Metal Complexes
... • Co(en)2Cl2+ – # ligands = 4 (two en’s, two Cl-’s) – C.N. = 6 (not 4!) because each en ligand makes two coordinate covalent bonds to the Co3+ using two different N atoms per ligand TM I-Intro to Complexes 15 ...
... • Co(en)2Cl2+ – # ligands = 4 (two en’s, two Cl-’s) – C.N. = 6 (not 4!) because each en ligand makes two coordinate covalent bonds to the Co3+ using two different N atoms per ligand TM I-Intro to Complexes 15 ...
Proteins S
... o Peptide bonds are planar Tendency to drag e- away from double bonds Fluctuating double bond stops rotation fixed part Pair of linked acids 6 atoms (Ca, C, O, N, H and Ca) lie in a plane Mostly trans not cis steric clashes Two side chains close not enough space steric clashes ...
... o Peptide bonds are planar Tendency to drag e- away from double bonds Fluctuating double bond stops rotation fixed part Pair of linked acids 6 atoms (Ca, C, O, N, H and Ca) lie in a plane Mostly trans not cis steric clashes Two side chains close not enough space steric clashes ...
chapter3_Sections 1
... • Molecule that consists primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
... • Molecule that consists primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions
... - Pigments in photosystem I absorb light, which is used to recharge the electrons that have passed along chain - Electrons leave thylakoid using a second transport chain and get picked up by NADP+ o NADP+ also picks up a H+ to become NADPH D. Hydrogen Ion Movement and ATP Formation - Hydrogen ions a ...
... - Pigments in photosystem I absorb light, which is used to recharge the electrons that have passed along chain - Electrons leave thylakoid using a second transport chain and get picked up by NADP+ o NADP+ also picks up a H+ to become NADPH D. Hydrogen Ion Movement and ATP Formation - Hydrogen ions a ...
(A) and B chains - Michael P. Ready
... RIP (ricin-A, ricin-B, and lectin RCAA and RCA-B from castor bean; abrin-A, abrina/b-B, and agglutinin APA-A and APA-B from A. precatorius; SNAI-A and SNAI-B, SNAV-A and SNAV-B, SNAI'-A and SNAI'-B, LRPSN1-A and LRPSN1-B, LRPSN2-A and LRPSN2-B, and SNAIV from S. nigra; sieboldinb-A, sieboldinb-B, SS ...
... RIP (ricin-A, ricin-B, and lectin RCAA and RCA-B from castor bean; abrin-A, abrina/b-B, and agglutinin APA-A and APA-B from A. precatorius; SNAI-A and SNAI-B, SNAV-A and SNAV-B, SNAI'-A and SNAI'-B, LRPSN1-A and LRPSN1-B, LRPSN2-A and LRPSN2-B, and SNAIV from S. nigra; sieboldinb-A, sieboldinb-B, SS ...
Chapter 2: The Chemical Level Of Organization
... via catabolic pathways – see above) for their chemical energy. Thus they too could be considered “high-energy compounds,” though Martini uses this term only in reference to ATP and similar molecules. Let us make a few additional points about these types of compounds without dwelling too much on thei ...
... via catabolic pathways – see above) for their chemical energy. Thus they too could be considered “high-energy compounds,” though Martini uses this term only in reference to ATP and similar molecules. Let us make a few additional points about these types of compounds without dwelling too much on thei ...
dopamineSummary
... Tyrosine (Tyr or Y) is a non-essential amino acid that can be synthesized in the human body from the amino acid phenylalanine. Tyrosine is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an aromatic ring containing a hydroxyl (OH) group on the fourth carbon of the ring. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
... Tyrosine (Tyr or Y) is a non-essential amino acid that can be synthesized in the human body from the amino acid phenylalanine. Tyrosine is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an aromatic ring containing a hydroxyl (OH) group on the fourth carbon of the ring. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
Unit 10 The d-Block Elements
... (a)The common oxidation states for each element include +2 or +3 or both. +3 states are relatively more common at the beginning of the series, whereas +2 states are more common towards the end. (b)The highest oxidation states up to manganese correspond to the involvement of all the electron outside ...
... (a)The common oxidation states for each element include +2 or +3 or both. +3 states are relatively more common at the beginning of the series, whereas +2 states are more common towards the end. (b)The highest oxidation states up to manganese correspond to the involvement of all the electron outside ...
doc
... E. None of the above. 21. Which of the following is NOT part of the explanation for how complex functional molecules were assembled, despite the vastness of protein space? A. Gaia directs proteins, through negative feedback loops, to the correct region of protein space. B. There are multiple unrelat ...
... E. None of the above. 21. Which of the following is NOT part of the explanation for how complex functional molecules were assembled, despite the vastness of protein space? A. Gaia directs proteins, through negative feedback loops, to the correct region of protein space. B. There are multiple unrelat ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... formula mass (4.2) the mass of a formula unit of a compound relative to a standard (carbon-12). formula unit (4.2) the smallest collection of atoms from which the formula of a compound can be established. hydrate (4.2) any substance that has water molecules incorporated in its structure. law of cons ...
... formula mass (4.2) the mass of a formula unit of a compound relative to a standard (carbon-12). formula unit (4.2) the smallest collection of atoms from which the formula of a compound can be established. hydrate (4.2) any substance that has water molecules incorporated in its structure. law of cons ...
Electron Configuration Notation NTG
... Electron Configuration NTG Electron Configuration The ____________________________ of electrons in atoms. Element has a different # of electrons, so the electron configuration is _______________________ for each element. Electrons tend to make arrangements to obtain the ___________________ pos ...
... Electron Configuration NTG Electron Configuration The ____________________________ of electrons in atoms. Element has a different # of electrons, so the electron configuration is _______________________ for each element. Electrons tend to make arrangements to obtain the ___________________ pos ...
final-exam-backup
... The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As a protein is made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects ...
... The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As a protein is made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects ...
double-replacement reaction
... active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
... active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
practice final examination
... solid iron (III) oxide and gaseous carbon monoxide to form iron metal and gaseous carbon dioxide. ...
... solid iron (III) oxide and gaseous carbon monoxide to form iron metal and gaseous carbon dioxide. ...
Nucleotides, Vitamins, Cosubstrates, and Coenzymes
... BIOTIN was originally called vitamin H. Biotin serves as a coenzyme for enzymes that catalyze carboxylgroup-transfer reactions and ATP dependent carboxylation reactions (the addition of CO2). The cofactor is usually covalently linked to the enzyme by an amide bond to the amino group on a lysine side ...
... BIOTIN was originally called vitamin H. Biotin serves as a coenzyme for enzymes that catalyze carboxylgroup-transfer reactions and ATP dependent carboxylation reactions (the addition of CO2). The cofactor is usually covalently linked to the enzyme by an amide bond to the amino group on a lysine side ...
final-exam-tables-ba..
... The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As a protein is made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects ...
... The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As a protein is made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects ...
To the protocol
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... a. SALT: The salt ions interfere with some of the chemical bonds that maintain protein structure b. pH: The same is true of the extra hydrogen ions at very low pH 1. Optimal pH for most enzymes near neutral ...
... a. SALT: The salt ions interfere with some of the chemical bonds that maintain protein structure b. pH: The same is true of the extra hydrogen ions at very low pH 1. Optimal pH for most enzymes near neutral ...
chapter 1 - Revsworld
... protons, electrons protons, neutrons neutrons, electrons none of these ...
... protons, electrons protons, neutrons neutrons, electrons none of these ...
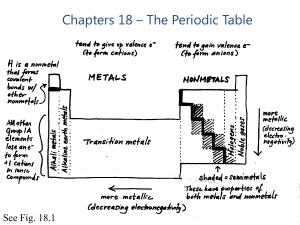
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating agent that removes water from any organic source. 4. Sulfur hexa ...
... from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating agent that removes water from any organic source. 4. Sulfur hexa ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
... How many grams of ammonia will be required to react with 80. g of O2? 4. In the commercial preparation of hydrogen chloride gas, what mass of HCl in grams may be obtained by heating 234 g of NaCl with excess H2SO4? The balanced equation for the reaction is 2NaCl + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + 2HCl 5. A chemi ...
Lecture 9
... A ligand with more than one lone pair can form more than one dative bond with the central atom if the lone pairs are the right distance apart. Because a ligand with two lone pairs looks rather like a claw, it is called a chelate from the Greek wordmeaning claw. If the ligand has two lone pairs it is ...
... A ligand with more than one lone pair can form more than one dative bond with the central atom if the lone pairs are the right distance apart. Because a ligand with two lone pairs looks rather like a claw, it is called a chelate from the Greek wordmeaning claw. If the ligand has two lone pairs it is ...
Chapter 7: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... • Series (I - IV) of protein complexes – Complexes one – three have increasing affinity for electrons ...
... • Series (I - IV) of protein complexes – Complexes one – three have increasing affinity for electrons ...
L4_bacterial metabolism7e
... • Precursor metabolites made from alphaketoglutarate and oxaloacetate ...
... • Precursor metabolites made from alphaketoglutarate and oxaloacetate ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.