Proteins and amino acids
... Amino acids – Hydrophobicity Hydrophobicity is the most important property It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
... Amino acids – Hydrophobicity Hydrophobicity is the most important property It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
Lecture 12
... Ribosomes are large complexes of protein and ribosomal RNA . They consist of two subunits—one large and one small—whose relative sizes are generally given in terms of their sedimentation coefficients, or S (Svedberg) values. The prokaryotic 50S and 30S ribosomal subunits together form a 70S ribosome ...
... Ribosomes are large complexes of protein and ribosomal RNA . They consist of two subunits—one large and one small—whose relative sizes are generally given in terms of their sedimentation coefficients, or S (Svedberg) values. The prokaryotic 50S and 30S ribosomal subunits together form a 70S ribosome ...
Expt 9-Amino Acids and Proteins
... ions. It is important to note that denaturation affects the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of a protein, but doesn’t affect the primary structure. Sometimes the denaturation is reversible and the protein can be renatured. Paper Chromatography of Amino Acids Chromatography is a techniq ...
... ions. It is important to note that denaturation affects the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of a protein, but doesn’t affect the primary structure. Sometimes the denaturation is reversible and the protein can be renatured. Paper Chromatography of Amino Acids Chromatography is a techniq ...
9-Amino Acids and Proteins
... ions. It is important to note that denaturation affects the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of a protein, but doesn’t affect the primary structure. Sometimes the denaturation is reversible and the protein can be renatured. Paper Chromatography of Amino Acids Chromatography is a techniq ...
... ions. It is important to note that denaturation affects the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of a protein, but doesn’t affect the primary structure. Sometimes the denaturation is reversible and the protein can be renatured. Paper Chromatography of Amino Acids Chromatography is a techniq ...
Supplemental data, Section 1: In the following section, we described
... identify a transport system for biotin or for pimelate, a precursor of biotin(1, 15). However, it has been observed that Bacillus sphaericus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas dentrificans are able to take up pimelate by passive diffusion (11). Therefore, it appears that such diffusion of pimelate m ...
... identify a transport system for biotin or for pimelate, a precursor of biotin(1, 15). However, it has been observed that Bacillus sphaericus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas dentrificans are able to take up pimelate by passive diffusion (11). Therefore, it appears that such diffusion of pimelate m ...
Biochem03 - Amit Kessel Ph.D
... E. Hexokinase. 15. The standard free energy change for a metabolic pathway: A. is positive for spontaneous pathways. B. is inversely proportional to the rate of the overall pathway. C. is lower in the presence of the pathway enzymes. D. is the sum of all the individual standard free energy values. E ...
... E. Hexokinase. 15. The standard free energy change for a metabolic pathway: A. is positive for spontaneous pathways. B. is inversely proportional to the rate of the overall pathway. C. is lower in the presence of the pathway enzymes. D. is the sum of all the individual standard free energy values. E ...
vitamins ( PPT )
... humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. So for us, and some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an imped ...
... humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. So for us, and some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an imped ...
Bchm2000_P1 - U of L Class Index
... Solute that diffuses into a bead flows more slowly through the column as the pores restrict flow down the column. Thus, smaller solutes are retarded relative to larger solutes which do not enter the pores. (27) The unknown protein must be exposed to conditions that (1) disrupt quaternary structure a ...
... Solute that diffuses into a bead flows more slowly through the column as the pores restrict flow down the column. Thus, smaller solutes are retarded relative to larger solutes which do not enter the pores. (27) The unknown protein must be exposed to conditions that (1) disrupt quaternary structure a ...
Chapter 18 Homework Assignment Chapter 18 Amino Acid
... protein synthesis. • For humans, 10 of the 20 natural amino acids are “essential”,, and must be obtained from the diet • Excess amino acids cannot be stored, but can be oxidized for energy – carnivores derive up to 90% of their energy needs from amino acid oxidation (for people it’s 10-15%) ...
... protein synthesis. • For humans, 10 of the 20 natural amino acids are “essential”,, and must be obtained from the diet • Excess amino acids cannot be stored, but can be oxidized for energy – carnivores derive up to 90% of their energy needs from amino acid oxidation (for people it’s 10-15%) ...
Insulin-Containing Amino Acids and Oligopeptides/β
... blood [1]. It has vital effects on the metabolic energy, cell permeability, and cellular homeostasis. Insulin is the most important physiological factor which controlling the glucose cell concentration (together with the corresponding antagonist, glucagon) [1]. Insulin is stored in the pancreatic β ...
... blood [1]. It has vital effects on the metabolic energy, cell permeability, and cellular homeostasis. Insulin is the most important physiological factor which controlling the glucose cell concentration (together with the corresponding antagonist, glucagon) [1]. Insulin is stored in the pancreatic β ...
biochem ch 20 [2-9
... o Heart failure can be cause by dietary deficiency of thiamine; pyruvate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes less functional than normal Because heart muscle, skeletal muscle, and nervous tissue have high rates of ATP production from ...
... o Heart failure can be cause by dietary deficiency of thiamine; pyruvate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes less functional than normal Because heart muscle, skeletal muscle, and nervous tissue have high rates of ATP production from ...
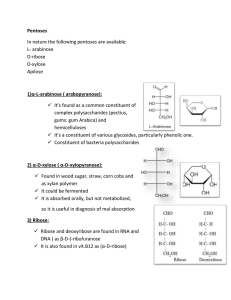
2) α-D-xylose
... 1. Maltodextrins: Mixture of polysaccharides resulting from partial hydrolysis of starch. “ have low Dextrose Equivalent (DE) < 20” uses: Infant food, Adhesive in bandages and in granulation. 2. Glucose syrup: DE> 20: used in agricultural food industry 3. Glucose syrups enriched in fructose: *known ...
... 1. Maltodextrins: Mixture of polysaccharides resulting from partial hydrolysis of starch. “ have low Dextrose Equivalent (DE) < 20” uses: Infant food, Adhesive in bandages and in granulation. 2. Glucose syrup: DE> 20: used in agricultural food industry 3. Glucose syrups enriched in fructose: *known ...
General and Physiological Chemistry
... (hydrogenation), water (hydration), hydrobromic or hydrochloric acids, and the halogens such as bromine or chlorine. Describe several properties of benzene including how it differs from cycloakenes. Draw the structures and name at least two aromatic hydrocarbons. Write an equation that illustrates t ...
... (hydrogenation), water (hydration), hydrobromic or hydrochloric acids, and the halogens such as bromine or chlorine. Describe several properties of benzene including how it differs from cycloakenes. Draw the structures and name at least two aromatic hydrocarbons. Write an equation that illustrates t ...
AMİNOASİTLERİN OKSİDASYONU
... used to replenish TCA cycle intermediates and as precursors for gluconeogenesis. In addition, organisms with a diet high in proteins can catabolize excess amino acids as fuel. Unlike carbohydrates or lipids, amino acids are not stored. They are either used or burned. For animals, amino acids (in the ...
... used to replenish TCA cycle intermediates and as precursors for gluconeogenesis. In addition, organisms with a diet high in proteins can catabolize excess amino acids as fuel. Unlike carbohydrates or lipids, amino acids are not stored. They are either used or burned. For animals, amino acids (in the ...
CHAPTER 26
... (2) In the second stage of amino acid degradation, ammonium ion is liberated from glutamate through oxidative deamination. (3) Dietary protein intake and protein turnover are the body’s only sources for providing amino acids for the amino acid pool. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the th ...
... (2) In the second stage of amino acid degradation, ammonium ion is liberated from glutamate through oxidative deamination. (3) Dietary protein intake and protein turnover are the body’s only sources for providing amino acids for the amino acid pool. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the th ...
polymers - wellswaysciences
... together with the loss of a water molecule. • If bifunctional single monomer then there is ONE REPEAT unit with an NH at one end and a carbonyl group at the other. • If 2 monomers are used the repeat unit has 2 adjacent N-H groups and 2 adjacent carbonyl ...
... together with the loss of a water molecule. • If bifunctional single monomer then there is ONE REPEAT unit with an NH at one end and a carbonyl group at the other. • If 2 monomers are used the repeat unit has 2 adjacent N-H groups and 2 adjacent carbonyl ...
Systems Biology Investigation to Discover Metabolic Biomarkers of
... hepatic necrosis. The metabolomics profiles, which primarily represent downstream changes in transcription and proteomic changes, have been adopted to investigate the mechanism of APAP-induced toxicity and to discover novel biomarkers of hepatotoxicity [12-17]. In previous studies, NMR spectroscopy ...
... hepatic necrosis. The metabolomics profiles, which primarily represent downstream changes in transcription and proteomic changes, have been adopted to investigate the mechanism of APAP-induced toxicity and to discover novel biomarkers of hepatotoxicity [12-17]. In previous studies, NMR spectroscopy ...
(18 , 19)
... o 1 s t nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by: free NH 3 (ammonia) o 2 n d nitrogen of the urea molecul e is supplied by: Aspartate ...
... o 1 s t nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by: free NH 3 (ammonia) o 2 n d nitrogen of the urea molecul e is supplied by: Aspartate ...
Metabolism—the lost child of cardiology∗
... than the sum of its parts, an understanding of the control and regulation of energy substrate metabolism remains an important field of research. Energy is the capacity to do work. The release of energy from fuels is achieved by the step-by-step processes of enzymatically controlled fuel metabolism a ...
... than the sum of its parts, an understanding of the control and regulation of energy substrate metabolism remains an important field of research. Energy is the capacity to do work. The release of energy from fuels is achieved by the step-by-step processes of enzymatically controlled fuel metabolism a ...
What limits the liver`s capacity to convert amino acids to glucose?
... transamination, conversion of the released NH4 + to urea and finally synthesis of glucose from amino acid residues. The key to understanding the physiological limitation of glucose formation from amino acids lies in the large amount of energy required to fuel these processes. Energy in the sense use ...
... transamination, conversion of the released NH4 + to urea and finally synthesis of glucose from amino acid residues. The key to understanding the physiological limitation of glucose formation from amino acids lies in the large amount of energy required to fuel these processes. Energy in the sense use ...
Validation of an HPLC method for the determination of
... determination of amino acids.4–26 Mostly, the methods were based on the technology developed by Moore and Stein,4 which includes post-column derivatisation and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, ...
... determination of amino acids.4–26 Mostly, the methods were based on the technology developed by Moore and Stein,4 which includes post-column derivatisation and detection in the visible region on an amino acid analyser. These analyses are reliable, but costly and time-consuming.9 The HPLC technique, ...
carbohydrate metabolism
... NEFA are released from the adipose tissue When the carbohydrate supply is limited, greater amount of NEFA is released. They are transported bound with albumins in the blood, 30% ar extracted by the liver: – Re-esterified to form TG – Metabolized by B-oxidation in mitochondria to form acetyl-CoA; thi ...
... NEFA are released from the adipose tissue When the carbohydrate supply is limited, greater amount of NEFA is released. They are transported bound with albumins in the blood, 30% ar extracted by the liver: – Re-esterified to form TG – Metabolized by B-oxidation in mitochondria to form acetyl-CoA; thi ...
Chapter 8- An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
... NAD+. In aerobic organisms the NAD+ is regenerated when NADH delivers the H+ and electrons to the electron transport chain. Remember, regardless of the organism, they all use glycolysis as the starting point. The pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis is then converted into different compounds dependin ...
... NAD+. In aerobic organisms the NAD+ is regenerated when NADH delivers the H+ and electrons to the electron transport chain. Remember, regardless of the organism, they all use glycolysis as the starting point. The pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis is then converted into different compounds dependin ...
KETONE BODY METABOLISM - Qassim College of Medicine
... – In starvation the fatty acids [and amino acids] are used for energy needs of the body after the glucose reserves are finished. – This results in overproduction of Acetyl CoA which is not fully handled by TCA cycle . – TCA cycle is impaired due to deficiency of oxaloacetate which is diverted to glu ...
... – In starvation the fatty acids [and amino acids] are used for energy needs of the body after the glucose reserves are finished. – This results in overproduction of Acetyl CoA which is not fully handled by TCA cycle . – TCA cycle is impaired due to deficiency of oxaloacetate which is diverted to glu ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.