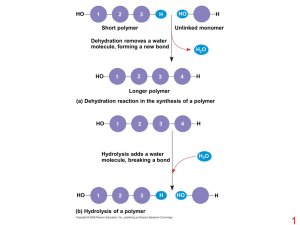
II. Amino acid SEQUENCE
... a) A specific codon codes for the same amino acid, regardless of the species (1) The genetic code is thought of as almost universal III. TRANSFER RNA AS ADAPTER MOLECULES A. Amino acids do not have direct affinity for nucleic acids 1. Therefore, mRNA can not directly serve as a template for protein ...
... a) A specific codon codes for the same amino acid, regardless of the species (1) The genetic code is thought of as almost universal III. TRANSFER RNA AS ADAPTER MOLECULES A. Amino acids do not have direct affinity for nucleic acids 1. Therefore, mRNA can not directly serve as a template for protein ...
Classic Methods of Genetic Analysis
... illadapted phenotypes in environments in which more common genotypes give rise to healthy phenotypes • The majority of human genes, and therefore the majority of genetic disorders are carried on the autosomes ...
... illadapted phenotypes in environments in which more common genotypes give rise to healthy phenotypes • The majority of human genes, and therefore the majority of genetic disorders are carried on the autosomes ...
Excellence
... Clear understanding that large leaved individuals of species A are better adapted to survive and reproduce. This enables species A to survive. ...
... Clear understanding that large leaved individuals of species A are better adapted to survive and reproduce. This enables species A to survive. ...
Guide for Bioinformatics Project Module 2 - SGD-Wiki
... data. These data networks are most easily viewed one at a time. To change this setting simply move to the right-‐hand portion of the screen and select ONLY ONE (for example, Co-‐expression) data ...
... data. These data networks are most easily viewed one at a time. To change this setting simply move to the right-‐hand portion of the screen and select ONLY ONE (for example, Co-‐expression) data ...
Heredity & Genetics
... The amount of pigment is controlled by genes in special cells called melanocytes. One way to end up with two different colored eyes is when an eye color gene works in one eye but not the other. ...
... The amount of pigment is controlled by genes in special cells called melanocytes. One way to end up with two different colored eyes is when an eye color gene works in one eye but not the other. ...
CH 3
... • If bacteria are such wonderful alternatives, why are our chemicals still made from environmentally hazardous feedstocks? ...
... • If bacteria are such wonderful alternatives, why are our chemicals still made from environmentally hazardous feedstocks? ...
chapt16_lecture_edited [Compatibility Mode]
... The nucleus of a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes, which are found in homologous pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. The maternal and paternal sets of homologous chromosomes are functionally equivalent; each set carries a full compl ...
... The nucleus of a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes, which are found in homologous pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. The maternal and paternal sets of homologous chromosomes are functionally equivalent; each set carries a full compl ...
Molecular Cell Biology - Biomedical Informatics
... Figure 9-30. Structure of the nucleosome. (a) Ribbon diagram of the nucleosome shown face-on (left) and from the side (right). One DNA strand is shown in green and the other in brown. H2A is yellow; H2B, red; H3, blue; H4, green. (b) Space-filling model shown from the side. DNA is shown in white; hi ...
... Figure 9-30. Structure of the nucleosome. (a) Ribbon diagram of the nucleosome shown face-on (left) and from the side (right). One DNA strand is shown in green and the other in brown. H2A is yellow; H2B, red; H3, blue; H4, green. (b) Space-filling model shown from the side. DNA is shown in white; hi ...
Bio 392: Study Guide for Final
... Know what you start with and what you end with Know the role of promoters and mRNA in the process Know what enzyme is involved and what its function is Describe the process of RNA editing Distinguish between introns and exons Describe the process of translation Know what you start with and ...
... Know what you start with and what you end with Know the role of promoters and mRNA in the process Know what enzyme is involved and what its function is Describe the process of RNA editing Distinguish between introns and exons Describe the process of translation Know what you start with and ...
Cloning and sequencing of glutamate mutase component E from
... precisely found again in the nucleotide sequence. The distribution of hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions in the protein is inconspicuous. A homology search of the protein sequence using the FASTA algorithm [17] revealed no significant homology to any known protein in the databases. No significant h ...
... precisely found again in the nucleotide sequence. The distribution of hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions in the protein is inconspicuous. A homology search of the protein sequence using the FASTA algorithm [17] revealed no significant homology to any known protein in the databases. No significant h ...
Gene Regulation
... • Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways; their synthesis is repressed by high levels of the end product • Regulation of the trp and lac operons involves negative control of genes because operons are switched off by the active form of the repressor ...
... • Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways; their synthesis is repressed by high levels of the end product • Regulation of the trp and lac operons involves negative control of genes because operons are switched off by the active form of the repressor ...
Comparative Analyses of Villus and Crypt Small Intestinal Cell Gene
... that >1000 genes were more highly expressed in the crypt epithelial cells than in villus cells. This list includes many genes related to apoptosis, cell cycle, DNA replication, and energy/metabolism. Genes (13%) more highly expressed in villus than crypt were associated with matrix or structural pro ...
... that >1000 genes were more highly expressed in the crypt epithelial cells than in villus cells. This list includes many genes related to apoptosis, cell cycle, DNA replication, and energy/metabolism. Genes (13%) more highly expressed in villus than crypt were associated with matrix or structural pro ...
1. The molecular “machines” (those components that do things) of
... is one of the adenosine phosphates. is one of the nucleotide coenzymes. contains protein-building instructions. ...
... is one of the adenosine phosphates. is one of the nucleotide coenzymes. contains protein-building instructions. ...
Semester 2 review sheet - Summit School District
... -Explain how the liver and the kidneys work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. Define homeostasis: -Using a negative feedback mechanism, describe how the pancreas and the liver work together to maintain blood-glucose levels in the body Please compare and contrast positive feedback mechani ...
... -Explain how the liver and the kidneys work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. Define homeostasis: -Using a negative feedback mechanism, describe how the pancreas and the liver work together to maintain blood-glucose levels in the body Please compare and contrast positive feedback mechani ...
Patterns Of Inheritance
... • Classical genetics uses an understanding of meiosis to make predictions about the kinds of genes that will be inherited by the offspring of a sexually reproducing pair of organisms. • Offspring are the descendants of a set of parents. ...
... • Classical genetics uses an understanding of meiosis to make predictions about the kinds of genes that will be inherited by the offspring of a sexually reproducing pair of organisms. • Offspring are the descendants of a set of parents. ...
Escherichia coli
... Figure 14.12. Deletion mutations. In the top sequence three nucleotides comprising a single codon are deleted. This shortens the resulting protein product by one amino acid but does not affect the rest of its sequence. In the lower section, a single nucleotide is deleted. This results in a frameshi ...
... Figure 14.12. Deletion mutations. In the top sequence three nucleotides comprising a single codon are deleted. This shortens the resulting protein product by one amino acid but does not affect the rest of its sequence. In the lower section, a single nucleotide is deleted. This results in a frameshi ...
y 1
... “Mutation” of a gene might be due to changes elsewhere! •ald is Drosophila mps1 homolog; isolated four mutations (all rescued by ald+ transgene) •two ald alleles cause meiotic and mitotic defects (ald sequence changes) •two ald “mutations” cause only meiotic defects (normal ald sequence) •both cont ...
... “Mutation” of a gene might be due to changes elsewhere! •ald is Drosophila mps1 homolog; isolated four mutations (all rescued by ald+ transgene) •two ald alleles cause meiotic and mitotic defects (ald sequence changes) •two ald “mutations” cause only meiotic defects (normal ald sequence) •both cont ...
w12-proteins
... The direct detection and quantification of the proteins in a biological system o Can also assay protein “states” [post-translational modifications (PTMs), e.g. phosphorylation] o Provides high-confidence detection of proteins/validation of putative coding genes o Provides more accurate protein abu ...
... The direct detection and quantification of the proteins in a biological system o Can also assay protein “states” [post-translational modifications (PTMs), e.g. phosphorylation] o Provides high-confidence detection of proteins/validation of putative coding genes o Provides more accurate protein abu ...
CHANGES TO THE GENETIC CODE
... amounts or not make it at all (see Figure 4.1) • Faulty genes (mutated genes) may cause a problem with the development and functioning of different body systems or organs and result in a genetic condition (see Genetics Fact Sheet 2) • Further information about mutations is provided in Genetics Fac ...
... amounts or not make it at all (see Figure 4.1) • Faulty genes (mutated genes) may cause a problem with the development and functioning of different body systems or organs and result in a genetic condition (see Genetics Fact Sheet 2) • Further information about mutations is provided in Genetics Fac ...
Ninth Grade Biology Unit 3 – Growth and Heredity Asexual and
... chemical) biological resistance point mutation ...
... chemical) biological resistance point mutation ...
PDF
... cerevisiae reveals >6000 open reading frames (ORFs). About 3000 have been assigned functions (Goffeau et al., 1996). The transcription is largely controlled and regulated by their promoter region located upstream of the coding regions (e.g. Hampsey, 1998). There are ∼200 known yeast transcription fa ...
... cerevisiae reveals >6000 open reading frames (ORFs). About 3000 have been assigned functions (Goffeau et al., 1996). The transcription is largely controlled and regulated by their promoter region located upstream of the coding regions (e.g. Hampsey, 1998). There are ∼200 known yeast transcription fa ...







![chapt16_lecture_edited [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000263591_1-cfed90f240fe045be4528c9a104d2a9a-300x300.png)