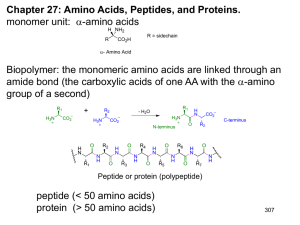
Amino acids
... production of pyruvate or Krebs cycle intermediates, such as a-ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate, all of which are precursors to glucose via gluconeogenesis. ...
... production of pyruvate or Krebs cycle intermediates, such as a-ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate, all of which are precursors to glucose via gluconeogenesis. ...
Enduring Understanding: Growth, reproduction and maintenance of
... ◦ Facultative Anaerobes- an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration when oxygen is available but switches to fermentation when oxygen is not available ◦ Obligate Anaerobes – carry out only fermentation (anaerobic respiration) and cannot survive in the presence of oxygen ...
... ◦ Facultative Anaerobes- an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration when oxygen is available but switches to fermentation when oxygen is not available ◦ Obligate Anaerobes – carry out only fermentation (anaerobic respiration) and cannot survive in the presence of oxygen ...
7 rounds of beta oxidation
... Fatty acids (FA) from the diet or from the degradation of triglycerides stored in adipose cells are broken down further to smaller molecules to completely metabolize them and therefore release energy. This process of catabolism of FA includes three major parts: ...
... Fatty acids (FA) from the diet or from the degradation of triglycerides stored in adipose cells are broken down further to smaller molecules to completely metabolize them and therefore release energy. This process of catabolism of FA includes three major parts: ...
an introduction to alpha-fetoprotein and the growth inhibitory peptide
... the polypeptide backbone- and then checking individual fragments for particular activity. Alternatively, the DNA, encoding a particular protein, can be subjected to mutagenesis so that segments of the protein’s backbone are removed or changed. The activity of the truncated or altered protein product ...
... the polypeptide backbone- and then checking individual fragments for particular activity. Alternatively, the DNA, encoding a particular protein, can be subjected to mutagenesis so that segments of the protein’s backbone are removed or changed. The activity of the truncated or altered protein product ...
Gluconeogenesis by Dr Tarek
... • Glucogenic amino acids: amino acids by deamination can be converted into keto acids as pyruvic, α-ketoglutaric and oxaloacetic acid. • Proteins are considered as one of the main sources of blood glucose especially after 18 hr due to depletion of liver glycogen. ...
... • Glucogenic amino acids: amino acids by deamination can be converted into keto acids as pyruvic, α-ketoglutaric and oxaloacetic acid. • Proteins are considered as one of the main sources of blood glucose especially after 18 hr due to depletion of liver glycogen. ...
Microbial ecosystem in the oral cavity: Metabolic diversity in an
... succinyl-CoA synthase that bridges the acetic–succinic pathway to the propionic–butyric pathway [10]. Valine and leucine are also degraded to isobutyric and isovaleric acids, respectively. In general, ammonia is produced through amino acid deamination, and oxygen is consumed by coupling with a reduc ...
... succinyl-CoA synthase that bridges the acetic–succinic pathway to the propionic–butyric pathway [10]. Valine and leucine are also degraded to isobutyric and isovaleric acids, respectively. In general, ammonia is produced through amino acid deamination, and oxygen is consumed by coupling with a reduc ...
Amino acids
... production of pyruvate or Krebs cycle intermediates, such as a-ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate, all of which are precursors to glucose via gluconeogenesis. ...
... production of pyruvate or Krebs cycle intermediates, such as a-ketoglutarate or oxaloacetate, all of which are precursors to glucose via gluconeogenesis. ...
E. coli
... studied for more than three decades on the sore carbon source of glucose or acetate. • Important to biotechnology industry – Acetate accumulation in medium during industrial fermentation – An obstacle to reach high cell density cultivation ...
... studied for more than three decades on the sore carbon source of glucose or acetate. • Important to biotechnology industry – Acetate accumulation in medium during industrial fermentation – An obstacle to reach high cell density cultivation ...
9. Wakil, S. J., Green, DE, Mii, S., and Mahler, HR (1954) Studies on
... cryomicroscopy. A three-dimensional structure was proposed for the yeast enzyme as a prolate ellipsoid and that the six fatty acid synthesizing centers are composed of two complementary halves - α subunit and a β subunit, an arrangement having all the activities of the multifunctional enzyme require ...
... cryomicroscopy. A three-dimensional structure was proposed for the yeast enzyme as a prolate ellipsoid and that the six fatty acid synthesizing centers are composed of two complementary halves - α subunit and a β subunit, an arrangement having all the activities of the multifunctional enzyme require ...
Gluconeogenesis
... reciprocal effect, only one of the two enzymes is active at any given time. The liver also contains glucokinase inhibitor protein, which is activated by fructose-6phosphate. When bound to F6P, glucokinase inhibitor protein sequesters and inactivates glucokinase, shutting down the first step in glyco ...
... reciprocal effect, only one of the two enzymes is active at any given time. The liver also contains glucokinase inhibitor protein, which is activated by fructose-6phosphate. When bound to F6P, glucokinase inhibitor protein sequesters and inactivates glucokinase, shutting down the first step in glyco ...
The Reactions of Diazonium Compounds with Amino Acids and
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
... in the normal manner, gave a product with an unchanged As/N quotient of 0-842, but the other, kept at 370 for the same time, gave a product with a diminished As/N quotient of 0-765. A product obtained from bovine-plasma albumin, having an initial As/N quotient of 0 774, was also dissolved in NaHCO2. ...
Cellular Respiration
... anaerobic respiration pathway. Most anaerobes are bacteria. Anaerobes do NOT require oxygen. ...
... anaerobic respiration pathway. Most anaerobes are bacteria. Anaerobes do NOT require oxygen. ...
Incomplete citric acid cycle obliges aminolevulinic
... formation of oxaloacetate in 20 mwpotassium phosphate (pH 7 . 9 , 0.5 mM-NAD+ or 0.2 mM-NADP', 0.2 mM-acetyl-CoA, 0.1 m ~ - 5 , 5 ' dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid), 5.8 U porcine-heart citrate synthase and 1 mwmalate. 2-Oxoglutarate decarboxylase was monitored by coupling the thiamin pyrophosphate an ...
... formation of oxaloacetate in 20 mwpotassium phosphate (pH 7 . 9 , 0.5 mM-NAD+ or 0.2 mM-NADP', 0.2 mM-acetyl-CoA, 0.1 m ~ - 5 , 5 ' dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid), 5.8 U porcine-heart citrate synthase and 1 mwmalate. 2-Oxoglutarate decarboxylase was monitored by coupling the thiamin pyrophosphate an ...
ppt - Vanderbilt University
... Fibrous. Polypeptides strands that “bundle” to form elongated fibrous assemblies; insoluble; Globular. Proteins that fold into a “spherical” conformation . Hydrophobic effect. Proteins will fold so that hydrophobic amino acids are on the inside (shielded from water) and hydrophilic amino acids are o ...
... Fibrous. Polypeptides strands that “bundle” to form elongated fibrous assemblies; insoluble; Globular. Proteins that fold into a “spherical” conformation . Hydrophobic effect. Proteins will fold so that hydrophobic amino acids are on the inside (shielded from water) and hydrophilic amino acids are o ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
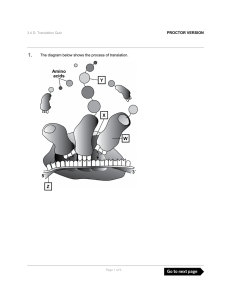
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
395
... made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids fatty acids – carbon and hydrogen chains with a COOH group on the end glycerol – modified simple sugar – 3 carbon molecule triglyceride is 3 fatty acids joined to a glycerol backbone they do not mix with water they are the most efficient and compact f ...
... made of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids fatty acids – carbon and hydrogen chains with a COOH group on the end glycerol – modified simple sugar – 3 carbon molecule triglyceride is 3 fatty acids joined to a glycerol backbone they do not mix with water they are the most efficient and compact f ...
CHAPTER 6
... • Neither of the carbon atoms of a labeled acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits t ...
... • Neither of the carbon atoms of a labeled acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acetyl-CoA survives two cycles completely, but half of what's left exits t ...
Biologically Active Oxylipins from Enzymatic and Nonenzymatic
... major algal PUFA, including the human-essential linoleic (1) and α-linolenic (2) acids, as well as stearidonic (3), eicosapentaenoic (4), and docosahexaenoic (5) acids (Figure 1), are not only important membrane components, but may also be involved in the regulation of physiological processes, by se ...
... major algal PUFA, including the human-essential linoleic (1) and α-linolenic (2) acids, as well as stearidonic (3), eicosapentaenoic (4), and docosahexaenoic (5) acids (Figure 1), are not only important membrane components, but may also be involved in the regulation of physiological processes, by se ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
... The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy ...
What Is the Chemical Logic of the TCA Cycle?
... The Carbon Atoms of Acetyl-CoA Have Different Fates in the TCA Cycle • Neither of the carbon atoms of a labeled acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acet ...
... The Carbon Atoms of Acetyl-CoA Have Different Fates in the TCA Cycle • Neither of the carbon atoms of a labeled acetate unit is lost as CO2 in the first turn of the cycle • Carbonyl C of acetyl-CoA turns to CO2 only in the second turn of the cycle (following entry of acetyl-CoA ) • Methyl C of acet ...
Abstract-- Lactic acid bacteria are characterized
... presence of Met-Pro or Leu-Pro as source of methionine or leucine respectively, the final cell concentration was 20% lower as regards to basal medium (Fig. 2A). The growth rates (Fig. 2B) were identical to that obtained in basal medium, except when Gly was added as part of the dipeptide Gly-Gly. In ...
... presence of Met-Pro or Leu-Pro as source of methionine or leucine respectively, the final cell concentration was 20% lower as regards to basal medium (Fig. 2A). The growth rates (Fig. 2B) were identical to that obtained in basal medium, except when Gly was added as part of the dipeptide Gly-Gly. In ...
Dyeing of Wool, Silk and Acrylic
... – They have average substantivity that’s why they have average levelling property. – applied in 5-6 pH, ...
... – They have average substantivity that’s why they have average levelling property. – applied in 5-6 pH, ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.