Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas Pathway
... • Without step II, the aldose cleavage would have resulted in two fragments: ...
... • Without step II, the aldose cleavage would have resulted in two fragments: ...
23 Metabolism and Energy Production
... Match each with their function: 1) FMN 2) Q 3) Cyt c A. 1 Accepts H and electrons from NADH + H+. B. 3 A mobile carrier between Complex II and III. C. 2 Carries electrons from Complex I and II to Complex III. D. 2 Accepts H and electrons from FADH2. ...
... Match each with their function: 1) FMN 2) Q 3) Cyt c A. 1 Accepts H and electrons from NADH + H+. B. 3 A mobile carrier between Complex II and III. C. 2 Carries electrons from Complex I and II to Complex III. D. 2 Accepts H and electrons from FADH2. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... of glycolysis Several steps are different so that control of one pathway does not inactivate the other. However many steps are the same. Three steps are different from glycolysis. 1 Pyruvate to PEP 2 Fructose 1,6- bisphosphate to Fructose-6phosphate 3 Glucose-6-Phosphate to Glucose ...
... of glycolysis Several steps are different so that control of one pathway does not inactivate the other. However many steps are the same. Three steps are different from glycolysis. 1 Pyruvate to PEP 2 Fructose 1,6- bisphosphate to Fructose-6phosphate 3 Glucose-6-Phosphate to Glucose ...
TFE3 contains two activation domains, one acidic and the other
... TFE3 shown to be sufficient for activation (Fig. 1 A). Interestingly, although the proline content in the highly conserved region is low (3/38), all three prolines are perfectly conserved. The two TFE3 activation domains activate transcription synergistically We showed previously that TFE3L is capab ...
... TFE3 shown to be sufficient for activation (Fig. 1 A). Interestingly, although the proline content in the highly conserved region is low (3/38), all three prolines are perfectly conserved. The two TFE3 activation domains activate transcription synergistically We showed previously that TFE3L is capab ...
Chapter 6
... Glycolysis is the first group of reactions that takes place in respiration. It means ‘breaking glucose apart’. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glucose is broken down in a series of steps, each catalysed by an enzyme. In the process, a small proportion ...
... Glycolysis is the first group of reactions that takes place in respiration. It means ‘breaking glucose apart’. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glucose is broken down in a series of steps, each catalysed by an enzyme. In the process, a small proportion ...
lec 7 Metabolism of purine nucleotides
... blood (hyperuricemia), with deposition of monosodium urate crystals in special sites in the body like joints, and surrounding tissues and sometimes in the kidney. Gout is a type of arthritis ...
... blood (hyperuricemia), with deposition of monosodium urate crystals in special sites in the body like joints, and surrounding tissues and sometimes in the kidney. Gout is a type of arthritis ...
Short transmembrane domains with high
... hypothesis is that the more voluminous exoplasmic hemiTMDs of Golgi proteins negatively affect their fit into the highly curved membrane domains from which Golgi transport carriers enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids originate (Duran et al., 2012; Klemm et al., 2009; Polishchuk et al., 2003). ...
... hypothesis is that the more voluminous exoplasmic hemiTMDs of Golgi proteins negatively affect their fit into the highly curved membrane domains from which Golgi transport carriers enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids originate (Duran et al., 2012; Klemm et al., 2009; Polishchuk et al., 2003). ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
... motifs TENEP and ITENG, which contain the two glutamic acids (Glu-191 and Glu-406) involved in the general acid/base catalysis and the respective family 1 b-glucosidases nucleophiles (San-Aparicio et al. 1998). A part slot-like active site (Davies and Henrissat 1995) was formed by these residues nec ...
Recombinant expression and characterisation of monofunctional S-
... conserved area KTCTG) results in inactive enzyme demonstrating an important role for the small subunit in the catalytic activity of mature AdoMetDC since the majority of these residues are present on this subunit (Cohen, 1998; Stanley and Pegg, 1991). The pyruvoyl-containing pocket includes residue ...
... conserved area KTCTG) results in inactive enzyme demonstrating an important role for the small subunit in the catalytic activity of mature AdoMetDC since the majority of these residues are present on this subunit (Cohen, 1998; Stanley and Pegg, 1991). The pyruvoyl-containing pocket includes residue ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry 2 ed William H. Brown
... 18 The a-Helix • Structural features of the a-helix • there are 3.6 amino acids per turn of the helix • each peptide bond is s-trans and planar • N-H groups of all peptide bonds point in the same direction, which is roughly parallel to the axis of the helix • C=O groups of all peptide bonds point i ...
... 18 The a-Helix • Structural features of the a-helix • there are 3.6 amino acids per turn of the helix • each peptide bond is s-trans and planar • N-H groups of all peptide bonds point in the same direction, which is roughly parallel to the axis of the helix • C=O groups of all peptide bonds point i ...
Evolution of strategies to prepare synthetic mimics of carboxylate
... To reduce the geometric constraints of the ligand platform, bulky terphenylcarboxylates were employed. Unlike simple benzoates that form polynuclear clusters with iron [69-71], the sterically hindered 2,6-bis(p-tolyl)benzoate (ArTolCO2–, Table 1) and 2,6-bis(pfluorophenyl)benzoate (Ar4-FPhCO2–) liga ...
... To reduce the geometric constraints of the ligand platform, bulky terphenylcarboxylates were employed. Unlike simple benzoates that form polynuclear clusters with iron [69-71], the sterically hindered 2,6-bis(p-tolyl)benzoate (ArTolCO2–, Table 1) and 2,6-bis(pfluorophenyl)benzoate (Ar4-FPhCO2–) liga ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
WRL3116.tmp
... A. a ping-pong reaction B. * metabolite channeling C. the activity pathway D. the sequential mode E. All of the above 38. In a ping-pong reaction which does not occur? A. One product is released before a second substrate is bound. B. The enzyme covalently binds a portion of the first substrate. ...
... A. a ping-pong reaction B. * metabolite channeling C. the activity pathway D. the sequential mode E. All of the above 38. In a ping-pong reaction which does not occur? A. One product is released before a second substrate is bound. B. The enzyme covalently binds a portion of the first substrate. ...
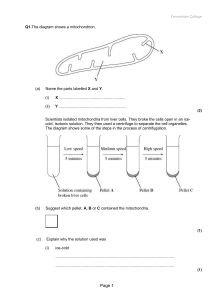
Identification of a molecular component of the mitochondrial
... However, eukaryotic orthologues to Pat have not been identified in either the mitochondrial or nuclear genome [9]. An alternative scenario in eukaryotes could be that mitochondrial proteins are acetylated in the cytosol prior to mitochondrial import. However, as fasting and feeding result in a dynam ...
... However, eukaryotic orthologues to Pat have not been identified in either the mitochondrial or nuclear genome [9]. An alternative scenario in eukaryotes could be that mitochondrial proteins are acetylated in the cytosol prior to mitochondrial import. However, as fasting and feeding result in a dynam ...
Chapter 16 Solubility Equilibrium
... • Consider the following equilibrium: Mg(OH)2(s) ⇌ Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq); • Increasing the pH means increasing [OH-] and equilibrium will shift to the left, causing some of Mg(OH)2 to precipitate out. • If the pH is lowered, [OH-] decreases and equilibrium shifts to the right, causing solid Mg(OH)2 t ...
... • Consider the following equilibrium: Mg(OH)2(s) ⇌ Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq); • Increasing the pH means increasing [OH-] and equilibrium will shift to the left, causing some of Mg(OH)2 to precipitate out. • If the pH is lowered, [OH-] decreases and equilibrium shifts to the right, causing solid Mg(OH)2 t ...
Lipid Biosynthesis
... acid pool is restocked by the amino acids absorbed from the meal. These amino acids are used to synthesize proteins and other nitrogen containing compounds. Dietary lipids are transported from the gut and stored in the tissues, especially the adipose, or they are used to refurbish cell membranes. An ...
... acid pool is restocked by the amino acids absorbed from the meal. These amino acids are used to synthesize proteins and other nitrogen containing compounds. Dietary lipids are transported from the gut and stored in the tissues, especially the adipose, or they are used to refurbish cell membranes. An ...
Amino Acid Interrelationships in Cysteine Toxicity in
... The results in Tables 1 and 3 show that in the examined strains of Neurospora crassa, S-methyl-L-cysteinewas a powerful and competitive antagonist of L-cysteine. In view of the reported occurrence of S-methyl-L-cysteineas a normal metabolite in the wild and methionineless strains of N . crassa and t ...
... The results in Tables 1 and 3 show that in the examined strains of Neurospora crassa, S-methyl-L-cysteinewas a powerful and competitive antagonist of L-cysteine. In view of the reported occurrence of S-methyl-L-cysteineas a normal metabolite in the wild and methionineless strains of N . crassa and t ...
Plant and Soil
... Sweden observed the factor independently. They derived the activating agent from NaC1 extracts of chromatophore membranes. They also reported that it was sensitive to oxygen, reacted specifically with the Fe protein of nitrogenase and that its activity required ATP and Mg 2+. Ludden and Burris (1979 ...
... Sweden observed the factor independently. They derived the activating agent from NaC1 extracts of chromatophore membranes. They also reported that it was sensitive to oxygen, reacted specifically with the Fe protein of nitrogenase and that its activity required ATP and Mg 2+. Ludden and Burris (1979 ...
Slide 1
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
ch 6 notes
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
1 Introduction
... protein molecules of colloidal size [e. g., poly(amino acids)]. Some of them act in dissolved form in cells, while others are chemically bound to to cell membranes or on surfaces. Enzymes can be classified somewhere between molecular homogeneous catalysts and macroscopic heterogeneous catalysts. Enz ...
... protein molecules of colloidal size [e. g., poly(amino acids)]. Some of them act in dissolved form in cells, while others are chemically bound to to cell membranes or on surfaces. Enzymes can be classified somewhere between molecular homogeneous catalysts and macroscopic heterogeneous catalysts. Enz ...
CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS : A TOOL FOR PROTEIN
... functional features of the proteins refers to the modification of their chemical structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduct ...
... functional features of the proteins refers to the modification of their chemical structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduct ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.