuries. • All ES cell research (UK) uses cells derived from in vitro fertilisation (IVF) embryos donated by couples for research when they are not needed for inf ...