2009
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this informa ...
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this informa ...
Human Saliva Amylase Alpha
... 590 Units/mg Protein.One unit will catalyze the hydrolysis of one micromole of malto pentaose, which through coupled reactions results in the formation of 5 micromoles of glucose-6-phosphate per minute at 37°C. Measured at 340nm as an equimolar amount of NADH produced by a coupled reaction. ...
... 590 Units/mg Protein.One unit will catalyze the hydrolysis of one micromole of malto pentaose, which through coupled reactions results in the formation of 5 micromoles of glucose-6-phosphate per minute at 37°C. Measured at 340nm as an equimolar amount of NADH produced by a coupled reaction. ...
The Complete Post-Exercise Muscle Hydration Recovery
... (HSP). HSP are molecular chaperones that aid in the transport of proteins throughout the cell’s various compartments to support protein synthesis. HSP or chaperones also protect the newly synthesized proteins against denaturation. HSP stabilize proteins as a result of altered pH due to high intensit ...
... (HSP). HSP are molecular chaperones that aid in the transport of proteins throughout the cell’s various compartments to support protein synthesis. HSP or chaperones also protect the newly synthesized proteins against denaturation. HSP stabilize proteins as a result of altered pH due to high intensit ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... The TG curve shows a second plateau after 733 K. This indicates completion of the decomposition[17]. The first stage of decomposition initiates at 373 K and occurs at (393 K- 513 K) is due to the mass loss of two nitrate moiety, making mass loss of 14.43 %. The decomposition continues with a gradual ...
... The TG curve shows a second plateau after 733 K. This indicates completion of the decomposition[17]. The first stage of decomposition initiates at 373 K and occurs at (393 K- 513 K) is due to the mass loss of two nitrate moiety, making mass loss of 14.43 %. The decomposition continues with a gradual ...
Amino acid catabolism
... intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
... intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
CHAPTER-8 NCERT SOLUTIONS
... On taking the O.N. of O as –2, the O.N. of Fe is found to be . However, O.N. cannot be fractional. Here, one of the three Fe atoms exhibits the O.N. of +2 and the other two Fe atoms exhibit the O.N. of +3. ...
... On taking the O.N. of O as –2, the O.N. of Fe is found to be . However, O.N. cannot be fractional. Here, one of the three Fe atoms exhibits the O.N. of +2 and the other two Fe atoms exhibit the O.N. of +3. ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1 Key Concepts
... After carbon, nitrogen is the second most abundant element in the biosphere, and in addition to its presence in amino acids and nucleotides, it is also found in some carbohydrates (glucosamine) and lipids (sphingosine), as well as, the enzyme cofactors thiamine, NAD+, and FAD. Nitrogen in biological ...
... After carbon, nitrogen is the second most abundant element in the biosphere, and in addition to its presence in amino acids and nucleotides, it is also found in some carbohydrates (glucosamine) and lipids (sphingosine), as well as, the enzyme cofactors thiamine, NAD+, and FAD. Nitrogen in biological ...
Solution Preparation Final Goueth
... 24. One way of writing the Lewis structure of the cyanate ion, OCN¯, places one double bond between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom and another double bond between the carbon atom and the nitrogen atom. What are the formal charges on the oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen atoms, respectively for this ...
... 24. One way of writing the Lewis structure of the cyanate ion, OCN¯, places one double bond between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom and another double bond between the carbon atom and the nitrogen atom. What are the formal charges on the oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen atoms, respectively for this ...
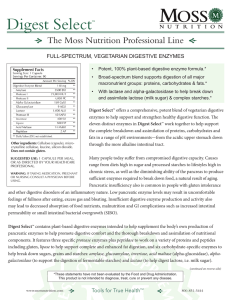
Digest Select - Moss Nutrition
... Beyond their role in protein synthesis, dietary proteins and their breakdown products (e.g. bioactive peptides) have been shown to influence a wide range of physiological, metabolic and regulatory functions. Proper and complete digestion of dietary proteins into component amino acids is therefore cr ...
... Beyond their role in protein synthesis, dietary proteins and their breakdown products (e.g. bioactive peptides) have been shown to influence a wide range of physiological, metabolic and regulatory functions. Proper and complete digestion of dietary proteins into component amino acids is therefore cr ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... methionine was removed and amino acid frequencies were plotted against each other, Figure 1.b. The largest increase in frequency of an amino acid is found in cysteines that account for 1.8% of amino acids in non-LSGs and 3.% of amino acids in LSGs (a 72.97% increase), Figure 1.b. Consistent with the ...
... methionine was removed and amino acid frequencies were plotted against each other, Figure 1.b. The largest increase in frequency of an amino acid is found in cysteines that account for 1.8% of amino acids in non-LSGs and 3.% of amino acids in LSGs (a 72.97% increase), Figure 1.b. Consistent with the ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... In these reactions one of the products formed is an insoluble solid called a precipitate. For example, when solutions of potassium chromate,K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. ...
... In these reactions one of the products formed is an insoluble solid called a precipitate. For example, when solutions of potassium chromate,K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. ...
Supplement I
... label in proteinaceous and free amino acids for the [U-13C6]-glucose (Glc) and [U-13C5]glutamine (Gln) labeling experiments. 13C % labeled amino acid ...
... label in proteinaceous and free amino acids for the [U-13C6]-glucose (Glc) and [U-13C5]glutamine (Gln) labeling experiments. 13C % labeled amino acid ...
KISS Notes
... From these 3 patterns of reaction, it seems there is a further, underlying pattern. Certain metals, like sodium, always seem to react readily and vigorously. Others, like copper, always react slowly or not at all. ...
... From these 3 patterns of reaction, it seems there is a further, underlying pattern. Certain metals, like sodium, always seem to react readily and vigorously. Others, like copper, always react slowly or not at all. ...
Novel eukaryotic enzymes modifying cell
... is vastly expanded in several plant lineages (called domain of unknown function DUF231 in PFAM), including some of the early-branching forms such as chlorophyte algae. Given the evolutionary relationship to the larger GDSL/SGNH superfamily it is likely the PCesterases branched off from them relative ...
... is vastly expanded in several plant lineages (called domain of unknown function DUF231 in PFAM), including some of the early-branching forms such as chlorophyte algae. Given the evolutionary relationship to the larger GDSL/SGNH superfamily it is likely the PCesterases branched off from them relative ...
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... chelate has implications beyond mere definition. It is the key to a chelate’s nutritional functionality. How large can a metal amino acid chelate be and still not require digestion? Can a chelate above a certain size avoid the digestive process? The size of the ligand is the main variable, and logic ...
... chelate has implications beyond mere definition. It is the key to a chelate’s nutritional functionality. How large can a metal amino acid chelate be and still not require digestion? Can a chelate above a certain size avoid the digestive process? The size of the ligand is the main variable, and logic ...
metal-water interactions and hydrogen bond strength
... HDO molecules (2568, 2520 and 2334 cm-1, ambient temperature) which shift to lower frequencies on cooling. Furthermore, the band at the lowest wavenumber transforms into two bands at 2282 and 2212 cm-1 (liquid nitrogen temperature, see Fig. 4). The spectroscopic experiments allow us to deduce the ex ...
... HDO molecules (2568, 2520 and 2334 cm-1, ambient temperature) which shift to lower frequencies on cooling. Furthermore, the band at the lowest wavenumber transforms into two bands at 2282 and 2212 cm-1 (liquid nitrogen temperature, see Fig. 4). The spectroscopic experiments allow us to deduce the ex ...
molybdenum(O)
... to the olefinic carbon atoms and the other two are due to the nitrile carbon atoms. This unequivocally indicates that the FN ligand is coordinated to the M (CO)5 moiety through one nitrile nitrogen atom. A symmetric coordination of FN would give only two 13C NMR signals, one for the olefinic and one ...
... to the olefinic carbon atoms and the other two are due to the nitrile carbon atoms. This unequivocally indicates that the FN ligand is coordinated to the M (CO)5 moiety through one nitrile nitrogen atom. A symmetric coordination of FN would give only two 13C NMR signals, one for the olefinic and one ...
Ribosomal Protein L11 (N-17): sc
... families that consist predominantly of multiple processed pseudogenes and one functional intro-containing gene within their coding regions. The rpS6 gene gives rise to Ribosomal Protein S6 (also designated RPS6), which has a molecular mass of 27.5 kDa and Ribosomal protein L28 which has a molecular ...
... families that consist predominantly of multiple processed pseudogenes and one functional intro-containing gene within their coding regions. The rpS6 gene gives rise to Ribosomal Protein S6 (also designated RPS6), which has a molecular mass of 27.5 kDa and Ribosomal protein L28 which has a molecular ...
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
... NH3(aq) + H2O <=> NH4+ + OHis only 1.8 X 10-5. This means that it mostly exists as NH3(aq) in water. Ammonia is one of the most used chemical in industry. It is mostly used in the production of fertilizers (ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate); manufacture of explosives, plastics, pulp & paper, t ...
... NH3(aq) + H2O <=> NH4+ + OHis only 1.8 X 10-5. This means that it mostly exists as NH3(aq) in water. Ammonia is one of the most used chemical in industry. It is mostly used in the production of fertilizers (ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate); manufacture of explosives, plastics, pulp & paper, t ...
CHEMCO M M
... artificial genes by solid phase techniques. The second method of course allows maximum freedom in designing the target sequence. Because many structural proteins are characterized by repetitive amino acid sequences, it is often possible to multimerize a smaller oligonucleotide sequence to prepare an ...
... artificial genes by solid phase techniques. The second method of course allows maximum freedom in designing the target sequence. Because many structural proteins are characterized by repetitive amino acid sequences, it is often possible to multimerize a smaller oligonucleotide sequence to prepare an ...
A) Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
medbiochem exam 1, 2000
... C. allows skeletal muscle to produce free glucose. D. is stimulated by high levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. E. uses acetyl CoA as a substrate. 44. Which of the following statements about Coenzymes is FALSE? A. Coenzymes are the non-protein portion of the enzyme. B. Coenzymes do not affect the r ...
... C. allows skeletal muscle to produce free glucose. D. is stimulated by high levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. E. uses acetyl CoA as a substrate. 44. Which of the following statements about Coenzymes is FALSE? A. Coenzymes are the non-protein portion of the enzyme. B. Coenzymes do not affect the r ...
EXAM 2 Lecture 15 1. What are cofactors? A: They are small organic
... A: They are small organic molecules or ions that work in concert with an enzyme to catalyze biochemical reactions. They provide special chemical reactivity or structural properties that can drive these special reactions. 2. What are the two subdivisions of cofactors? A: Essential ions and coenzymes ...
... A: They are small organic molecules or ions that work in concert with an enzyme to catalyze biochemical reactions. They provide special chemical reactivity or structural properties that can drive these special reactions. 2. What are the two subdivisions of cofactors? A: Essential ions and coenzymes ...
Cellular respiration 2
... Images from: http://www.miranda.com/library.en/Images/Pictures/girls-runners.jpg ...
... Images from: http://www.miranda.com/library.en/Images/Pictures/girls-runners.jpg ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.