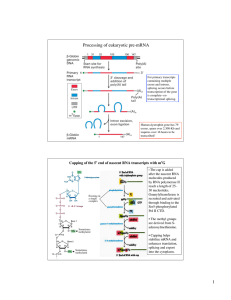
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... The correct 5’ GU and 3’ AG splice sites are recognized by splicing factors on the basis of their proximity to exons. The exons contain exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) that are binding sites for SR proteins. When bound to ESEs, the SR proteins interact with one another and promote the cooperative b ...
... The correct 5’ GU and 3’ AG splice sites are recognized by splicing factors on the basis of their proximity to exons. The exons contain exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) that are binding sites for SR proteins. When bound to ESEs, the SR proteins interact with one another and promote the cooperative b ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
... Determines the chemical properties of the atom During chemical processes, interactions occur between the outermost electrons of each atom The electron properties of the atom will define the type(s) of interaction ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions Proteins
... Please Note: In the above table the net charge has been reported as the nearest integer. To be completely accurate, the net charge at pH 2.2 is +0.5, then net charge at pH 4.2 is -0.5 and the net charge at 9.4 is -1.5. (18) The peptide bonds are shown in red. ...
... Please Note: In the above table the net charge has been reported as the nearest integer. To be completely accurate, the net charge at pH 2.2 is +0.5, then net charge at pH 4.2 is -0.5 and the net charge at 9.4 is -1.5. (18) The peptide bonds are shown in red. ...
Are You Getting It??
... Which of the following mechanisms could be used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction? (multiple answers) a) The substrate is exactly complementary to the active site. b) A histidine residue donates a proton to the substrate. c) A ferric ion prosthetic group stabilizes a negatively charged transition ...
... Which of the following mechanisms could be used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction? (multiple answers) a) The substrate is exactly complementary to the active site. b) A histidine residue donates a proton to the substrate. c) A ferric ion prosthetic group stabilizes a negatively charged transition ...
02. Titration method
... • The utility of complexation titrations improved following the introduction by Schwarzenbach, in 1945, of aminocarboxylic acids as multidentate ligands capable of forming stable 1:1 complexes with metal ions. The most widely used of these new ligands was ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, EDTA, which ...
... • The utility of complexation titrations improved following the introduction by Schwarzenbach, in 1945, of aminocarboxylic acids as multidentate ligands capable of forming stable 1:1 complexes with metal ions. The most widely used of these new ligands was ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, EDTA, which ...
Carbohydrates
... (x) Dehydrogenation –IV: Finally malic acid changes to oxaloacetic acid in presence of enzyme malate dehydrogenase. The pair of hydrogen atoms is accepted by NAD + and is passed on to the electron transport system (ETS) where it releases 3 ATP. Oxaloacetic acid again combines with acetyl coenzyme A ...
... (x) Dehydrogenation –IV: Finally malic acid changes to oxaloacetic acid in presence of enzyme malate dehydrogenase. The pair of hydrogen atoms is accepted by NAD + and is passed on to the electron transport system (ETS) where it releases 3 ATP. Oxaloacetic acid again combines with acetyl coenzyme A ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Inadequate amount of carbohydrates in the diet influences the slowdown in glycogen storage and muscle building protein breakdown. It is associated with including too rapid fatigue during exercise. ...
... Inadequate amount of carbohydrates in the diet influences the slowdown in glycogen storage and muscle building protein breakdown. It is associated with including too rapid fatigue during exercise. ...
poster
... of amino acids, there was a need for a new solution not using pre-mentioned reagents. In this context, a new LC-MS/MS method was developed, for the simultaneous high sensitive quantification of 49 amino acids, using a mixed-mode column (hydrophilic and ion exchange interactions) and typical volatile ...
... of amino acids, there was a need for a new solution not using pre-mentioned reagents. In this context, a new LC-MS/MS method was developed, for the simultaneous high sensitive quantification of 49 amino acids, using a mixed-mode column (hydrophilic and ion exchange interactions) and typical volatile ...
IGCSE SoW 2013
... Recall the noble gases (Group 0) as a family of inert gases and explain their lack of reactivity in terms of their electronic configuration ...
... Recall the noble gases (Group 0) as a family of inert gases and explain their lack of reactivity in terms of their electronic configuration ...
Theoretical Inversion of Amino Acids (Alanine and Aspartic Acid) by
... Racemization is a chemical reaction and a number of factors influence its rate(5). These include; amino acid structure, the sequence of amino acids in peptides, pH, buffering effects, metallic cations, the presence of water and temperature. To establish a dating method the kinetics and mechanisms of ...
... Racemization is a chemical reaction and a number of factors influence its rate(5). These include; amino acid structure, the sequence of amino acids in peptides, pH, buffering effects, metallic cations, the presence of water and temperature. To establish a dating method the kinetics and mechanisms of ...
π bonded ligands
... Cyclobutadienes on the other hand are highyl reactive when not complexed to a late transition metal. The free molecule, with four π electrons, is antiaromatic and rectangular, but the ligand is square and appears to be aromatic. By populating the LUMO of the free diene the ligand is stabilized by me ...
... Cyclobutadienes on the other hand are highyl reactive when not complexed to a late transition metal. The free molecule, with four π electrons, is antiaromatic and rectangular, but the ligand is square and appears to be aromatic. By populating the LUMO of the free diene the ligand is stabilized by me ...
Document
... • by bringing the reactive atoms together in the optimal geometry for the reaction. • lowering the activation energy (G‡) by stabilizing the transition state and/or high energy intermediate. • many enzymes use the functional groups of the amino acid sidechain to carry out the reactions Proteases (p ...
... • by bringing the reactive atoms together in the optimal geometry for the reaction. • lowering the activation energy (G‡) by stabilizing the transition state and/or high energy intermediate. • many enzymes use the functional groups of the amino acid sidechain to carry out the reactions Proteases (p ...
Full Text
... sharing important properties conserved in evolution. Further, they are often able to identify structurally or functionally important regions within protein families, such as active sites and protein–protein interaction sites. In addition to identifying these regions, biologists would often like to d ...
... sharing important properties conserved in evolution. Further, they are often able to identify structurally or functionally important regions within protein families, such as active sites and protein–protein interaction sites. In addition to identifying these regions, biologists would often like to d ...
Did you know that elements found in our soils are important to the
... Stalks weak and plants lodge easily. Shriveled seeds or fruits. Toxicity: Plant Suffers Deficiency In Mg And Ca ...
... Stalks weak and plants lodge easily. Shriveled seeds or fruits. Toxicity: Plant Suffers Deficiency In Mg And Ca ...
8 Cellular Respiration-An Overview
... Glucose, or any carbon-based molecule, can be burned in oxygen (oxidized) to produce carbon dioxide and water. Combustion reactions release large amounts of energy. However, the energy release is uncontrolled. An organism would not be able to handle all that energy at once to do the work of the cell ...
... Glucose, or any carbon-based molecule, can be burned in oxygen (oxidized) to produce carbon dioxide and water. Combustion reactions release large amounts of energy. However, the energy release is uncontrolled. An organism would not be able to handle all that energy at once to do the work of the cell ...
Prediction of protein function using a deep convolutional
... The building blocks of proteins are amino acids which are linked together by peptide bonds into a chain. The polypeptide folds into a specific conformation depending on the interactions between its amino acid side chains which have different chemistries. Many conformations of this chain are possible ...
... The building blocks of proteins are amino acids which are linked together by peptide bonds into a chain. The polypeptide folds into a specific conformation depending on the interactions between its amino acid side chains which have different chemistries. Many conformations of this chain are possible ...
Patterns of nucleotide and amino acid substitution
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
... are those at which any of the four nucleotides can be present in a codon for a single amino acid. In some cases there is redundancy in the first codon position, e.g, both AGA and CGA are codons for arginine. Thus, many nucleotide substitutions at third positions do not lead to amino acid substitutio ...
Cellular Respiration (Chapter 8) Outline The Killers Are Coming
... 3. But NADH from the cytoplasm cannot enter the mitochondrion and must transfer its electrons! a. In most cells (skeletal, brain) the electrons are transferred to FAD and thus yield two ATP (for a total yield of thirty-six). ...
... 3. But NADH from the cytoplasm cannot enter the mitochondrion and must transfer its electrons! a. In most cells (skeletal, brain) the electrons are transferred to FAD and thus yield two ATP (for a total yield of thirty-six). ...
Find the gene
... Physiology: cells need glucose and oxygen to make energy – how do they get oxygen? Red blood cells: circulating; loading oxygen in lungs; unloading oxygen in tissue Why red? Iron. Hemoglobin molecule: consists of four pairwise identical subunits: hemoglobin alpha (HBA) and hemoglobin beta (HBB). Eac ...
... Physiology: cells need glucose and oxygen to make energy – how do they get oxygen? Red blood cells: circulating; loading oxygen in lungs; unloading oxygen in tissue Why red? Iron. Hemoglobin molecule: consists of four pairwise identical subunits: hemoglobin alpha (HBA) and hemoglobin beta (HBB). Eac ...
Chapter 9: The Need for Energy
... Photosynthesis Step 1: Light Reaction – occurs in the thylakoids inside the chloroplast ...
... Photosynthesis Step 1: Light Reaction – occurs in the thylakoids inside the chloroplast ...
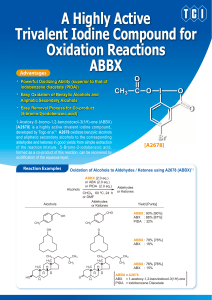
A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for
... A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for Oxidation Reactions ABBX ...
... A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for Oxidation Reactions ABBX ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.