2,3-BPG and the O 2
... red cells in blood carry O2 from lung to tissues by hemoglobin, a 4-subunit protein having an O2-binding prosthetic group, heme, that gives blood its color (Hb also carries (some) CO2 and H+ back to the lung) ...
... red cells in blood carry O2 from lung to tissues by hemoglobin, a 4-subunit protein having an O2-binding prosthetic group, heme, that gives blood its color (Hb also carries (some) CO2 and H+ back to the lung) ...
1 5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. Nocera Lecture 27 April 11
... Why? The radial extension of the wavefunctions of 2nd and 3rd row transition metal ions is much greater than their first row relatives. Thus SML is larger, leading to the following trend in ∆O for a given ligand field and metal of a given charge, 1st row TM << 2nd row TM ~ 3rd row TM Data supporting ...
... Why? The radial extension of the wavefunctions of 2nd and 3rd row transition metal ions is much greater than their first row relatives. Thus SML is larger, leading to the following trend in ∆O for a given ligand field and metal of a given charge, 1st row TM << 2nd row TM ~ 3rd row TM Data supporting ...
FST 123 - Enzymology Homework IS `13
... 2. If a protein is composed of 225 amino acids: a. What is its approximate molecular weight? What is its approximate volume? b. Assuming it is a sphere, what is its radius? 3. The course website contains a link to a Kinemage file depicting the structures of four proteins. Download them, view them us ...
... 2. If a protein is composed of 225 amino acids: a. What is its approximate molecular weight? What is its approximate volume? b. Assuming it is a sphere, what is its radius? 3. The course website contains a link to a Kinemage file depicting the structures of four proteins. Download them, view them us ...
CH 3 Biochemistry - Belle Vernon Area School District
... made of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, and sometimes sulfur. ...
... made of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, and sometimes sulfur. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... possible isomers. Thus the structure must be Oh. iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
... possible isomers. Thus the structure must be Oh. iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
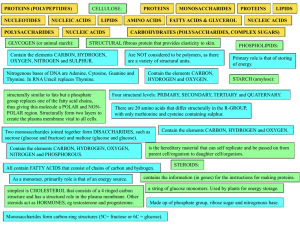
Chapter 3: Molecules of Life The molecules of life contain a high
... Carbon’s importance to life arises from its versatile ______________________________ Carbon has ______________________________ Many organic molecules have a backbone: _____________________________________ ____________________: consists only of carbon and hydrogen atoms ____________________: an atom ...
... Carbon’s importance to life arises from its versatile ______________________________ Carbon has ______________________________ Many organic molecules have a backbone: _____________________________________ ____________________: consists only of carbon and hydrogen atoms ____________________: an atom ...
1. I can define valence electron and use the periodic
... #6. I can identify how many atoms are in a compound by looking at its molecular formula. 21. List how many of each atom is present in each of the following molecules: (Example: Al(OH)3 would be Al=1, O=3, H=3). a. CaF2 d. Al2(SO4)3 g. Na2CO3 b. Be(OH)2 e. NH4NO3 h. CH4 c. NO2 f. S2F2 #7. I can descr ...
... #6. I can identify how many atoms are in a compound by looking at its molecular formula. 21. List how many of each atom is present in each of the following molecules: (Example: Al(OH)3 would be Al=1, O=3, H=3). a. CaF2 d. Al2(SO4)3 g. Na2CO3 b. Be(OH)2 e. NH4NO3 h. CH4 c. NO2 f. S2F2 #7. I can descr ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... a chemical reaction takes place in which the sodium atom gives its electron to the chlorine atom. These two ions attract each other and form a new compound, NaCl (s). Name the compound by using the full name of the metal followed by the name of the nonmetal with the ‘ide’ ending. The above compound, ...
... a chemical reaction takes place in which the sodium atom gives its electron to the chlorine atom. These two ions attract each other and form a new compound, NaCl (s). Name the compound by using the full name of the metal followed by the name of the nonmetal with the ‘ide’ ending. The above compound, ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
... is the hereditary material that can self replicate and be passed on from parent cell/organism to daughter cell/organism. ...
... is the hereditary material that can self replicate and be passed on from parent cell/organism to daughter cell/organism. ...
Sample exam 2
... 22. Is the fixing of nitrogen an exothermic or endothermic process? 23. Which molecule is necessary for the assimilation of nitrogen into amino acids? a. b. c. d. ...
... 22. Is the fixing of nitrogen an exothermic or endothermic process? 23. Which molecule is necessary for the assimilation of nitrogen into amino acids? a. b. c. d. ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... • Atoms that are close to a noble gas (group 18 or VIII) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom • +1, +2, +3 skip -3, -2, -1 Noble Gases ...
... • Atoms that are close to a noble gas (group 18 or VIII) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom • +1, +2, +3 skip -3, -2, -1 Noble Gases ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... larger value of the indicated atomic property. a. Ionization energy, Na or Mg b. Ionization energy, Mg or Cl c. Electron affinity, Cl or Br d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br ...
... larger value of the indicated atomic property. a. Ionization energy, Na or Mg b. Ionization energy, Mg or Cl c. Electron affinity, Cl or Br d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br ...
The Chemical Basis for Life Chapter 2
... • Formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. • Transfer causes a ______ charge on the atom that gave up the electron and a ____________ charge on the atom that receives the electron. • Since opposites attract, the two atoms ...
... • Formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. • Transfer causes a ______ charge on the atom that gave up the electron and a ____________ charge on the atom that receives the electron. • Since opposites attract, the two atoms ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
6 CO + 6 H
... oxygen _ gas are the products because they are the compounds being produced. (4) carbon dioxide and (5) __ water __ are the reactant (the arrow is pointing away from it). WORD BANK (6-8): carbohydrate / glucose/ light/ photosynthesis In this reaction (6) ___ light __ energy is used to rearrange the ...
... oxygen _ gas are the products because they are the compounds being produced. (4) carbon dioxide and (5) __ water __ are the reactant (the arrow is pointing away from it). WORD BANK (6-8): carbohydrate / glucose/ light/ photosynthesis In this reaction (6) ___ light __ energy is used to rearrange the ...
Crossword Pazzle Across 4. the outer protein coat of a virus 5
... 7. an infectious particle made of protein rather than DNA or RNA 8. sphere-shaped bacterium 13. fype of infection in which the host cell bursts and is destroyed 14. single-celled microorganism that lacks a nucleus ...
... 7. an infectious particle made of protein rather than DNA or RNA 8. sphere-shaped bacterium 13. fype of infection in which the host cell bursts and is destroyed 14. single-celled microorganism that lacks a nucleus ...
Regents questions
... Sample Exercise: The element bismuth is the heaviest member of group 5A. A salt of the element bismuth subsalicylate, is the active ingredient in pepto-bismol. a) the bonding radii of thallium and lead are 1.48 A and 1.47 A respectively. Using these values and figure 7.6, predict the bonding atomic ...
... Sample Exercise: The element bismuth is the heaviest member of group 5A. A salt of the element bismuth subsalicylate, is the active ingredient in pepto-bismol. a) the bonding radii of thallium and lead are 1.48 A and 1.47 A respectively. Using these values and figure 7.6, predict the bonding atomic ...
Living things are energy rich complex chemical structures
... IT? endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
... IT? endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.