Supplementary Table S2 (doc 37K)
... this position may destabilize the local fold. Indeed, Ser 366 is hydrogen bound to W378 promoting stabilization of the beta-sheet encompassing the active site cleft thus correctly positioning it. Besides the lack of this hydrogen bond, the mutation of S366R would cause steric collision of the longer ...
... this position may destabilize the local fold. Indeed, Ser 366 is hydrogen bound to W378 promoting stabilization of the beta-sheet encompassing the active site cleft thus correctly positioning it. Besides the lack of this hydrogen bond, the mutation of S366R would cause steric collision of the longer ...
Chapter 5 - U of L Class Index
... elements in compounds are replaced by other elements. If only one compound has an element replaced, it is a single replacement reaction. If two compounds have elements replaced, then it is a double replacement reaction. e.g. Fe2O3 + 3C AgNO3 + NaCl ...
... elements in compounds are replaced by other elements. If only one compound has an element replaced, it is a single replacement reaction. If two compounds have elements replaced, then it is a double replacement reaction. e.g. Fe2O3 + 3C AgNO3 + NaCl ...
Document
... 1. Explain what is wrong with the statement “My friend burned a piece of paper (a hydrocarbon) that had the final exam on it and it disappeared”. (Be sure to use a chemical equation, identify reactants and product(s) and include energy). ANSWER: The paper (CxHy) was burned with oxygen and the atoms ...
... 1. Explain what is wrong with the statement “My friend burned a piece of paper (a hydrocarbon) that had the final exam on it and it disappeared”. (Be sure to use a chemical equation, identify reactants and product(s) and include energy). ANSWER: The paper (CxHy) was burned with oxygen and the atoms ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...
... you make about this substance from the formula. A. A is a metal and B is a non-metal C. B is a metal and A is a non-metal B. The name will contain the prefixes di and mono D. The compound contains a polyatomic ion 5. What statement about binary compounds is FALSE? A. Binary compounds are formed from ...
Topic 14-Chemical Bonding-Structure
... 14.1 Further aspects of covalent bonding and structure Nature of science: Principle of Occam’s razor—bonding theories have been modified over time. Newer theories need to remain as simple as possible while maximizing explanatory power, for example the idea of formal charge. (2.7) Understandings: ...
... 14.1 Further aspects of covalent bonding and structure Nature of science: Principle of Occam’s razor—bonding theories have been modified over time. Newer theories need to remain as simple as possible while maximizing explanatory power, for example the idea of formal charge. (2.7) Understandings: ...
Prescribed Practicals
... § Determining water of hydration/molar mass of hydrates § Molar mass of oxides § Combustion of magnesium/copper ...
... § Determining water of hydration/molar mass of hydrates § Molar mass of oxides § Combustion of magnesium/copper ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Nomenclature
... related to structure and nomenclature. 10.2. Common Names Early chemical characterizations could not be based on chemical composition, which usually wasn’t known, but rather on properties, such as color, taste, therapeutics (real or imagined), or origin. Substances were classified by value such as b ...
... related to structure and nomenclature. 10.2. Common Names Early chemical characterizations could not be based on chemical composition, which usually wasn’t known, but rather on properties, such as color, taste, therapeutics (real or imagined), or origin. Substances were classified by value such as b ...
Translation text
... - ribosome will eventually reach the stop codon in A binding site which has no corresponding amino acid - tRNA carrying pp chain stays on P site until protein called a release factor binds to A site recognize that the ribosome has stopped and release the polypeptide chain - the ribosome will break d ...
... - ribosome will eventually reach the stop codon in A binding site which has no corresponding amino acid - tRNA carrying pp chain stays on P site until protein called a release factor binds to A site recognize that the ribosome has stopped and release the polypeptide chain - the ribosome will break d ...
Chapter 1
... – Each amide H and carbonyl O is involved in H bonds locking the helix in place – Carbonyl O links to amide H 4 amino acids away – H bonds are parallel to the long axis of the helix – Helix is right-handed – Repeat distance or pitch is 5.4 angstroms – 3.6 amino acids per turn ...
... – Each amide H and carbonyl O is involved in H bonds locking the helix in place – Carbonyl O links to amide H 4 amino acids away – H bonds are parallel to the long axis of the helix – Helix is right-handed – Repeat distance or pitch is 5.4 angstroms – 3.6 amino acids per turn ...
specimen
... hydrochloric acid used. After carrying out the experiment, the student accidentally added some more calcium. The student was surprised that the extra calcium still reacted. Explain this observation. Include an equation in your answer. ...
... hydrochloric acid used. After carrying out the experiment, the student accidentally added some more calcium. The student was surprised that the extra calcium still reacted. Explain this observation. Include an equation in your answer. ...
Role of Water as a Solvent
... Step 1) Assign oxidation numbers to all elements in the equation. Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines betw ...
... Step 1) Assign oxidation numbers to all elements in the equation. Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines betw ...
Slide ()
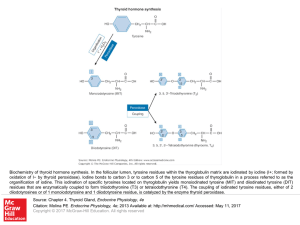
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
What`s in a Name? - Department of Chemistry | Washington
... Practice Problems (Answer key is located at the last page of this tutorial) ...
... Practice Problems (Answer key is located at the last page of this tutorial) ...
Chapter 5- Enzymes State Standard Standard 1.b. – Enzymes
... C. Amino acids D. Nucleic acids 4. The amount of energy that reactants need to start a chemical reaction is the _______. 5. When an enzyme catalyzes (speeds up) a chemical reaction A. It acts as a reactant B. It acts as a product C. It raises the activation energy of a reaction D. It lowers the acti ...
... C. Amino acids D. Nucleic acids 4. The amount of energy that reactants need to start a chemical reaction is the _______. 5. When an enzyme catalyzes (speeds up) a chemical reaction A. It acts as a reactant B. It acts as a product C. It raises the activation energy of a reaction D. It lowers the acti ...
A.P. Chemistry Writing Chemical Reactions Generally students do
... Of course, CO2 is not an acid. However the actual unstable product of the reaction is the weak acid carbonic acid , H2CO3. As we know, this spontaneously breaks down into CO2 and H2O. We can generalize this process with the generic salt of a weak acid, NaA: NaA + H+ → HA + Na+ This can get tricky wi ...
... Of course, CO2 is not an acid. However the actual unstable product of the reaction is the weak acid carbonic acid , H2CO3. As we know, this spontaneously breaks down into CO2 and H2O. We can generalize this process with the generic salt of a weak acid, NaA: NaA + H+ → HA + Na+ This can get tricky wi ...
Transcription - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... A second tRNA bringsthe second amino acid to the ribosome The amino acids are joined together to begin the protein ...
... A second tRNA bringsthe second amino acid to the ribosome The amino acids are joined together to begin the protein ...
Protein Synthesis
... molecule of water. This is called a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids. The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. A peptide bond can be broken down by hydrolysis (the adding of water). The peptide bonds that are formed within ...
... molecule of water. This is called a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids. The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. A peptide bond can be broken down by hydrolysis (the adding of water). The peptide bonds that are formed within ...
ch_9 - WordPress.com
... (c) Phosphoric Acids : It contains a phosphate group. It combines two nucleotides together by formation of phosphodiester bond. ...
... (c) Phosphoric Acids : It contains a phosphate group. It combines two nucleotides together by formation of phosphodiester bond. ...
Chap 2-3 Notes - WordPress.com
... Chap 2 Section 3 Carbon Compounds: The Chemistry of Carbon Organic Chemistry : the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Macromolecules: formed by a process known as polymerization. Monomers: small units that can join together with other small units to form Polymers larg ...
... Chap 2 Section 3 Carbon Compounds: The Chemistry of Carbon Organic Chemistry : the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Macromolecules: formed by a process known as polymerization. Monomers: small units that can join together with other small units to form Polymers larg ...
Molecular Symmetry Chem 332.3 Fall 2005 Inorganic Chemistry II
... complexometric titration of Ca2+or Zn2+ ...
... complexometric titration of Ca2+or Zn2+ ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I
... above with the double bond and single bond. The double bond should be shorter than the single bond however, from experimentation it has been found that the bonds in ozone are ...
... above with the double bond and single bond. The double bond should be shorter than the single bond however, from experimentation it has been found that the bonds in ozone are ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.