File - Wk 1-2
... beta-oxidation, amino acid breakdown, TCA cycle and electron transport chain. For each, include the cellular location, the major organs in which each pathway is active and the effect of starvation or flux of substrates through the pathway. 4. Outline how chemical energy released from the oxidation o ...
... beta-oxidation, amino acid breakdown, TCA cycle and electron transport chain. For each, include the cellular location, the major organs in which each pathway is active and the effect of starvation or flux of substrates through the pathway. 4. Outline how chemical energy released from the oxidation o ...
Cellular respiration 2
... Images from: http://www.miranda.com/library.en/Images/Pictures/girls-runners.jpg ...
... Images from: http://www.miranda.com/library.en/Images/Pictures/girls-runners.jpg ...
UNIVERSITAT ROVIRA I VIRGILI
... different reaction media. It was found that the polyketone products produced with the phosphine catalysts show number-average molecular weights up to five times bigger than those obtained with the diphosphonium-diphosphine catalysts. The results have been interpreted in terms of faster chain-transfe ...
... different reaction media. It was found that the polyketone products produced with the phosphine catalysts show number-average molecular weights up to five times bigger than those obtained with the diphosphonium-diphosphine catalysts. The results have been interpreted in terms of faster chain-transfe ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration Without O2 all that is left is NADH, Pyruvate, and Glucose with nowhere to go. ...
... Fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration Without O2 all that is left is NADH, Pyruvate, and Glucose with nowhere to go. ...
Nutrition Wars: Choosing Better Protein
... not make your immune system more powerful or increase muscle mass. The risks of very high protein intake (more than two times the RDA) are: 9 High protein intakes are associated with increasing the risk of kidney stones and raising blood uric acid levels which causes gout. 9 High protein intakes cau ...
... not make your immune system more powerful or increase muscle mass. The risks of very high protein intake (more than two times the RDA) are: 9 High protein intakes are associated with increasing the risk of kidney stones and raising blood uric acid levels which causes gout. 9 High protein intakes cau ...
CHAPTER 1
... the pyrophosphate to produce a substrate; production of a metal bound hydroxo ligand as a nucleophile by an adjacent basic amino acid residue and stabilization of the substrate by interaction with cationic amino acid residue (in this case arginine). ...
... the pyrophosphate to produce a substrate; production of a metal bound hydroxo ligand as a nucleophile by an adjacent basic amino acid residue and stabilization of the substrate by interaction with cationic amino acid residue (in this case arginine). ...
ENZYMES
... They have highly specific for their substrate They accelerate the chemical reactions Many inhibitors can affect the enzyme activity . Enzyme have site which is lined with amino acids and this site is known as ACTIVE SITE. ...
... They have highly specific for their substrate They accelerate the chemical reactions Many inhibitors can affect the enzyme activity . Enzyme have site which is lined with amino acids and this site is known as ACTIVE SITE. ...
Poster
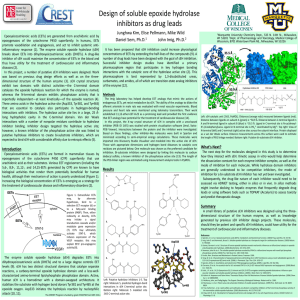
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
Post-Transition Metals
... Often referred to as the “group oxidation state” – “old” nomenclature. The value of this group (N) oxidation state is simple N = group number – 10. Group 11 forms N+1, … N+4 (AuV) oxidation states, by ionising the (n-1)d electrons or involving the (n-1)d orbitals in covalent bonding (transition meta ...
... Often referred to as the “group oxidation state” – “old” nomenclature. The value of this group (N) oxidation state is simple N = group number – 10. Group 11 forms N+1, … N+4 (AuV) oxidation states, by ionising the (n-1)d electrons or involving the (n-1)d orbitals in covalent bonding (transition meta ...
Understanding nature`s catalytic toolkit
... residues, it is helpful to see which residues are used most often in catalytic sites. Figure 1 shows the numbers of each residue that are catalytic in our data set and the catalytic propensity of each residue. The catalytic propensity of a residue is defined as the percentage of catalytic residues c ...
... residues, it is helpful to see which residues are used most often in catalytic sites. Figure 1 shows the numbers of each residue that are catalytic in our data set and the catalytic propensity of each residue. The catalytic propensity of a residue is defined as the percentage of catalytic residues c ...
NAME_________________ 1 BIO 451 14
... B. Why did the athlete mentioned above feel that he was fortunate not to be ADO-deficient, rather than lacking in muscle AMPD? ...
... B. Why did the athlete mentioned above feel that he was fortunate not to be ADO-deficient, rather than lacking in muscle AMPD? ...
Chapter 12 Role of tunnels, channels and gates in enzymatic catalysis
... complexes, which contain separate active sites interconnected by the tunnels. These enzymes are able to carry out sequential reactions, in which an internal pathway conducts the intermediate products from one catalytic site to another. This mechanism may be necessary to increase the enzyme's efficie ...
... complexes, which contain separate active sites interconnected by the tunnels. These enzymes are able to carry out sequential reactions, in which an internal pathway conducts the intermediate products from one catalytic site to another. This mechanism may be necessary to increase the enzyme's efficie ...
... a) the binding of the first ligand has no effect on the binding of subsequent ligands. b) the binding of the first ligand raises the KD for binding of the second. c) the binding of the first ligand raises the KA for binding of the second. d) cannot bind more than one ligand. 10. The hormones, glucag ...
peptides - WordPress.com
... Hydrogen has the lowest redox potential (-0.42 volt ) while oxygen has the highest redox potential (+0.82 volt). The redox potential of all other substances lie between that of hydrogen and oxygen. Electrons are transferred from substances with low redox potential to substances with higher redox po ...
... Hydrogen has the lowest redox potential (-0.42 volt ) while oxygen has the highest redox potential (+0.82 volt). The redox potential of all other substances lie between that of hydrogen and oxygen. Electrons are transferred from substances with low redox potential to substances with higher redox po ...
Chemistry of silver(II): a cornucopia of peculiarities
... record large magnetic superexchange constants, (v) ease of thermal decomposition of its salts with O-, N- or C-ligands, as well as (vi) robust Jahn–Teller effect which is preserved even at high pressure. These intriguing features of the compounds of Ag(II) will be discussed here together with (vii) ...
... record large magnetic superexchange constants, (v) ease of thermal decomposition of its salts with O-, N- or C-ligands, as well as (vi) robust Jahn–Teller effect which is preserved even at high pressure. These intriguing features of the compounds of Ag(II) will be discussed here together with (vii) ...
L23 HH Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle e
... • NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain where they cascade down the chain, releasing energy. The energy is used to pump H ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The return flow of H ions drives ATP synthase and produces the bulk of the ATP generated ...
... • NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain where they cascade down the chain, releasing energy. The energy is used to pump H ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The return flow of H ions drives ATP synthase and produces the bulk of the ATP generated ...
Lecture 3 – Secondary Structure - LCQB
... toward tertiary structure prediction • PSSP algorithms historically rely on amino acid preferences for certain types of secondary structure to infer general rules • The predictions can be refined by the use of multiple sequence alignments or some 3D-structural knowledge ...
... toward tertiary structure prediction • PSSP algorithms historically rely on amino acid preferences for certain types of secondary structure to infer general rules • The predictions can be refined by the use of multiple sequence alignments or some 3D-structural knowledge ...
Enzymes Powerpoint
... 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site. Examples o Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase. o Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, combine with –SH groups. These ...
... 2. Non-competitive: These are not influenced by the concentration of the substrate. It inhibits by binding irreversibly to the enzyme but not at the active site. Examples o Cyanide combines with the Iron in the enzymes cytochrome oxidase. o Heavy metals, Ag or Hg, combine with –SH groups. These ...
molar mass - WordPress.com
... formula, then you multiply the number of atoms of anything next to that subscript by the number of the subscript. For most compounds, this is easy. For example, in iron (II) chloride, or FeCl2, you have one atom of iron and two atoms of chlorine. The molar mass will be equal to (1 atom x 56 grams/mo ...
... formula, then you multiply the number of atoms of anything next to that subscript by the number of the subscript. For most compounds, this is easy. For example, in iron (II) chloride, or FeCl2, you have one atom of iron and two atoms of chlorine. The molar mass will be equal to (1 atom x 56 grams/mo ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN:2319-7676.
... studies, which shown the point of the structure within a range. Energy plot for modeled protein implies using “PROSA” tool [27], where Z score is -6.8 and represent native conformation quality is good (fig 5). The Physico-chemical characteristics of the modeled protein is calculated using Expasy’s p ...
... studies, which shown the point of the structure within a range. Energy plot for modeled protein implies using “PROSA” tool [27], where Z score is -6.8 and represent native conformation quality is good (fig 5). The Physico-chemical characteristics of the modeled protein is calculated using Expasy’s p ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.