3-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... It is selectively damaged in Syringomyelia The central canal becomes enlarged forming a cavity compressing the adjacent nerve fibres Fibres serving pain and temperature are damaged as they decussate in the ventral white commissure close to the central canal causing selective loss of pain and tempera ...
... It is selectively damaged in Syringomyelia The central canal becomes enlarged forming a cavity compressing the adjacent nerve fibres Fibres serving pain and temperature are damaged as they decussate in the ventral white commissure close to the central canal causing selective loss of pain and tempera ...
L4-As.Tracts 2014 (final).
... The central canal becomes enlarged forming a cavity compressing the adjacent nerve fibres Fibres serving pain and temperature are damaged as they decussate in the ventral white commissure close to the central canal causing selective loss of pain and temperature in the upper limbs ...
... The central canal becomes enlarged forming a cavity compressing the adjacent nerve fibres Fibres serving pain and temperature are damaged as they decussate in the ventral white commissure close to the central canal causing selective loss of pain and temperature in the upper limbs ...
L1 Nervous System Neurons File
... L1: Reflex Arc A nerve pathway designed to react quickly to painful/ motor stimuli. Consists of.. ...
... L1: Reflex Arc A nerve pathway designed to react quickly to painful/ motor stimuli. Consists of.. ...
Unit II: Body and Mind
... – Brain structures located under the cortex – Involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation – Thalamus • Relays sensory information from the lower part of the brain to areas of cortex • Processes some sensory information ...
... – Brain structures located under the cortex – Involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation – Thalamus • Relays sensory information from the lower part of the brain to areas of cortex • Processes some sensory information ...
1096-Basic Introduction to Nervous System Presentation
... Relay neurones links used to relay messages from sensory neurone to motor neurone and make up the brain and spinal cord usually much smaller cells, with many connections. ...
... Relay neurones links used to relay messages from sensory neurone to motor neurone and make up the brain and spinal cord usually much smaller cells, with many connections. ...
the human brain the cerebrum
... • The second largest region of the brain is the cerebellum. • Information about muscle and joint position, as well as other sensory inputs, are sent to the cerebellum. ...
... • The second largest region of the brain is the cerebellum. • Information about muscle and joint position, as well as other sensory inputs, are sent to the cerebellum. ...
Nervous System Part 3
... from the body’s sensory receptors Located in the parietal lobe Allows you to recognize pain, coldness, or a ...
... from the body’s sensory receptors Located in the parietal lobe Allows you to recognize pain, coldness, or a ...
Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
... fungi and some protozoa. These pathogens enter our bodies through openings (e.g., eye, nose, mouth). To prevent invasions, the immune system has three lines of defense: (1) barriers (e.g., skin), (2) secretions (e.g., mucus, gastric juices) that wash away, expel or kill invaders and (3) prevention v ...
... fungi and some protozoa. These pathogens enter our bodies through openings (e.g., eye, nose, mouth). To prevent invasions, the immune system has three lines of defense: (1) barriers (e.g., skin), (2) secretions (e.g., mucus, gastric juices) that wash away, expel or kill invaders and (3) prevention v ...
control of muscle movement
... • LATERAL SIDE NEURONS SYNAPSE IPSILATERALLY (TO DISTAL LIMB MUSCLES) • MIDLINE NEURONS SYNAPSE BOTH SIDES (MUSCLES FOR POSTURE) ALPHA MOTOR NEURONS:EXCITE SYNERGISTIC AND INHIBIT ANTAGONISTIC ...
... • LATERAL SIDE NEURONS SYNAPSE IPSILATERALLY (TO DISTAL LIMB MUSCLES) • MIDLINE NEURONS SYNAPSE BOTH SIDES (MUSCLES FOR POSTURE) ALPHA MOTOR NEURONS:EXCITE SYNERGISTIC AND INHIBIT ANTAGONISTIC ...
Gross Anatomy Lecture 1: Spinal Cord and Nerves I. Basic
... 6. Relationship between spinal cord level and vertebral level in adult a. Vertebral level – position of an individual vertebrate along vertebral column b. Spinal cord level – location of an individual spinal cord segment along the SC i. Spinal cord segment – region of spinal cord that contains all t ...
... 6. Relationship between spinal cord level and vertebral level in adult a. Vertebral level – position of an individual vertebrate along vertebral column b. Spinal cord level – location of an individual spinal cord segment along the SC i. Spinal cord segment – region of spinal cord that contains all t ...
Ross Chezem
... cerebellum he would reach the occipital lobe. After crossing the occipital lobe he would reach the parietal lobe. From the parietal lobe he would enter the frontal lobe and move down to the bottom of the frontal lobe to reach the cerebral cortex. This may sound very simple but along the way Travis w ...
... cerebellum he would reach the occipital lobe. After crossing the occipital lobe he would reach the parietal lobe. From the parietal lobe he would enter the frontal lobe and move down to the bottom of the frontal lobe to reach the cerebral cortex. This may sound very simple but along the way Travis w ...
Document
... __________________________1. Period of repolarization of the neuron during which it cannot respond to a second stimulus __________________________2. State in which the resting potential is reversed as sodium ions rush into the neuron __________________________3. Electrical condition of the plasma me ...
... __________________________1. Period of repolarization of the neuron during which it cannot respond to a second stimulus __________________________2. State in which the resting potential is reversed as sodium ions rush into the neuron __________________________3. Electrical condition of the plasma me ...
3-As.Tracts 2016-17
... • Carry impulses concerned with proprioception (movement and joint position) and discriminative touch from ipsilateral side of the body • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received ...
... • Carry impulses concerned with proprioception (movement and joint position) and discriminative touch from ipsilateral side of the body • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received ...
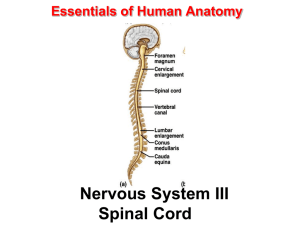
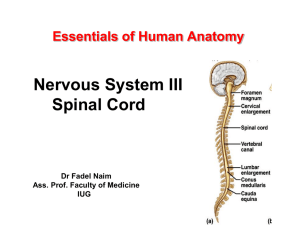
Essentials of Human Anatomy Nervous System III Spinal Cord The
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
Part 1 - Kirkwood Community College
... • Choroid plexus – a structure that secretes cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) ...
... • Choroid plexus – a structure that secretes cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) ...
The Peripheral Nervous System - Advanced
... The autonomic nervous system ( ANS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that maintains homeostasis in the body. Your body carries out most of these maintenance activities without your conscious control, which is why the autonomic nervous system is also called the involuntary nervous system. ...
... The autonomic nervous system ( ANS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that maintains homeostasis in the body. Your body carries out most of these maintenance activities without your conscious control, which is why the autonomic nervous system is also called the involuntary nervous system. ...
Nervous Tissue: Neurons
... • Found in neural pathways in the ______ nervous system • Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... • Found in neural pathways in the ______ nervous system • Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
3-As.Tracts 2015 (final).
... • Primary afferents reach dorsal horn through dorsal roots and terminate on 2nd order neurons. • The cell bodies of 2nd order neuron lie in base of the dorsal horn. • Axons of 2nd order neuron cross to opposite side, and project to the periaquiductal gray matter and superior colliculus in the midbra ...
... • Primary afferents reach dorsal horn through dorsal roots and terminate on 2nd order neurons. • The cell bodies of 2nd order neuron lie in base of the dorsal horn. • Axons of 2nd order neuron cross to opposite side, and project to the periaquiductal gray matter and superior colliculus in the midbra ...
Chapter 12 - Neural Tissue
... Astrocytes: largest & most numerous BBB, control of environment structural framework & repairs regulation of ions, nutrients, gases ...
... Astrocytes: largest & most numerous BBB, control of environment structural framework & repairs regulation of ions, nutrients, gases ...
Class X Episode 5 A. P State HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The
... The Other part of fore brain is Diencephalons. It is concealed by the cerebrum. Diencephalon has two constituents. They are: a) Thallamus. And b) Hypothallamus. ...
... The Other part of fore brain is Diencephalons. It is concealed by the cerebrum. Diencephalon has two constituents. They are: a) Thallamus. And b) Hypothallamus. ...
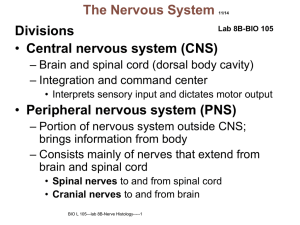
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.