Biological Science, 4e (Freeman)
... control is required. The downside is that it is relatively slow. B) Post-translational control is very fast and is useful when a quick response to a changing environment is required. The downside is that it requires a lot of energy. Ans: B 12) Codons, the three base sequences that code for specific ...
... control is required. The downside is that it is relatively slow. B) Post-translational control is very fast and is useful when a quick response to a changing environment is required. The downside is that it requires a lot of energy. Ans: B 12) Codons, the three base sequences that code for specific ...
NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
... As dATP level rise, ribonucleotide reductase is inhibited↓ production of all deoxyribose containing nucleotidescells cannot make DNA and divide. Most severe form: severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID)lack of T and B cells ...
... As dATP level rise, ribonucleotide reductase is inhibited↓ production of all deoxyribose containing nucleotidescells cannot make DNA and divide. Most severe form: severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID)lack of T and B cells ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Hour Exam 2
... B) is efficient at nick translation. C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication. D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells. E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer. ...
... B) is efficient at nick translation. C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication. D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells. E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer. ...
Lena Huang
... successfully used another genome editing tool called TALEN to alter a donor’s immune system T cells to seek out and kill leukemia cells in a baby girl that saved her life. At the National Cancer ...
... successfully used another genome editing tool called TALEN to alter a donor’s immune system T cells to seek out and kill leukemia cells in a baby girl that saved her life. At the National Cancer ...
Gene therapy for metabolic disorders
... constantly being replaced, repeat treatments are needed. These findings, while encouraging, are not completely conclusive, since it is not yet certain that they are the result of gene therapy alone. Protocols are being designed for transducing hematopoietic stem cells in such a way that even at a lo ...
... constantly being replaced, repeat treatments are needed. These findings, while encouraging, are not completely conclusive, since it is not yet certain that they are the result of gene therapy alone. Protocols are being designed for transducing hematopoietic stem cells in such a way that even at a lo ...
PPT - NC BioGrid
... USDA-IFAFS project Oct 2000 “Gene discovery in the rice blast fungus: ESTs and sequence of chromosome 7” 1. Generate ~5 X draft sequence of ...
... USDA-IFAFS project Oct 2000 “Gene discovery in the rice blast fungus: ESTs and sequence of chromosome 7” 1. Generate ~5 X draft sequence of ...
Organic
... • The “code of life” • Specifically they code for proteins • Each NA’s role: DNA—stores the info (w/in chromosomes) for all of life’s processes (growth, metabolism, reproduction, etc.) RNA—messenger that carries the info out ...
... • The “code of life” • Specifically they code for proteins • Each NA’s role: DNA—stores the info (w/in chromosomes) for all of life’s processes (growth, metabolism, reproduction, etc.) RNA—messenger that carries the info out ...
Document
... 5.2 Penetrance and Expressivity Describe How Genes Are Expressed as Phenotype • For some characters, the genotype does not always produce the expected phenotype= incomplete penetrance. ...
... 5.2 Penetrance and Expressivity Describe How Genes Are Expressed as Phenotype • For some characters, the genotype does not always produce the expected phenotype= incomplete penetrance. ...
Document
... closer than gene expression studies to what’s actually happening in the cell. • Structural genomics initiatives are being launched worldwide to generate the 3-D structures of one or more proteins from each protein family, thus offering clues to function and biological targets for drug design. ...
... closer than gene expression studies to what’s actually happening in the cell. • Structural genomics initiatives are being launched worldwide to generate the 3-D structures of one or more proteins from each protein family, thus offering clues to function and biological targets for drug design. ...
A Healthy Pregnancy
... protein and the fetus’s blood has it. ( the fetus may inherit this blood factor from the father). The mothers blood will produce anti-bodies that attack the protein in the fetus’s blood as though it were a germ. Doctors can inject a chemical into the mother o prevent the problem from arising. ...
... protein and the fetus’s blood has it. ( the fetus may inherit this blood factor from the father). The mothers blood will produce anti-bodies that attack the protein in the fetus’s blood as though it were a germ. Doctors can inject a chemical into the mother o prevent the problem from arising. ...
new lab 9 chromosomal map
... haploid parental genotypes . The recombinants can be most easily visualized by test crosses. Gene Linkage All the genes that are located on the same chromosome and that control the dissemination of one or two trait of certain Linkage : is a method that allows us to determine regions of chromosomes t ...
... haploid parental genotypes . The recombinants can be most easily visualized by test crosses. Gene Linkage All the genes that are located on the same chromosome and that control the dissemination of one or two trait of certain Linkage : is a method that allows us to determine regions of chromosomes t ...
Exam #1
... in this problem because initial green bird would be homozygous for one allele, and initial white bird would be homozygous for the other. Since the F1 birds were mated with each other, you still only have two total alleles that can contribute to the F2 progeny. Epistasis is incorrect because there wo ...
... in this problem because initial green bird would be homozygous for one allele, and initial white bird would be homozygous for the other. Since the F1 birds were mated with each other, you still only have two total alleles that can contribute to the F2 progeny. Epistasis is incorrect because there wo ...
Chapter 11
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
Association of Functional Polymorphisms of the Human Tryptophan
... Effect of tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene (TPH2) promoter polymorphism on gene expression in the reporter system. A, Promoter activity of the TPH2 T − 703G and T − 473A polymorphisms. The human neuroblastoma cell lines SH-SY5Y and IMR-32 were transfected with plasmid constructs containing different ha ...
... Effect of tryptophan hydroxylase 2 gene (TPH2) promoter polymorphism on gene expression in the reporter system. A, Promoter activity of the TPH2 T − 703G and T − 473A polymorphisms. The human neuroblastoma cell lines SH-SY5Y and IMR-32 were transfected with plasmid constructs containing different ha ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis – Grade 10
... 1. The amino acid sequence “AUG” is the start codon. The mRNA begins coding at that point. Three specific amino acids (TAA, TAG and TGA) inform the mRNA to stop reading the code and the amino acid chain is released. 2. If one base is changed, the amino acid that is coded for may be changed, changing ...
... 1. The amino acid sequence “AUG” is the start codon. The mRNA begins coding at that point. Three specific amino acids (TAA, TAG and TGA) inform the mRNA to stop reading the code and the amino acid chain is released. 2. If one base is changed, the amino acid that is coded for may be changed, changing ...
Overview of Basic Genetic Concepts and Terminology
... (messenger RNA), which, in turn, is translated into protein. ...
... (messenger RNA), which, in turn, is translated into protein. ...
Chapter 20
... Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome Cloned genes are useful for making copies of a particular gene and produci ...
... Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome Cloned genes are useful for making copies of a particular gene and produci ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... b. Describe the isolation and importance of flavones. ...
... b. Describe the isolation and importance of flavones. ...
BioSc 231 Exam 4 2005
... (2 pts) The protein produced by the above mRNA functions as a signal molecule and scientists predict that the Lysine (K) in this protein is necessary for its function. What mutation(s) would you make to test this hypothesis? (Note, the typical strategy for determining the function of a single amino ...
... (2 pts) The protein produced by the above mRNA functions as a signal molecule and scientists predict that the Lysine (K) in this protein is necessary for its function. What mutation(s) would you make to test this hypothesis? (Note, the typical strategy for determining the function of a single amino ...
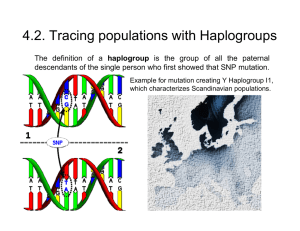
4.2. Tracing populations with Haplogroups
... descendants of the single person who first showed that SNP mutation. Example for mutation creating Y Haplogroup I1, ...
... descendants of the single person who first showed that SNP mutation. Example for mutation creating Y Haplogroup I1, ...


![[001-072] pierce student man](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022334386_1-9de543484cd36eb36195da727e3238d8-300x300.png)