Metabolismo dos aminoácidos e proteínas. II. Anabolismo
... - Quantitative analysis of 15NH4+ in Lemna minor is consistent with incorporation of 15N primarily into glutamineamide, followed by transfer to glutamate and the amino-group of glutamine via the action of GOGAT and GS, respectively, provided that it is assumed that the GS-GOGAT cycle is compartmenti ...
... - Quantitative analysis of 15NH4+ in Lemna minor is consistent with incorporation of 15N primarily into glutamineamide, followed by transfer to glutamate and the amino-group of glutamine via the action of GOGAT and GS, respectively, provided that it is assumed that the GS-GOGAT cycle is compartmenti ...
Study of η6 - cyclic π-perimeter hydrocarbon ruthenium complexes
... Within the large family of η5 - and η6 -cyclichydrocarbon metal complexes, piano stool complexes of ruthenium are undeniably the most studied classes of complexes. In particular, η6 -arene metal complexes have emerged as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis as a consequence of the ease with ...
... Within the large family of η5 - and η6 -cyclichydrocarbon metal complexes, piano stool complexes of ruthenium are undeniably the most studied classes of complexes. In particular, η6 -arene metal complexes have emerged as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis as a consequence of the ease with ...
Chemistry Unit 1
... Acidic oxides are the oxides formed by the chemical combination of oxygen with nonmetals. Thus, acidic oxides are non-metal oxides. These oxides are also called acid anhydrides, since they form acidic solutions when reacted or dissolved in water. Acid anhydride means acid without water. ...
... Acidic oxides are the oxides formed by the chemical combination of oxygen with nonmetals. Thus, acidic oxides are non-metal oxides. These oxides are also called acid anhydrides, since they form acidic solutions when reacted or dissolved in water. Acid anhydride means acid without water. ...
Yeast ING Protein Yeast Protein Human Ortholog Description of
... P) into Pi residues; located in the cytosol, plasma membrane, and mitochondrial matrix catalyze formation of phosphatidylethanolamine from phosphatidylserine. targeted to the inner mitochondrial membrane Asn rich cytoplasmic protein that contains RGG motifs; high-copy suppressor of group II intron-s ...
... P) into Pi residues; located in the cytosol, plasma membrane, and mitochondrial matrix catalyze formation of phosphatidylethanolamine from phosphatidylserine. targeted to the inner mitochondrial membrane Asn rich cytoplasmic protein that contains RGG motifs; high-copy suppressor of group II intron-s ...
Time course of differential mitochondrial energy metabolism
... In the heart, mitochondria provide, through oxidative phosphorylation, more than 95% of the energy supply in the form of ATP. In the course of oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred through the respiratory enzymatic complexes of the mitochondrial inner membrane, thus releasing energy u ...
... In the heart, mitochondria provide, through oxidative phosphorylation, more than 95% of the energy supply in the form of ATP. In the course of oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred through the respiratory enzymatic complexes of the mitochondrial inner membrane, thus releasing energy u ...
Cellular Respiration - Spokane Public Schools
... Oxidative phosphorylation. electron transport and chemiosmosis ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation. electron transport and chemiosmosis ...
Chemistry - Edexcel
... 9 During a titration between acidified manganate(VII) ions and sulfate(IV) ions, the manganate(VII) ions are reduced to manganese(II) ions and the sulfate(IV) ions are oxidized to sulfate(VI) ions. The mole ratio of manganate(VII) ions to sulfate(IV) ions in this reaction is A 5:2 B 7:4 C 2:5 D 4:7 ...
... 9 During a titration between acidified manganate(VII) ions and sulfate(IV) ions, the manganate(VII) ions are reduced to manganese(II) ions and the sulfate(IV) ions are oxidized to sulfate(VI) ions. The mole ratio of manganate(VII) ions to sulfate(IV) ions in this reaction is A 5:2 B 7:4 C 2:5 D 4:7 ...
Epsilon glutathione transferases possess a unique class
... in Epsilon class, which is involved in GSH glutamyl binding, is also one of the ‘wafer’ histidines in the interface motif. This position has a significant role in GSH-binding affinity, substrate specificity and protein folding. As a result, His69 , which links the subunits across the dimeric interfa ...
... in Epsilon class, which is involved in GSH glutamyl binding, is also one of the ‘wafer’ histidines in the interface motif. This position has a significant role in GSH-binding affinity, substrate specificity and protein folding. As a result, His69 , which links the subunits across the dimeric interfa ...
Sample Midterm Exam Chemistry 241 R.H. Langley Choose the best
... _____ 5. The "Uniqueness Principle" applies to all the following elements except A. B. C. D. E. ...
... _____ 5. The "Uniqueness Principle" applies to all the following elements except A. B. C. D. E. ...
Krebs Cycle
... Synopsis 3.5b - Krebs cycle involves the oxidation of acetyl group of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) to CO2 with concomitant release of NADH, FADH2, and GTP - Such oxidation of acetyl groups occurs via a “cycle” rather than a “pathway”—since both the substrate and the product are identical (oxaloac ...
... Synopsis 3.5b - Krebs cycle involves the oxidation of acetyl group of acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) to CO2 with concomitant release of NADH, FADH2, and GTP - Such oxidation of acetyl groups occurs via a “cycle” rather than a “pathway”—since both the substrate and the product are identical (oxaloac ...
A Requirement for Sodium in the Growth of
... which I made in the course of studying the amino acid nutrition of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides, seemed significant. This bacterium can grow very well in media of ordinary ionic strength and thus is not obviously marine. I observed that it did not grow in a medium in which an artificial mixture of am ...
... which I made in the course of studying the amino acid nutrition of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides, seemed significant. This bacterium can grow very well in media of ordinary ionic strength and thus is not obviously marine. I observed that it did not grow in a medium in which an artificial mixture of am ...
Surface chemistry of carbon dioxide - Max-Planck
... the "Kolbe-Schmitt" process from CO 2 and sodium phenolate; (c) cyclic organic carbonates are synthesized from CO 2 and epoxides which are used as solvents or in the production of polyacryl "fibres"; (d) methanol synthesis involves CO 2 through the water gas-shift reaction. It was the realization th ...
... the "Kolbe-Schmitt" process from CO 2 and sodium phenolate; (c) cyclic organic carbonates are synthesized from CO 2 and epoxides which are used as solvents or in the production of polyacryl "fibres"; (d) methanol synthesis involves CO 2 through the water gas-shift reaction. It was the realization th ...
PDF file
... with an antisense primer containing a stop codon after amino acid residue 206. Plasmids were sequenced to confirm their authenticity. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins—E. coli BL21(DE3) cells transformed with the GST-PIR1 constructs were grown in LB containing 100 mg/ml ampicilin a ...
... with an antisense primer containing a stop codon after amino acid residue 206. Plasmids were sequenced to confirm their authenticity. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins—E. coli BL21(DE3) cells transformed with the GST-PIR1 constructs were grown in LB containing 100 mg/ml ampicilin a ...
Ken Wu`s Metabolism Tutorial Dec 2012
... • Substrate-level phosphorylation is the production of ATP by the direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate substrate in a biochemical pathway to ADP, such as occurs in glycolysis. • Oxidative phosphorylation: – Electron transport chain, proton pump, needs oxygen – ATP ge ...
... • Substrate-level phosphorylation is the production of ATP by the direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate substrate in a biochemical pathway to ADP, such as occurs in glycolysis. • Oxidative phosphorylation: – Electron transport chain, proton pump, needs oxygen – ATP ge ...
Feature-Based Classification of Amino Acid Substitutions outside
... numbers are transformed by digital-signal processing techniques such as wavelet and Fourier transformations (FT). PseAAC is one method relying on the analysis of the hydrophobic, hydrophilic, side chain mass, pK and pI patterns for prediction of protein attributes, like subcellular localization and ...
... numbers are transformed by digital-signal processing techniques such as wavelet and Fourier transformations (FT). PseAAC is one method relying on the analysis of the hydrophobic, hydrophilic, side chain mass, pK and pI patterns for prediction of protein attributes, like subcellular localization and ...
glycolysis and respiration
... depending on oxygen availability. Our own muscles must metabolize glucose anaerobically when we work them vigorously because they deplete oxygen faster than the circulatory system can supply l it. it Relatively little ATP can be obtained from fermentation of a single molecule of glucose, glucose but ...
... depending on oxygen availability. Our own muscles must metabolize glucose anaerobically when we work them vigorously because they deplete oxygen faster than the circulatory system can supply l it. it Relatively little ATP can be obtained from fermentation of a single molecule of glucose, glucose but ...
Nitrogen source governs the patterns of growth and
... species (Brana et al., 1986) and an alternative pathway involving alanine dehydrogenase (ADH) has been proposed in the same high ammonium conditions (Novak et al., 1992). In this case, the synthesis of glutamate would require the function of an alanine transaminase (AT) and would yield the same glob ...
... species (Brana et al., 1986) and an alternative pathway involving alanine dehydrogenase (ADH) has been proposed in the same high ammonium conditions (Novak et al., 1992). In this case, the synthesis of glutamate would require the function of an alanine transaminase (AT) and would yield the same glob ...
3.Redox
... the solution, (b) the Molarity of the solution. 10. Suppose a 8.75 M aqueous CH3OH solution has a density of 0.789 g / mL. Calculate the mole fraction of CH3OH in the solution.. 11. A solution prepared by dissolving 6.0 g of NaCl in enough water to give 500 mL of solution has a density of 1.05 g / m ...
... the solution, (b) the Molarity of the solution. 10. Suppose a 8.75 M aqueous CH3OH solution has a density of 0.789 g / mL. Calculate the mole fraction of CH3OH in the solution.. 11. A solution prepared by dissolving 6.0 g of NaCl in enough water to give 500 mL of solution has a density of 1.05 g / m ...
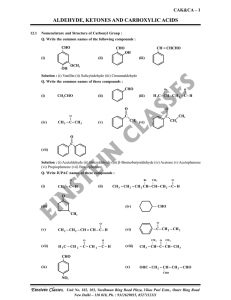
aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids
... approximately perpendicular to the plane of sp2 hybridised orbitals of carbonyl carbon. The hybridisation of carbon changes from sp2 to sp3 in this process, and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is produced. This intermediate captures a proton from the reaction medium to give the electrically neut ...
... approximately perpendicular to the plane of sp2 hybridised orbitals of carbonyl carbon. The hybridisation of carbon changes from sp2 to sp3 in this process, and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is produced. This intermediate captures a proton from the reaction medium to give the electrically neut ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Orienting the net hydrophobic moment of each helix to point toward the membrane (phobic orientation): In this procedure (denoted as CoarseRot-H), the helical face with the maximum hydrophobic moment is calculated for the middle section of each helix, denoted as the hydrophobic midregion (HMR). The f ...
... Orienting the net hydrophobic moment of each helix to point toward the membrane (phobic orientation): In this procedure (denoted as CoarseRot-H), the helical face with the maximum hydrophobic moment is calculated for the middle section of each helix, denoted as the hydrophobic midregion (HMR). The f ...
Design of molecular structure and synthetic approaches
... SSP can be developed by applying the concept of geometrical molecular structure design, which is based on the choice of a type proper of molecular structure and its completion with ligands, providing the necessary number of donor atoms for the chosen core as well as sterical protection. Key words: p ...
... SSP can be developed by applying the concept of geometrical molecular structure design, which is based on the choice of a type proper of molecular structure and its completion with ligands, providing the necessary number of donor atoms for the chosen core as well as sterical protection. Key words: p ...
Chemistry - Government College for Women (Autonomous
... allenes,spiranes(atropisomerism) Stereochemistry of ansa compounds,cyclophanes and trans cyclic alkens,defination of terms like prochirality,enentiotopic and diastereotopic groups/faces asymmetric synthesis-Cram’s rule. Unit III Organic stereochemistry-II: Geometrical isomerism: E and Z nomenclature ...
... allenes,spiranes(atropisomerism) Stereochemistry of ansa compounds,cyclophanes and trans cyclic alkens,defination of terms like prochirality,enentiotopic and diastereotopic groups/faces asymmetric synthesis-Cram’s rule. Unit III Organic stereochemistry-II: Geometrical isomerism: E and Z nomenclature ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.