Chapter 1-1 Integers and Absolute Values
... Pre-assessment: Draw a number line. Graph the following numbers: 2, 5, 0. Identifying opposite situations - Write an opposite for each word. a. win b. simple ...
... Pre-assessment: Draw a number line. Graph the following numbers: 2, 5, 0. Identifying opposite situations - Write an opposite for each word. a. win b. simple ...
WHOLE NUMBERS REVIEW A set is a collection of objects. The set
... When an exact answer is not necessary, an estimate can be used. The most common method of estimating sums and differences is called “front-end rounding”, which is to round each number to its largest place value, so that all but the first digit of the number is 0. Examples: Estimate 4,894 + 429 Round ...
... When an exact answer is not necessary, an estimate can be used. The most common method of estimating sums and differences is called “front-end rounding”, which is to round each number to its largest place value, so that all but the first digit of the number is 0. Examples: Estimate 4,894 + 429 Round ...
Factors: The numbers that are multiplied to give a product
... Equivalent Fractions: Fraction that have the same amount ...
... Equivalent Fractions: Fraction that have the same amount ...
35 Common constructions (algebraic expressions) for 2 types 1
... Adding 0.1 to 10 hardly changes the 10, so we can ignore the 0.1 when adding. When rounding, we should keep the highest 1 or 2 place values, since adding more than 2 digits becomes complicated. Estimating Sums Procedure 1. Choose the largest number and round it to the highest 1 or 2 place values. 2. ...
... Adding 0.1 to 10 hardly changes the 10, so we can ignore the 0.1 when adding. When rounding, we should keep the highest 1 or 2 place values, since adding more than 2 digits becomes complicated. Estimating Sums Procedure 1. Choose the largest number and round it to the highest 1 or 2 place values. 2. ...
Intro to Decimals Place Value The word form, decimal form, and
... One hundred thirty two and four hundred twenty four thousandths. ...
... One hundred thirty two and four hundred twenty four thousandths. ...
6.3-power-point
... adding or taking away a negative sign (-). For example, the opposite of -13 is 13, and the opposite of -8 is +8. absolute value On a number line it is the distance between the number and zero. Uses l l symbol. Ex-symbol for absolute value |-20| = 20 and read "The absolute value of -20 equals 20". ...
... adding or taking away a negative sign (-). For example, the opposite of -13 is 13, and the opposite of -8 is +8. absolute value On a number line it is the distance between the number and zero. Uses l l symbol. Ex-symbol for absolute value |-20| = 20 and read "The absolute value of -20 equals 20". ...
Section 1 - Pioneer Student
... 0.1 = .1 (Leading zero is a general convention used to help eliminate error) Trailing 0 0.10 = 0.1 (Trailing zero is an engineering/scientific convention use to display accuracy) Rounding Round from the right just like with whole numbers. Adding & 1. Line up Decimal points Subtracting 2. Add trailin ...
... 0.1 = .1 (Leading zero is a general convention used to help eliminate error) Trailing 0 0.10 = 0.1 (Trailing zero is an engineering/scientific convention use to display accuracy) Rounding Round from the right just like with whole numbers. Adding & 1. Line up Decimal points Subtracting 2. Add trailin ...
Summer Packet 8th to 9th
... Remember, when multiplying and dividing fractions there is no need to have a common denominator. Change all whole and mixed numbers to improper fractions. If it is a division problem, don’t forget to change it to multiplication, and flip the 2nd fraction. Cross cancel then multiply. ...
... Remember, when multiplying and dividing fractions there is no need to have a common denominator. Change all whole and mixed numbers to improper fractions. If it is a division problem, don’t forget to change it to multiplication, and flip the 2nd fraction. Cross cancel then multiply. ...
basic_math_computation
... The math skills required for success in chemistry are equal to "hard algebra 1". The following set includes instructions on how to calculate answers. These instructions may not be within your current comfort zone but they have been used over twenty-seven years and have led to success for many studen ...
... The math skills required for success in chemistry are equal to "hard algebra 1". The following set includes instructions on how to calculate answers. These instructions may not be within your current comfort zone but they have been used over twenty-seven years and have led to success for many studen ...
Study Guide - East Lyme Public Schools
... Estimation by rounding to the highest place value, or rounding to 10, 100, or 1000. 2 by 2, 3 by 1 or 3by 2-digit multiplication with or without decimals. You can use traditional, expanded or array method. When asked to use a model, use array or place value (dot) methods. With decimals, multiply as ...
... Estimation by rounding to the highest place value, or rounding to 10, 100, or 1000. 2 by 2, 3 by 1 or 3by 2-digit multiplication with or without decimals. You can use traditional, expanded or array method. When asked to use a model, use array or place value (dot) methods. With decimals, multiply as ...
s01.pdf
... The maximum and minimum numbers the computer can represent are xed. When an attempt to exceed the maximum number is made, an over ow takes place. When an attempt to go below the minimum number is made, an under ow takes place. The following FORTRAN program nds the value of the smallest number tha ...
... The maximum and minimum numbers the computer can represent are xed. When an attempt to exceed the maximum number is made, an over ow takes place. When an attempt to go below the minimum number is made, an under ow takes place. The following FORTRAN program nds the value of the smallest number tha ...
Section 1.2 Round-off Errors and Computer Arithmetic
... • In a computer model, a memory storage unit – word is used to store a number. • A word has only a finite number of bits. • These facts imply: 1. Only a small set of real numbers (rational numbers) can be accurately represented on computers. 2. (Rounding) errors are inevitable when computer memory ...
... • In a computer model, a memory storage unit – word is used to store a number. • A word has only a finite number of bits. • These facts imply: 1. Only a small set of real numbers (rational numbers) can be accurately represented on computers. 2. (Rounding) errors are inevitable when computer memory ...
Math 111
... Part II: What place value is each underlined digit? 1) 146,789,000.04: ____________________ 2) 65, 933.7782: ______________________ ...
... Part II: What place value is each underlined digit? 1) 146,789,000.04: ____________________ 2) 65, 933.7782: ______________________ ...
Math 111
... Part II: What place value is each underlined digit? 1) 146,789,000.04: ____________________ 2) 65, 933.7782: ______________________ ...
... Part II: What place value is each underlined digit? 1) 146,789,000.04: ____________________ 2) 65, 933.7782: ______________________ ...
Roundoff Errors and Computer Arithmetic
... positive number that when multiplied by itself produces the integer 3. • In the computational world, however, each representable number has only a fixed and finite number of digits. ...
... positive number that when multiplied by itself produces the integer 3. • In the computational world, however, each representable number has only a fixed and finite number of digits. ...
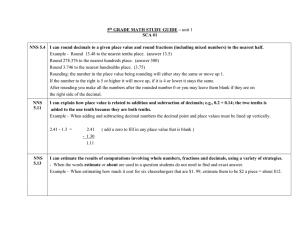
5th GRADE MATH STUDY GUIDE – unit 1
... (The test WILL NOT consist of a vocabulary list. However, you must understand the meaning of the following words.): difference, sum, decimal number, decimal place, decimal point, place value, estimate, about, equals, total, add, subtract Integer -Any of the counting numbers, their opposites, and zer ...
... (The test WILL NOT consist of a vocabulary list. However, you must understand the meaning of the following words.): difference, sum, decimal number, decimal place, decimal point, place value, estimate, about, equals, total, add, subtract Integer -Any of the counting numbers, their opposites, and zer ...
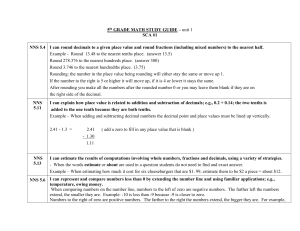
5th GRADE MATH STUDY GUIDE – unit 1
... (The test WILL NOT consist of a vocabulary list. However, you must understand the meaning of the following words.): difference, sum, decimal number, decimal place, decimal point, place value, estimate, about, equals, total, add, subtract Integer -Any of the counting numbers, their opposites, and zer ...
... (The test WILL NOT consist of a vocabulary list. However, you must understand the meaning of the following words.): difference, sum, decimal number, decimal place, decimal point, place value, estimate, about, equals, total, add, subtract Integer -Any of the counting numbers, their opposites, and zer ...
Date - Bonham Middle School
... 1. Maggie owes the candy store $35. Each of 5 friends will help her pay off her debt. How much will each friend pay? ...
... 1. Maggie owes the candy store $35. Each of 5 friends will help her pay off her debt. How much will each friend pay? ...
Place Value and Money
... Students should be able to read and write numbers through the thousands. All numbers are made from the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. There are different ways to represent a number. Standard Form: 2,106 Expanded Form: 2,000 + 100 + 6 Word Form: two thousand, one hundred six Students will l ...
... Students should be able to read and write numbers through the thousands. All numbers are made from the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. There are different ways to represent a number. Standard Form: 2,106 Expanded Form: 2,000 + 100 + 6 Word Form: two thousand, one hundred six Students will l ...
Chapter 0 – Section 01 - Dr. Abdullah Almutairi
... Accuracy and Rounding One more point, though: If, in a long calculation, you round the intermediate results, your final answer may be even less accurate than you think. As a general rule, When calculating, don’t round intermediate results. Rather, use the most accurate results obtainable or have yo ...
... Accuracy and Rounding One more point, though: If, in a long calculation, you round the intermediate results, your final answer may be even less accurate than you think. As a general rule, When calculating, don’t round intermediate results. Rather, use the most accurate results obtainable or have yo ...