Cellular Respiration (Chapter 8) Outline The Killers Are Coming
... 3. But NADH from the cytoplasm cannot enter the mitochondrion and must transfer its electrons! a. In most cells (skeletal, brain) the electrons are transferred to FAD and thus yield two ATP (for a total yield of thirty-six). ...
... 3. But NADH from the cytoplasm cannot enter the mitochondrion and must transfer its electrons! a. In most cells (skeletal, brain) the electrons are transferred to FAD and thus yield two ATP (for a total yield of thirty-six). ...
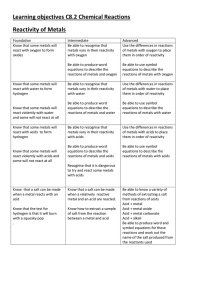
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... of a metal is linked to the method by which it is extracted Understand that the value of the voltage cell depends on the difference in reactivity of the 2 metals used ...
... of a metal is linked to the method by which it is extracted Understand that the value of the voltage cell depends on the difference in reactivity of the 2 metals used ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism
... the cell membrane which is the site of the electron transport system (Figure 8.12). The electron carriers NADH and FADH2 will transfer the electrons, thereby becoming oxidized, to proteins in the cell membrane called cytochromes. There are numerous cytochromes invovled in the electron transport syst ...
... the cell membrane which is the site of the electron transport system (Figure 8.12). The electron carriers NADH and FADH2 will transfer the electrons, thereby becoming oxidized, to proteins in the cell membrane called cytochromes. There are numerous cytochromes invovled in the electron transport syst ...
All chemical equations must be balanced, that is, they must have the
... Occurs when an element and a compound react to form a different element and a new compound. These reactions usually involve an element reacting with an ionic compound. The element can only replace the part of the compound that forms the same type of ion that the element forms : a metallic element wi ...
... Occurs when an element and a compound react to form a different element and a new compound. These reactions usually involve an element reacting with an ionic compound. The element can only replace the part of the compound that forms the same type of ion that the element forms : a metallic element wi ...
Geomicrobiological Cycling of Iron
... Redox transformations of iron, as weIl as dissolution and precipitation and thus mobilization and redistribution, are causedby chemical and to--asignificant extent by microbial processes (Fig. 1). Microorganisms catalyze the oxidation of Fe(ll) under oxic or anoxic conditions as weIl as the reductio ...
... Redox transformations of iron, as weIl as dissolution and precipitation and thus mobilization and redistribution, are causedby chemical and to--asignificant extent by microbial processes (Fig. 1). Microorganisms catalyze the oxidation of Fe(ll) under oxic or anoxic conditions as weIl as the reductio ...
ENZYMES PPT
... Some substances can inhibit enzyme function – Inhibitors Some substances can enhance enzyme function – activators ...
... Some substances can inhibit enzyme function – Inhibitors Some substances can enhance enzyme function – activators ...
Name - Piscataway High School
... Most end in -ate and -ite, only a few (cyanide, hydroxide) have an -ide ending. ...
... Most end in -ate and -ite, only a few (cyanide, hydroxide) have an -ide ending. ...
Three functionally diverged major structural proteins of white spot
... conserved regions (Fig. 3 b). In the N-terminal region a wellconserved stretch of amino acids is observed at positions 15–30. A strong hydrophobic region with an α-helix is observed for all three proteins in the hydrophilicity plots (Fig. 3 a). These residues might represent a transmembrane region, ...
... conserved regions (Fig. 3 b). In the N-terminal region a wellconserved stretch of amino acids is observed at positions 15–30. A strong hydrophobic region with an α-helix is observed for all three proteins in the hydrophilicity plots (Fig. 3 a). These residues might represent a transmembrane region, ...
Ch 7 ppt - mvhs
... Elements in a binary molecular compound are given oxidations numbers equal to the charges they would have as ions Flourine always has an oxidation number of -1. Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 in every compound except for peroxides (like H2O2), where it is -1, and with halogens, has oxidation n ...
... Elements in a binary molecular compound are given oxidations numbers equal to the charges they would have as ions Flourine always has an oxidation number of -1. Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 in every compound except for peroxides (like H2O2), where it is -1, and with halogens, has oxidation n ...
Cellular Respiration
... Heart attack – blood can’t flow to pick up oxygen – without oxygen you can’t make ATP – you die Gunshot – If you are shot in the lungs they can’t bring in oxygen – without oxygen you can’t make ATP – you die Diabetes – Your cells can’t get glucose inside of them – If your cells can’t get gluc ...
... Heart attack – blood can’t flow to pick up oxygen – without oxygen you can’t make ATP – you die Gunshot – If you are shot in the lungs they can’t bring in oxygen – without oxygen you can’t make ATP – you die Diabetes – Your cells can’t get glucose inside of them – If your cells can’t get gluc ...
Structural aspects of l-asparaginases, their friends and relations*
... compared to that of classic serine proteases, whose activity depends on a set of amino-acid residues, typically Ser-His-Asp, known as the “catalytic triad” (Carter & Wells, 1988). This set includes a nucleophilic residue (Ser), a general base (His), and an additional, acidic, residue (Asp), all conn ...
... compared to that of classic serine proteases, whose activity depends on a set of amino-acid residues, typically Ser-His-Asp, known as the “catalytic triad” (Carter & Wells, 1988). This set includes a nucleophilic residue (Ser), a general base (His), and an additional, acidic, residue (Asp), all conn ...
cellular respiration
... – Cellular respiration requires a cell to exchange gases with its surroundings. ...
... – Cellular respiration requires a cell to exchange gases with its surroundings. ...
25.4 ATP yield
... can make three molecules of AIP by cellular respiration; FADH2produces two molecules of AIP in the sameway. It was sho',,rm that 38 AIP molecules is the total useful energyyield of aerobic glucosecatabolism. Molecules of acetyf CoA are the sam-e,regardlessof their source. Like acetyl CoA molecules p ...
... can make three molecules of AIP by cellular respiration; FADH2produces two molecules of AIP in the sameway. It was sho',,rm that 38 AIP molecules is the total useful energyyield of aerobic glucosecatabolism. Molecules of acetyf CoA are the sam-e,regardlessof their source. Like acetyl CoA molecules p ...
Hacking nature: genetic tools for reprograming enzymes
... 14. Farwell, C.C. et al. (2015) Enantioselective enzyme-catalyzed aziridination enabled by active-site evolution of a cytochrome P450. ACS Cent. Sci. 1, 89–93. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.5b00056 15. Renata, H. et al. (2016) Identification of mechanism-based inactivation in P450catalyzed cyclopropanation ...
... 14. Farwell, C.C. et al. (2015) Enantioselective enzyme-catalyzed aziridination enabled by active-site evolution of a cytochrome P450. ACS Cent. Sci. 1, 89–93. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.5b00056 15. Renata, H. et al. (2016) Identification of mechanism-based inactivation in P450catalyzed cyclopropanation ...
Sample Question Set 5a
... 18. When the F1 prtion of the ATP synthase complex is removed from the mitochondrial membrane and studied in solution, it functions as an ATPase, i.e. it hydrolyzes ATP. Why does it not function as an ATP synthase? ...
... 18. When the F1 prtion of the ATP synthase complex is removed from the mitochondrial membrane and studied in solution, it functions as an ATPase, i.e. it hydrolyzes ATP. Why does it not function as an ATP synthase? ...
Asgeirsson, B., Renzetti, G., Invernizzi, G ., Papaleo, E. (2013)
... shown. (B) The =me‐dependent rmsf profiles calculated on =me‐windows of 3 ns of subunit A (purple shade of colors) and B (blue shade of colors) show the progressive changes in residue mobili=es. (C) Regions characterized by differen=al flexibility in subunit A and B are m ...
... shown. (B) The =me‐dependent rmsf profiles calculated on =me‐windows of 3 ns of subunit A (purple shade of colors) and B (blue shade of colors) show the progressive changes in residue mobili=es. (C) Regions characterized by differen=al flexibility in subunit A and B are m ...
Chapter 20 The Transition Elements
... Transistion elements Transition Elements – are the most familiar because they often occur in nature as uncombined elements unlike groups 1 and 2. Transition elements often from colored compounds. Cobalt – Blue Cadmium – Yellow From left to right, aqueous solutions of: Co(NO3)2 (red); K2Cr2O ...
... Transistion elements Transition Elements – are the most familiar because they often occur in nature as uncombined elements unlike groups 1 and 2. Transition elements often from colored compounds. Cobalt – Blue Cadmium – Yellow From left to right, aqueous solutions of: Co(NO3)2 (red); K2Cr2O ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.