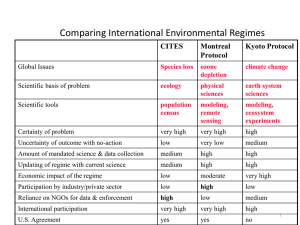
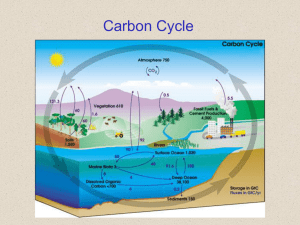
Document
... Protocol, for a second commitment period of comparable, single number, unconditional, and legally-binding emission reduction targets for developed countries under the Kyoto Protocol, to be applied starting on 1 January 2013. In order to be meaningful, the emission reduction targets of Annex I partie ...
... Protocol, for a second commitment period of comparable, single number, unconditional, and legally-binding emission reduction targets for developed countries under the Kyoto Protocol, to be applied starting on 1 January 2013. In order to be meaningful, the emission reduction targets of Annex I partie ...
Glossary Of Climate Change Terms
... attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere. Global Warming An increase in the near surface temperature of the Earth is called global warming. Global warming has occurred in the distant past as the result of natural influences. However, ...
... attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere. Global Warming An increase in the near surface temperature of the Earth is called global warming. Global warming has occurred in the distant past as the result of natural influences. However, ...
Ensuring environmental integrity through transparent accounting of
... Contributions”). And those are certainly crucial. But while the INDCs that have been announced over the course of this year are important, they are only the first step. That is because what drives climate change is the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, not the amount emitted in one ...
... Contributions”). And those are certainly crucial. But while the INDCs that have been announced over the course of this year are important, they are only the first step. That is because what drives climate change is the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, not the amount emitted in one ...
Major issues unresolved as Bali meeting approaches its end by
... Another draft at 6 pm today had rather minor changes in some parts, while retaining the language in the most important parts. There are at least four major areas of contention. First is the reference in two paragraphs of the Chapeau to scientific findings on climate change and that points to emissio ...
... Another draft at 6 pm today had rather minor changes in some parts, while retaining the language in the most important parts. There are at least four major areas of contention. First is the reference in two paragraphs of the Chapeau to scientific findings on climate change and that points to emissio ...
The need for mitigation
... remove carbon from the atmosphere in other countries: 1. The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) Funding sustainable development projects in non-Annex I Parties that reduce emissions (or enhance sinks through afforestation or reforestation.) ...
... remove carbon from the atmosphere in other countries: 1. The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) Funding sustainable development projects in non-Annex I Parties that reduce emissions (or enhance sinks through afforestation or reforestation.) ...
Ireland and the Kyoto Protocol
... of the warming observed over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the increase in greenhouse gas concentration’ ...
... of the warming observed over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the increase in greenhouse gas concentration’ ...
Document
... The Kyoto Protocol is generally seen as an important first step towards a truly global emission reduction regime that will stabilize GHG emissions, and provides the basic architecture for any future international agreement on climate change (UNFCCC, 2010). The Institutional Framework Several institu ...
... The Kyoto Protocol is generally seen as an important first step towards a truly global emission reduction regime that will stabilize GHG emissions, and provides the basic architecture for any future international agreement on climate change (UNFCCC, 2010). The Institutional Framework Several institu ...
Decision 1/CMP.6 The Cancun Agreements: Outcome of the work of
... resulting from anthropogenic land use, land-use change and forestry activities shall continue to be available to Annex I Parties as a means to reach their quantified emission limitation and reduction objectives, in accordance with decision 2/CMP.6; (d) The global warming potentials used to calculate ...
... resulting from anthropogenic land use, land-use change and forestry activities shall continue to be available to Annex I Parties as a means to reach their quantified emission limitation and reduction objectives, in accordance with decision 2/CMP.6; (d) The global warming potentials used to calculate ...
Robert Stavins - Sustainable Energy Institute
... train without their paying for tickets: – Trigger mechanism whereby developing countries are obligated to take on binding commitments once their per capita GDP reaches agreed levels – “Growth targets” that become more rigorous as countries become wealthier – Well-designed international tradeable per ...
... train without their paying for tickets: – Trigger mechanism whereby developing countries are obligated to take on binding commitments once their per capita GDP reaches agreed levels – “Growth targets” that become more rigorous as countries become wealthier – Well-designed international tradeable per ...
“Made in Ontario” solutions
... targets. The Kyoto Protocol includes emissions trading provisions that would allow countries to buy emission reductions from each other, thus adjusting their targets. This means that manufacturers within signatory countries would have to track GHG emissions and meet their own targets. The emissions ...
... targets. The Kyoto Protocol includes emissions trading provisions that would allow countries to buy emission reductions from each other, thus adjusting their targets. This means that manufacturers within signatory countries would have to track GHG emissions and meet their own targets. The emissions ...
high
... Article 17: Emissions trading=Carbon market – Parties with commitments under Kyoto accept targets—expressed as levels of allowed emissions between 2008-2012—for limiting or reducing emissions. Countries with emission units to spare can sell excess capacity to countries over their targets. – Trading ...
... Article 17: Emissions trading=Carbon market – Parties with commitments under Kyoto accept targets—expressed as levels of allowed emissions between 2008-2012—for limiting or reducing emissions. Countries with emission units to spare can sell excess capacity to countries over their targets. – Trading ...
The Greenhouse Effect
... An example of opposition to the Protocol can be seen by looking at the US. The United States, while under the Clinton Administration signed the treaty but never sent it to the Senate because the Senate had already voted 95-0, objecting to any treaty that would incur new commitments by US without pa ...
... An example of opposition to the Protocol can be seen by looking at the US. The United States, while under the Clinton Administration signed the treaty but never sent it to the Senate because the Senate had already voted 95-0, objecting to any treaty that would incur new commitments by US without pa ...
Brief on state of play in international climate change talks Climate
... has 195 parties. To realise the ultimate objective of the convention, viz. stabilisation of Green House Gases (GHG), the Kyoto Protocol (KP) was adopted in 1997. It called for emissions reductions target for Annex I Parties, wherein they agreed to reduce their overall emissions of six greenhouse gas ...
... has 195 parties. To realise the ultimate objective of the convention, viz. stabilisation of Green House Gases (GHG), the Kyoto Protocol (KP) was adopted in 1997. It called for emissions reductions target for Annex I Parties, wherein they agreed to reduce their overall emissions of six greenhouse gas ...
What is Joint Implementation (JI)?
... In practice, this will likely mean facilities built in the countries of Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union - the "transition economies" - paid for by Western European and North American countries. ...
... In practice, this will likely mean facilities built in the countries of Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union - the "transition economies" - paid for by Western European and North American countries. ...
Climate Change and the Kyoto Protocol
... Emissions Trading (“The Carbon Market”) “Assigned Amount Units” Sell excess units to countries over their targets. Joint Implementation Earn emission reduction units from a reduction in emissions by enhancement of removals by sinks. The Clean Development Mechanism Implement an emission ...
... Emissions Trading (“The Carbon Market”) “Assigned Amount Units” Sell excess units to countries over their targets. Joint Implementation Earn emission reduction units from a reduction in emissions by enhancement of removals by sinks. The Clean Development Mechanism Implement an emission ...
... The historical responsibility of countries listed in the Annex I of the Convention on Climate Change has been used extensively as a justification for the lack of action of countries not included in Annex I to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. We analyzed the contribution of non-Annex I countrie ...
Origins of CDM - Capacity Development for the CDM
... Average sea level has increased (0.1-0.2m in the 20th century). ...
... Average sea level has increased (0.1-0.2m in the 20th century). ...
Review of Kyoto so far and finishing it off
... Kyoto Protocol 1997 • Was A global Agreement that set targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions • 175 countries signed up • The aim of the treaty was "stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous human interference with the climate sys ...
... Kyoto Protocol 1997 • Was A global Agreement that set targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions • 175 countries signed up • The aim of the treaty was "stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous human interference with the climate sys ...
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty, which extends the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits State Parties to reduce greenhouse gases emissions, based on the premise that (a) global warming exists and (b) man-made CO2 emissions have caused it. The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan, on 11 December, 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005. There are currently 192 Parties (Canada withdrew effective December 2012) to the Protocol. The Kyoto Protocol implemented the objective of the UNFCCC to fight global warming by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere to ""a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system"" (Art. 2). The Protocol is based on the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities: it puts the obligation to reduce current emissions on developed countries on the basis that they are historically responsible for the current levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.The Protocol’s first commitment period started in 2008 and ended in 2012. A second commitment period was agreed on in 2012, known as the Doha Amendment to the protocol, in which 37 countries have binding targets: Australia, the European Union (and its 28 member states), Belarus, Iceland, Kazakhstan, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, and Ukraine. Belarus, Kazakhstan and Ukraine have stated that they may withdraw from the Protocol or not put into legal force the Amendment with second round targets. Japan, New Zealand and Russia have participated in Kyoto's first-round but have not taken on new targets in the second commitment period. Other developed countries without second-round targets are Canada (which withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol in 2012) and the United States (which has not ratified the Protocol). As of July 2015, 36 states have accepted the Doha Amendment, while entry into force requires the acceptances of 144 states.Negotiations were held in Lima in 2014 to agree on a post-Kyoto legal framework that would obligate all major polluters to pay for CO2 emissions. China, India, and the United States have all signaled that they will not ratify any treaty that will commit them legally to reduce CO2 emissions.