Chapter 9 / Energy-Releasing Pathways and Biosynthesis I
... X. The Versatility of Catabolism Use of nutrients other than carbohydrates in aerobic respiration can catabolize proteins and neutral fats --enter at different points along pathways XI. Aspects of Biosynthesis--Anabolism A. The body uses small molecules to build other substances B. These small molec ...
... X. The Versatility of Catabolism Use of nutrients other than carbohydrates in aerobic respiration can catabolize proteins and neutral fats --enter at different points along pathways XI. Aspects of Biosynthesis--Anabolism A. The body uses small molecules to build other substances B. These small molec ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
Water Oxidation By Metal Complexes
... said. "If I take that sunlight and I take water, I can solve the entire energy problem." They've come up with a system that can use the sun's oomph to split water molecules into their constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen. The idea is that those elements could then be recombined in a fuel cell, ...
... said. "If I take that sunlight and I take water, I can solve the entire energy problem." They've come up with a system that can use the sun's oomph to split water molecules into their constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen. The idea is that those elements could then be recombined in a fuel cell, ...
6-Premedical-From-Gene-to
... Posttranslational modifications: certain amino acid are modified by attachment of sugars, lipids, phosphate groups. Two or more polypeptides may join to become the subunits of a protein. ...
... Posttranslational modifications: certain amino acid are modified by attachment of sugars, lipids, phosphate groups. Two or more polypeptides may join to become the subunits of a protein. ...
ans - Gogarten Lab
... C. The unit of life is the entire Earth and the entire biosphere is alive, because no single species can exist in complete isolation. The ecosystems on the Earth are protected by negative feedback loops that help maintain homeostasis. D. Mars cooled faster than the Earth and therefore was a more ...
... C. The unit of life is the entire Earth and the entire biosphere is alive, because no single species can exist in complete isolation. The ecosystems on the Earth are protected by negative feedback loops that help maintain homeostasis. D. Mars cooled faster than the Earth and therefore was a more ...
Practice Exam 3
... Part (2) - Show all your work. ( 8 points each) 21. For CO3 2 - , sulfate ion, draw the Lewis structure (by counting valence electrons of each atom), determine the electron-domain geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, and show the angle between the bonds in a drawing. S is the central atom, ...
... Part (2) - Show all your work. ( 8 points each) 21. For CO3 2 - , sulfate ion, draw the Lewis structure (by counting valence electrons of each atom), determine the electron-domain geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, and show the angle between the bonds in a drawing. S is the central atom, ...
Photosynthesis
... NADP+ picks up two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). It is then converted into NADPH. The NADPH can then carry the high-energy electrons to be used in chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell. ...
... NADP+ picks up two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). It is then converted into NADPH. The NADPH can then carry the high-energy electrons to be used in chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell. ...
Chemical Basis of Life packet #2
... 1. Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form four bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that ...
... 1. Which statement correctly describes how carbon’s ability to form four bonds makes it uniquely suited to form macromolecules? A. It forms short, simple carbon chains. B. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. C. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. D. It forms covalent bonds that ...
Irreversible Changes
... Rusting and the burning of a fuel in the presence of oxygen are both chemical reactions known as oxidation. Iron, in the presence of water and oxygen, reacts to form iron oxide or rust. Whilst the rust can be rubbed off to reveal the ‘good’ iron underneath, the top layer has been changed and removed ...
... Rusting and the burning of a fuel in the presence of oxygen are both chemical reactions known as oxidation. Iron, in the presence of water and oxygen, reacts to form iron oxide or rust. Whilst the rust can be rubbed off to reveal the ‘good’ iron underneath, the top layer has been changed and removed ...
Ch 24 Part 2 PowerPoint
... A plot of absorption intensity of light versus wavelength is called an absorption spectrum for the complex or compound. ...
... A plot of absorption intensity of light versus wavelength is called an absorption spectrum for the complex or compound. ...
pO 2
... being a change in the shape and activity of a protein (as an enzyme) that results from combination with another substance at a point other than the chemically active site ...
... being a change in the shape and activity of a protein (as an enzyme) that results from combination with another substance at a point other than the chemically active site ...
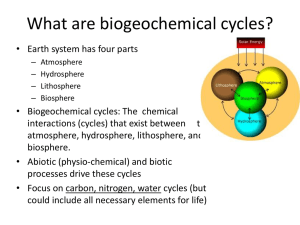
What are biogeochemical cycles?
... biosphere. • Abiotic (physio-chemical) and biotic processes drive these cycles • Focus on carbon, nitrogen, water cycles (but could include all necessary elements for life) ...
... biosphere. • Abiotic (physio-chemical) and biotic processes drive these cycles • Focus on carbon, nitrogen, water cycles (but could include all necessary elements for life) ...
BSCA Questions: Biochemistry
... Glucose 6 phosphate ----- > fructose 6 phosphate B. Glucose ------ > glucose 6 phosphate C. Fructose 6 phosphate ----- > fructose 1,6 bis phosphate D. Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate ---- > dihydroxyacetone phosphate ...
... Glucose 6 phosphate ----- > fructose 6 phosphate B. Glucose ------ > glucose 6 phosphate C. Fructose 6 phosphate ----- > fructose 1,6 bis phosphate D. Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate ---- > dihydroxyacetone phosphate ...
ppt Oxygen Debt-Energy Systems - NCEA-Physical
... sec. of activity result is pyruvate ATP-PC used Converted to up in 10-15 lactic acid if sec. of activity anaerobic envir. ...
... sec. of activity result is pyruvate ATP-PC used Converted to up in 10-15 lactic acid if sec. of activity anaerobic envir. ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
... Oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions, are technically defined as any chemical reaction in which the oxidation number of the participating atom, ion, or molecule of a chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynth ...
Biology I Honors Chapter 3 Biochemistry I. Cells Contain Organic
... A. Most Common Elements 1. Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. 2. Chemistry of carbon allows the formation of an enormous variety of organic molecules. 3. Organic molecules have carbon and hyd ...
... A. Most Common Elements 1. Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. 2. Chemistry of carbon allows the formation of an enormous variety of organic molecules. 3. Organic molecules have carbon and hyd ...
lecture08_12
... GO (gene ontology) http://www.geneontology.org/ • The GO project is aimed to develop three structured, controlled vocabularies (ontologies) that describe gene products in terms of their associated • molecular functions (F) • biological processes (P) • cellular components (C) Ontology is a descripti ...
... GO (gene ontology) http://www.geneontology.org/ • The GO project is aimed to develop three structured, controlled vocabularies (ontologies) that describe gene products in terms of their associated • molecular functions (F) • biological processes (P) • cellular components (C) Ontology is a descripti ...
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... a) Which has the largest atomic radius? K b) Place the elements in order of increasing ionization energy. K < Li < C < N 109) Which group of the periodic table has elements with high first ionization potentials and very negative electron affinities? Explain this behavior. The halogens. For a given r ...
... a) Which has the largest atomic radius? K b) Place the elements in order of increasing ionization energy. K < Li < C < N 109) Which group of the periodic table has elements with high first ionization potentials and very negative electron affinities? Explain this behavior. The halogens. For a given r ...
Translation Tjian lec 26
... 2. Control of alternative splicing by positive and negative splicing factors ( analogous to transcriptional activators and repressors) 3. Complexity of organisms reflected by exon numbers and ...
... 2. Control of alternative splicing by positive and negative splicing factors ( analogous to transcriptional activators and repressors) 3. Complexity of organisms reflected by exon numbers and ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.