2015 department of medicine research day
... acid translocase (Cd36/Fat). Gene expression of the following hepatic key regulatory enzymes of fatty acid β-oxidation was increased significantly by GT: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and 2 (Cpt1a, Cpt1b, Cpt2) regulate transport of cytosolic fatty acids to mitochondria and long chain and very l ...
... acid translocase (Cd36/Fat). Gene expression of the following hepatic key regulatory enzymes of fatty acid β-oxidation was increased significantly by GT: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and 2 (Cpt1a, Cpt1b, Cpt2) regulate transport of cytosolic fatty acids to mitochondria and long chain and very l ...
Unit 1 Page 1 Unit Vocabulary Terms Carbohydrate
... that allows for the utilization of glucose by cells. ● Hemoglobin - An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the bloodstream. ● Lipids - Family of compounds, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, that are insoluble in water. ● Phospholipids ...
... that allows for the utilization of glucose by cells. ● Hemoglobin - An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the bloodstream. ● Lipids - Family of compounds, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, that are insoluble in water. ● Phospholipids ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... acid translocase (Cd36/Fat). Gene expression of the following hepatic key regulatory enzymes of fatty acid β-oxidation was increased significantly by GT: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and 2 (Cpt1a, Cpt1b, Cpt2) regulate transport of cytosolic fatty acids to mitochondria and long chain and very l ...
... acid translocase (Cd36/Fat). Gene expression of the following hepatic key regulatory enzymes of fatty acid β-oxidation was increased significantly by GT: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 and 2 (Cpt1a, Cpt1b, Cpt2) regulate transport of cytosolic fatty acids to mitochondria and long chain and very l ...
Sucrase Mechanism
... neither cofactor nor apoenzyme can catalyze reactions by themselves A cofactor can be either an inorganic ion or an organic molecule, called a coenzyme Many coenzymes are derived from vitamins, organic molecules that are dietary requirements for metabolism and/or growth ...
... neither cofactor nor apoenzyme can catalyze reactions by themselves A cofactor can be either an inorganic ion or an organic molecule, called a coenzyme Many coenzymes are derived from vitamins, organic molecules that are dietary requirements for metabolism and/or growth ...
macromolecules
... • Disaccharides – consists of 2 monosaccharides • glucose + glucose = maltose • glucose + fructose = sucrose ...
... • Disaccharides – consists of 2 monosaccharides • glucose + glucose = maltose • glucose + fructose = sucrose ...
Macromolecule Notes
... Monomer: single building block for a macromolecule Proteins (polypeptides) Monomer: amino acid (a.a.) Compound in your body with nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen 20 essential amino acids in your body Linked by a peptide bond Examples: o Beef o Hair o Eggs o Hemoglobin (blood component ...
... Monomer: single building block for a macromolecule Proteins (polypeptides) Monomer: amino acid (a.a.) Compound in your body with nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen 20 essential amino acids in your body Linked by a peptide bond Examples: o Beef o Hair o Eggs o Hemoglobin (blood component ...
Document
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
... This overview of the metabolic networks show why we now need computers, particulary if we want to predict cell behaviour! In recent years these needs have led to the development of ”Systems Biology”, which involves mathematical analysis and modelling of living cells. Hint: think about this figure b ...
Original
... Dipeptide : (Figure 3–8a) shows how two amino acids bond to form a dipeptide. In this condensation reaction, the two amino acids form a covalent bond (peptide bond) and release a water molecule. ...
... Dipeptide : (Figure 3–8a) shows how two amino acids bond to form a dipeptide. In this condensation reaction, the two amino acids form a covalent bond (peptide bond) and release a water molecule. ...
07-Quiz 3 Key
... b. This structure represents a common vitamin. From the structure, which statement about this vitamin is correct? a. It is expected to be very soluble in fats, making an overdose possible. b. It will playa role in metabolizing minerals in the body, making an overdose ...
... b. This structure represents a common vitamin. From the structure, which statement about this vitamin is correct? a. It is expected to be very soluble in fats, making an overdose possible. b. It will playa role in metabolizing minerals in the body, making an overdose ...
Summary of fatty acid synthesis
... Fatty acids must be activated before they can be transported into mitochondria and oxidized 1. Acyl CoA synthetase catalyzes the activation of a fatty acid in two steps: a) It catalyzes the reaction of the fatty acid with ATP to form an acyl adenylate. b) Subsequently, it catalyzes the attack by CoA ...
... Fatty acids must be activated before they can be transported into mitochondria and oxidized 1. Acyl CoA synthetase catalyzes the activation of a fatty acid in two steps: a) It catalyzes the reaction of the fatty acid with ATP to form an acyl adenylate. b) Subsequently, it catalyzes the attack by CoA ...
Biochemistry http://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry
... Glycogen (in animals) – highly branched starch – glycogen. (In mammals, glycogen stored in liver and muscles provides a quick source of energy. – Excess glucose ? taken up from the blood - stored where ? ...
... Glycogen (in animals) – highly branched starch – glycogen. (In mammals, glycogen stored in liver and muscles provides a quick source of energy. – Excess glucose ? taken up from the blood - stored where ? ...
Exam 3 - Chemistry Courses: About
... C. ____________All of the irreversible reactions of glycolysis are catalyzed by kinases. D. ____________ In glycolysis, the chemical purpose of isomerizing glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate is to allow an oxidation to take place in the next step. E. ____________ Fermentation reactions occu ...
... C. ____________All of the irreversible reactions of glycolysis are catalyzed by kinases. D. ____________ In glycolysis, the chemical purpose of isomerizing glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate is to allow an oxidation to take place in the next step. E. ____________ Fermentation reactions occu ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 85. What is catecholamine synthesized from? A. Epinephrine 86. How many essential amino acids are aromatic? A. 2 87. Thyroxime is derived from? A. Threonine B. Tyrosine C. Tyramine D. Thiamine 88. Enzymes that catalyze the interconversion of UDP-Galactose with UDP –glucose is an? A. Epimerase 89. En ...
... 85. What is catecholamine synthesized from? A. Epinephrine 86. How many essential amino acids are aromatic? A. 2 87. Thyroxime is derived from? A. Threonine B. Tyrosine C. Tyramine D. Thiamine 88. Enzymes that catalyze the interconversion of UDP-Galactose with UDP –glucose is an? A. Epimerase 89. En ...
Organic Molecules - Dublin City Schools
... e. All the above must be affected for the protein to be denatured ...
... e. All the above must be affected for the protein to be denatured ...
1 How do the regulatory properties of glucokinase and hexokinase
... As a result of product inhibition by glucose-6-phospate, hexokinase I can only continue to act on glucose if the glucose-6-phosphate product is being used in subsequent processes such as glycogen storage or glycolysis, and this will be the case in an active person whose glycogen reserves have recent ...
... As a result of product inhibition by glucose-6-phospate, hexokinase I can only continue to act on glucose if the glucose-6-phosphate product is being used in subsequent processes such as glycogen storage or glycolysis, and this will be the case in an active person whose glycogen reserves have recent ...
Animal Research Programme – Animal Nutrition and Product Quality
... fatty acids (PUFA) increase cow fertility. For example, in-vitro studies show that the omega-3 PUFA eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids have pivotal roles in the suppression of uterine prostaglandin F2, a critical regulator of embryo survival, though the cellular mechanisms are as yet unclear ...
... fatty acids (PUFA) increase cow fertility. For example, in-vitro studies show that the omega-3 PUFA eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids have pivotal roles in the suppression of uterine prostaglandin F2, a critical regulator of embryo survival, though the cellular mechanisms are as yet unclear ...
Powerpoint
... Polymers (poly = many) many The polymers are: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and nucleic acids (DNA/RNA). A polymer is made up of a chain of many monomers linked together ...
... Polymers (poly = many) many The polymers are: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and nucleic acids (DNA/RNA). A polymer is made up of a chain of many monomers linked together ...
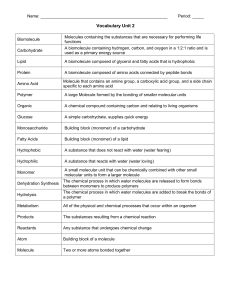
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... A substance that reacts with water (water loving) ...
... A substance that reacts with water (water loving) ...
Macro-molecule study guide / worksheet
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
www.salmate.com
... that cell is stimulated by its external environment. The balance of DGLA to arachidonic acid is controlled by the activity of a single enzyme - delta 5 desaturase. The more active the delta 5 desaturase enzyme, the greater the potential for manufacturing more arachidonic acid. The less active the en ...
... that cell is stimulated by its external environment. The balance of DGLA to arachidonic acid is controlled by the activity of a single enzyme - delta 5 desaturase. The more active the delta 5 desaturase enzyme, the greater the potential for manufacturing more arachidonic acid. The less active the en ...
没有幻灯片标题
... 2.4.2 Triacylglycerols serve as stored energy in animal adipocytes (fat cells) and plant seeds. 2.4.3 Oxidation of triacylglycerols yields more than twice the amount of energy than carbonhydrates or proteins, gram for gram (due to the higher level of reduction of the acyl(酰基) groups). ...
... 2.4.2 Triacylglycerols serve as stored energy in animal adipocytes (fat cells) and plant seeds. 2.4.3 Oxidation of triacylglycerols yields more than twice the amount of energy than carbonhydrates or proteins, gram for gram (due to the higher level of reduction of the acyl(酰基) groups). ...
practice exam
... 19. ______Which statement is false concerning the fate of glucose-6-phosphate in a muscle cell? A. G-6-P can be incorporated into glycogen. B. G-6-P can enter the pentose phosphate pathway. C. G-6-P can be converted to glucose. D. G-6-P can enter glycolysis. 20. ______ The net effect of the eight s ...
... 19. ______Which statement is false concerning the fate of glucose-6-phosphate in a muscle cell? A. G-6-P can be incorporated into glycogen. B. G-6-P can enter the pentose phosphate pathway. C. G-6-P can be converted to glucose. D. G-6-P can enter glycolysis. 20. ______ The net effect of the eight s ...
Macromolecules - Haiku Learning
... to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactions to obtain a better understanding of these processes. ...
... to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactions to obtain a better understanding of these processes. ...
Organic Molecules - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... four bonds It can even bond with itself This allows carbon to form long chains to form bigger compounds ...
... four bonds It can even bond with itself This allows carbon to form long chains to form bigger compounds ...
The Origins Of Life
... bombardment of comets and asteroids It was an essential for developing large plants, and were expected to give the plants in our solar systems most of ...
... bombardment of comets and asteroids It was an essential for developing large plants, and were expected to give the plants in our solar systems most of ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.