Abstract-- Lactic acid bacteria are characterized
... presence of Met-Pro or Leu-Pro as source of methionine or leucine respectively, the final cell concentration was 20% lower as regards to basal medium (Fig. 2A). The growth rates (Fig. 2B) were identical to that obtained in basal medium, except when Gly was added as part of the dipeptide Gly-Gly. In ...
... presence of Met-Pro or Leu-Pro as source of methionine or leucine respectively, the final cell concentration was 20% lower as regards to basal medium (Fig. 2A). The growth rates (Fig. 2B) were identical to that obtained in basal medium, except when Gly was added as part of the dipeptide Gly-Gly. In ...
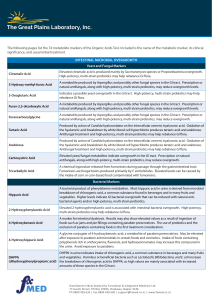
Metabolite Markers
... The following pages list the 74 metabolite markers of the Organic Acids Test. Included is the name of the metabolic marker, its clinical significance, and usual initial treatment. ...
... The following pages list the 74 metabolite markers of the Organic Acids Test. Included is the name of the metabolic marker, its clinical significance, and usual initial treatment. ...
$doc.title
... anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, no color change or turbidity is observed. When a pure culture of the same bacterium is incubated anaerobically ...
... anaerobically in a validated (that is, base broth was run) PR sucrose, no color change or turbidity is observed. When a pure culture of the same bacterium is incubated anaerobically ...
Trans-chalcone and quercetin down-regulate fatty acid synthase
... [2,3]. Infections caused by this species are difficult to treat and there is only a limited number of antifungal drugs available for clinical use, especially when compared to the arsenal of antibacterial drugs [4,5]. Therefore, novel drugs with more specific and effective mechanisms of action agains ...
... [2,3]. Infections caused by this species are difficult to treat and there is only a limited number of antifungal drugs available for clinical use, especially when compared to the arsenal of antibacterial drugs [4,5]. Therefore, novel drugs with more specific and effective mechanisms of action agains ...
Vitamins and Coenzymes - Rose
... vitamin B12 has only two known functions: 1) in the methionine synthase reaction, vitamin B12 accepts a methyl group from methyl-THF and donate it to homocysteine to form methionine and 2) vitamin B12 is a coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, which catalyzes the rearrangement of methylmalonyl-CoA ...
... vitamin B12 has only two known functions: 1) in the methionine synthase reaction, vitamin B12 accepts a methyl group from methyl-THF and donate it to homocysteine to form methionine and 2) vitamin B12 is a coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, which catalyzes the rearrangement of methylmalonyl-CoA ...
biochemistry-lect-4-n-34-amino-acid-and-peptides
... Since amino acids are ampholytes they act as buffers. However, the buffering action of amino acids in the blood is insignificant because of their low concentration. ...
... Since amino acids are ampholytes they act as buffers. However, the buffering action of amino acids in the blood is insignificant because of their low concentration. ...
The Cell, 5e
... glycolysis reactions • 3 critical irreversible steps have separate enzymes (these also regulated) ...
... glycolysis reactions • 3 critical irreversible steps have separate enzymes (these also regulated) ...
Translation Question from Text and Decoding Practice
... 2. Although you may not have thought about this particular point before, how does an amino acid (AA) become attached to a tRNA in the first place? Notice there are no AA’s attached to the two tRNAs in the figure above. ...
... 2. Although you may not have thought about this particular point before, how does an amino acid (AA) become attached to a tRNA in the first place? Notice there are no AA’s attached to the two tRNAs in the figure above. ...
Bile Acids and Bile Acid Sequestrants
... through association to produce a non-productive heterodimer. The protein has been shown to interact with retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors, inhibiting their ligand-dependent transcriptional activation. In addition, interaction with estrogen receptors has been demonstrated, leading to inhibition ...
... through association to produce a non-productive heterodimer. The protein has been shown to interact with retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors, inhibiting their ligand-dependent transcriptional activation. In addition, interaction with estrogen receptors has been demonstrated, leading to inhibition ...
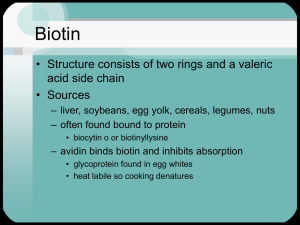
PowerPoint Presentation - Biotin Conclusion and Discussion
... – biotin reacts with a ATP (Mg required) – carboxylase joins the biotinyl moiety to form holoenzyme carboxylase with release of AMP ...
... – biotin reacts with a ATP (Mg required) – carboxylase joins the biotinyl moiety to form holoenzyme carboxylase with release of AMP ...
The Relationship between Chemiosmotic Parameters
... Organic acids, in general, are deleterious to Fe(I1) oxidation and cell viability. It has been suggested that one major factor contributing to the effectiveness of an organic acid in inhibiting Fe(1I) oxidation is the relative electronegativity of the species, and that they act (i) via a direct effe ...
... Organic acids, in general, are deleterious to Fe(I1) oxidation and cell viability. It has been suggested that one major factor contributing to the effectiveness of an organic acid in inhibiting Fe(1I) oxidation is the relative electronegativity of the species, and that they act (i) via a direct effe ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
... oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
Lecture notes Chapter 22-23
... collagen fibrils. As a person ages, additional cross-links form between the fibrils, which make collagen less elastic. Bones, cartilage, and tendons become more brittle, and wrinkles are seen as the skin loses elasticity. Tertiary structure: the tertiary structure of a protein involves attractions a ...
... collagen fibrils. As a person ages, additional cross-links form between the fibrils, which make collagen less elastic. Bones, cartilage, and tendons become more brittle, and wrinkles are seen as the skin loses elasticity. Tertiary structure: the tertiary structure of a protein involves attractions a ...
Comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis
... of FFA to methyl esters increased with the increase in catalyst amount. With 0.5% H2SO4, the acid value reduced to 11.40 mg KOH/g which further reduced to 6.50 with 1.3% of H2SO4. The acid value of mahua oil was further reduced to 2.07 mg KOH/g with 1.5% (v/v) H2SO4. Further increase in the catalyst ...
... of FFA to methyl esters increased with the increase in catalyst amount. With 0.5% H2SO4, the acid value reduced to 11.40 mg KOH/g which further reduced to 6.50 with 1.3% of H2SO4. The acid value of mahua oil was further reduced to 2.07 mg KOH/g with 1.5% (v/v) H2SO4. Further increase in the catalyst ...
The Roles of Amino Acids in Milk Yield and Components
... precursor or pathway can be distinguished by mass spectrometry from those bearing fewer 13C atoms that may result from recycling in connected pathways (see Bequette et al., 2006). It is important to recognise that for an AA to make a net contribution to liver gluconeogenesis, they must be catabolise ...
... precursor or pathway can be distinguished by mass spectrometry from those bearing fewer 13C atoms that may result from recycling in connected pathways (see Bequette et al., 2006). It is important to recognise that for an AA to make a net contribution to liver gluconeogenesis, they must be catabolise ...
Sample Questions 1 - U of L Class Index
... Solute that diffuses into a bead flows more slowly through the column as the pores restrict flow down the column. Thus, smaller solutes are retarded relative to larger solutes which do not enter the pores. (27) The unknown protein must be exposed to conditions that (1) disrupt quaternary structure a ...
... Solute that diffuses into a bead flows more slowly through the column as the pores restrict flow down the column. Thus, smaller solutes are retarded relative to larger solutes which do not enter the pores. (27) The unknown protein must be exposed to conditions that (1) disrupt quaternary structure a ...
Article PDF
... Lipid oxidation is a major cause of deteriorative changes in foods, especially in relation to sensory properties and concerning the formation of potentially harmful compounds. The oxidation process in food lipids involves a complex series of reactions and gives rise to a high number of different com ...
... Lipid oxidation is a major cause of deteriorative changes in foods, especially in relation to sensory properties and concerning the formation of potentially harmful compounds. The oxidation process in food lipids involves a complex series of reactions and gives rise to a high number of different com ...
INBORN ERRORS OF AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM
... When the body cannot break down tyrosine, high levels build up in the blood and form a toxic substance (known as succinylacetone) in the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system. This means that if tyrosinemia isn't treated, it may cause liver and kidney damage and brain-related problems, such as ...
... When the body cannot break down tyrosine, high levels build up in the blood and form a toxic substance (known as succinylacetone) in the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system. This means that if tyrosinemia isn't treated, it may cause liver and kidney damage and brain-related problems, such as ...
Amino acids in the seaweeds as an alternate source of protein for
... phycocolloids, as fodder, as fertilizer and for direct use in human nutrition (Abbott, 1996). Seaweeds cannot be considered as a main source of energy but they have nutritional value regarding vitamin, protein and mineral contents (Norziah and Ching, 2000). According to Chapman and Chapman (1980), 1 ...
... phycocolloids, as fodder, as fertilizer and for direct use in human nutrition (Abbott, 1996). Seaweeds cannot be considered as a main source of energy but they have nutritional value regarding vitamin, protein and mineral contents (Norziah and Ching, 2000). According to Chapman and Chapman (1980), 1 ...
DOC
... reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis occur in the mitochondria. The electrons are passed through the electron transport chain, a series of enzymes that transport electrons. The electrons eventually end up on oxygen, which is the terminal electron a ...
... reduced form that carries the electrons and protons. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis occur in the mitochondria. The electrons are passed through the electron transport chain, a series of enzymes that transport electrons. The electrons eventually end up on oxygen, which is the terminal electron a ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
Cell Size and Shape
... These two stages are preceded by an intermediate step in which pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl-CoA ...
... These two stages are preceded by an intermediate step in which pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl-CoA ...
Urinary Organic Acids - Peirson Center for Children
... 1. Is the production of mitochondrial energy adversely affected? 2. Are functional nutritional deficiencies present? 3. Are symptoms related to excessive growth of bacteria and fungi in the gut? 4. Is there an excessive toxic load and is this adversely affecting detoxification capacity?2 ...
... 1. Is the production of mitochondrial energy adversely affected? 2. Are functional nutritional deficiencies present? 3. Are symptoms related to excessive growth of bacteria and fungi in the gut? 4. Is there an excessive toxic load and is this adversely affecting detoxification capacity?2 ...
Protein Metabolism
... In acidosis urea synthesis is decreased and glutamine synthesis is increased in the liver. Glutamine is then transported from liver to kidney where it is deaminated by glutaminase to release NH3+glu. NH3 binds to H+ in renal tubule and excreted as NH4+ in urine. ...
... In acidosis urea synthesis is decreased and glutamine synthesis is increased in the liver. Glutamine is then transported from liver to kidney where it is deaminated by glutaminase to release NH3+glu. NH3 binds to H+ in renal tubule and excreted as NH4+ in urine. ...
Workshop: Protein Structure Introduction Learning Objectives
... e. Figure C.5 below shows one additional type of bond that can stabilize the tertiary structure of a protein. This bond is called a disulfide bond (or disulfide bridge), and it involves the sufhydryl (-SH) R groups from one particular type of amino acid. A disulfide bond can form only under certain ...
... e. Figure C.5 below shows one additional type of bond that can stabilize the tertiary structure of a protein. This bond is called a disulfide bond (or disulfide bridge), and it involves the sufhydryl (-SH) R groups from one particular type of amino acid. A disulfide bond can form only under certain ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.