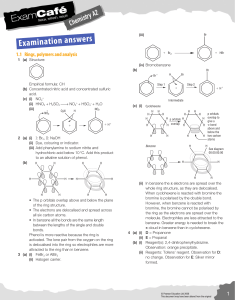
amino acids
... • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
... • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
hydrocarbon chains
... -Eukaryotic cells are distinguished from prokaryotic cells by the presence of ...
... -Eukaryotic cells are distinguished from prokaryotic cells by the presence of ...
Chapter 8 Cellular Respiration Dr. Harold Kay Njemanze 8.1
... 3) turns twice because two acetyl-CoA molecules enter the cycle per glucose molecule; 4) produces two immediate ATP molecules per glucose molecule. C. The electron transport chain: 1) is a series of carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accept electrons from glucose--electrons are passed ...
... 3) turns twice because two acetyl-CoA molecules enter the cycle per glucose molecule; 4) produces two immediate ATP molecules per glucose molecule. C. The electron transport chain: 1) is a series of carriers in the inner mitochondrial membrane that accept electrons from glucose--electrons are passed ...
Integrated search and alignment of protein structures
... We acknowledge that a sequential representation of the residue environments is very effective for their comparison, and utilize a similar representation in this study. We use the location of Cα atoms to represent the amino acids of a protein structure as a set of points in 3D space. The region of sp ...
... We acknowledge that a sequential representation of the residue environments is very effective for their comparison, and utilize a similar representation in this study. We use the location of Cα atoms to represent the amino acids of a protein structure as a set of points in 3D space. The region of sp ...
Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... 1. The oxidation number of elements in a neutral molecule sum to zero or sum to charge of the ion in an ion. 2. Oxidation state of an atom in an element = 0. 3. Oxidation state of monatomic ion = charge. 4. Fluorine = −1 in all compounds. 5. Hydrogen = +1, oxygen = −2 in most compounds (except in pe ...
... 1. The oxidation number of elements in a neutral molecule sum to zero or sum to charge of the ion in an ion. 2. Oxidation state of an atom in an element = 0. 3. Oxidation state of monatomic ion = charge. 4. Fluorine = −1 in all compounds. 5. Hydrogen = +1, oxygen = −2 in most compounds (except in pe ...
Chemistry of Natural Compounds
... form of a methyl group, derived from L-methionine (Figure 1.A). A two carbon atom unit is frequently supplied by acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA, Figure 1.B). The acetyl group is the building block of choice for the construction of a long alkyl chain (as in fatty acids) or may be part of aromatic syst ...
... form of a methyl group, derived from L-methionine (Figure 1.A). A two carbon atom unit is frequently supplied by acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA, Figure 1.B). The acetyl group is the building block of choice for the construction of a long alkyl chain (as in fatty acids) or may be part of aromatic syst ...
Chapter 5
... • Starch, a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers ...
... • Starch, a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers ...
tutorial protein set 1
... b) dissolved in biological fluids c) high content of polar amino acids d) low tensile strength e) often function as transport proteins Ans: a Link to: 3.4 Difficulty: Medium ...
... b) dissolved in biological fluids c) high content of polar amino acids d) low tensile strength e) often function as transport proteins Ans: a Link to: 3.4 Difficulty: Medium ...
Chapter 9 powerpoint and animations
... Allosteric regulation of phosphofructokinase sets the pace of respiration. ...
... Allosteric regulation of phosphofructokinase sets the pace of respiration. ...
Chapter 5 (part 4) Enzyme Regulation
... Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site and allosteric enzymes have 4o structure Fructose-6-P + ATP -----> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP ...
... Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site and allosteric enzymes have 4o structure Fructose-6-P + ATP -----> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP ...
Chapter 17 - Amino Acid Metabolism
... pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates) can supply gluconeogenesis pathway • Ketogenic amino acids (are degraded to acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) - can contribute to synthesis of fatty acids or ketone bodies • Some amino acids are both glucogenic and ...
... pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediates) can supply gluconeogenesis pathway • Ketogenic amino acids (are degraded to acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) - can contribute to synthesis of fatty acids or ketone bodies • Some amino acids are both glucogenic and ...
Biomolecular chemistry 3. Translating the genetic code
... as opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. • If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. • If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensica ...
... as opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. • If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. • If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensica ...
Chapter 16. Solids
... This is close to the experimental lattice spacing from x-ray analysis of 445.5 pm, confirming that Ne indeed does pack in the most efficient way. Since r = √2e/4 for FCC and e = 452.8 pm, r = 160 pm. 16.2. Lattice Energy The energy required to separate all the species (atoms, molecules or ions) at t ...
... This is close to the experimental lattice spacing from x-ray analysis of 445.5 pm, confirming that Ne indeed does pack in the most efficient way. Since r = √2e/4 for FCC and e = 452.8 pm, r = 160 pm. 16.2. Lattice Energy The energy required to separate all the species (atoms, molecules or ions) at t ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
... You can recognize an excited state electron configuration. If the configuration does not match that on the Periodic Table for that number of electrons, then it is an excited state. 9. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy ...
Structural Bioinformatics
... Remove structures with minimal long range interactions (low contact order) Remove structures with unrealistic strands ...
... Remove structures with minimal long range interactions (low contact order) Remove structures with unrealistic strands ...
CH_18_8_Degradation_Amino_Acids
... The urea cycle • removes toxic ammonium ions from amino acid degradation • converts ammonium ions to urea in the liver O ...
... The urea cycle • removes toxic ammonium ions from amino acid degradation • converts ammonium ions to urea in the liver O ...
Protein Composition of a High-Protein Barley Flour and Barley Grain
... The nitrogen contents of high-protein barley flour, barley grain, and their extracted fractions are shown in Table 1. The content of nitrogen in each protein fraction is also expressed as a percentage of the total nitrogen in the original sample. In the high-protein flour, the main protein fraction ...
... The nitrogen contents of high-protein barley flour, barley grain, and their extracted fractions are shown in Table 1. The content of nitrogen in each protein fraction is also expressed as a percentage of the total nitrogen in the original sample. In the high-protein flour, the main protein fraction ...
Lecture 9 Mass Spectrommetry Techniques
... introduced into trap, collisions will cause peptides to fragment usually the C-N peptide bond to produce b and y ions (see later) -Infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) – IR laser is fired into ions to excite the vibrations of peptides. -Electron capture dissociation (ECD) – electron beam is fir ...
... introduced into trap, collisions will cause peptides to fragment usually the C-N peptide bond to produce b and y ions (see later) -Infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) – IR laser is fired into ions to excite the vibrations of peptides. -Electron capture dissociation (ECD) – electron beam is fir ...
20.3 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
... range from 50°C to 120°C. • have enzymes with tertiary structures that are not destroyed by such high temperatures. ...
... range from 50°C to 120°C. • have enzymes with tertiary structures that are not destroyed by such high temperatures. ...
Aphelenchoides besseyi
... Rice white tip nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi, is a kind of plant parasitic nematodes that cause serious losses in rice and many other crops. Fatty acid and retinoid binding protein (FAR) is a specific protein in nematodes and is related to development, reproduction, infection to the host, and dis ...
... Rice white tip nematode, Aphelenchoides besseyi, is a kind of plant parasitic nematodes that cause serious losses in rice and many other crops. Fatty acid and retinoid binding protein (FAR) is a specific protein in nematodes and is related to development, reproduction, infection to the host, and dis ...
Biochemistry of connective tissue
... acids glycine, valine, alanine, and proline. It is a specialized protein with a molecular weight of 64 to 66 kDa, and an irregular or random coil conformation made up of 830 amino acids. • Elastin is made by linking many soluble tropoelastin protein molecules, in a reaction catalyzed by lysyl oxidas ...
... acids glycine, valine, alanine, and proline. It is a specialized protein with a molecular weight of 64 to 66 kDa, and an irregular or random coil conformation made up of 830 amino acids. • Elastin is made by linking many soluble tropoelastin protein molecules, in a reaction catalyzed by lysyl oxidas ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.