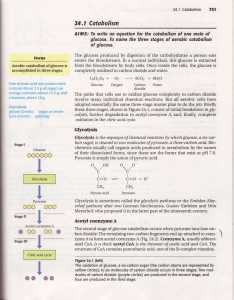
glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids
... protein that must be degraded to support gluconeogenesis. There is no "energystorage form" for protein because each protein has a specific function in the cell. Therefore, the shift from using glucose to ketones during starvation spares protein, which is essential for these other functions. Red bloo ...
... protein that must be degraded to support gluconeogenesis. There is no "energystorage form" for protein because each protein has a specific function in the cell. Therefore, the shift from using glucose to ketones during starvation spares protein, which is essential for these other functions. Red bloo ...
Unit 4 Test Review-Biomolecules Name Period ______ 1. Complete
... 24. Which is synthesized through the formation of peptide bonds? Protein 25. What are the differences between a saturated and unsaturated fat (min of 2)? What chemical structure accounts for this difference? Explain the effects of saturated versus unsaturated fats on a person’s health. Saturated fat ...
... 24. Which is synthesized through the formation of peptide bonds? Protein 25. What are the differences between a saturated and unsaturated fat (min of 2)? What chemical structure accounts for this difference? Explain the effects of saturated versus unsaturated fats on a person’s health. Saturated fat ...
H &
... The acetyl group of aceryl CoA enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid, rycle ls the pathway used by most organisms to oxidize completely to carbon dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide a ...
... The acetyl group of aceryl CoA enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid, rycle ls the pathway used by most organisms to oxidize completely to carbon dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide a ...
(i)
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
... (d) Lactate is water soluble/ dissolve in blood or tissue fluid causing outward movement of water from the tissue cells by osmosis. (e) Amino acid acts as buffer. Some ions such as HPO4=/ PO43- is a buffer. Haemoglobin of red blood cells is also a buffer. (any TWO) (f) Amino acids can be converted i ...
Biochemistry - El Camino College
... cells, digested to __________ in our bodies 3. ___________ - main component of plant cell walls; also known as _________; we can’t digest this because the covalent bonds between the glucose molecule are slightly different than those in starch and glycogen 4. Most carbohydrates are broken down to ___ ...
... cells, digested to __________ in our bodies 3. ___________ - main component of plant cell walls; also known as _________; we can’t digest this because the covalent bonds between the glucose molecule are slightly different than those in starch and glycogen 4. Most carbohydrates are broken down to ___ ...
Fibers, Proteins and Membranes
... bilayers are in a so-called liquid crystal state. That is to say, the overall structure of the layer remains but individual phospholipids can move around inside the layer. As you may know, at room temperature, many fats are about to become solid but clearly, a membrane of a living organism cannot be ...
... bilayers are in a so-called liquid crystal state. That is to say, the overall structure of the layer remains but individual phospholipids can move around inside the layer. As you may know, at room temperature, many fats are about to become solid but clearly, a membrane of a living organism cannot be ...
Cellular respiration
... • it is here that fats and proteins can ‘enter the picture’ (i.e., be used as a fuel source) • it is also when we move from the sarcoplasm into the mitochondria for the first time ...
... • it is here that fats and proteins can ‘enter the picture’ (i.e., be used as a fuel source) • it is also when we move from the sarcoplasm into the mitochondria for the first time ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... form is completed sufficiently and written evidence provided in order to allow the programme team to screen their application. Topic Overview of biological chemistry: o Organic chemistry and functional groups, free radicals, oxidation and reduction. o Biological molecules – carbohydrates, lipids and ...
... form is completed sufficiently and written evidence provided in order to allow the programme team to screen their application. Topic Overview of biological chemistry: o Organic chemistry and functional groups, free radicals, oxidation and reduction. o Biological molecules – carbohydrates, lipids and ...
Chapter 2 - Clinton Public Schools
... Carbon is special because they have unique bonding properties. •Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four _____________, including other ___________ atoms. •Carbon-based molecules have __________ general types of structures. –__________ chain –__________chain –_________ •Many carbon-based molecule ...
... Carbon is special because they have unique bonding properties. •Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four _____________, including other ___________ atoms. •Carbon-based molecules have __________ general types of structures. –__________ chain –__________chain –_________ •Many carbon-based molecule ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... Overview of biological chemistry: o Organic chemistry and functional groups, free radicals, oxidation and reduction. o Biological molecules – carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. o Enzymes o Metabolic pathways o Regulation of metabolic pathways 2) Carbohydrate metabolism – o overview of carbohydrate ...
... Overview of biological chemistry: o Organic chemistry and functional groups, free radicals, oxidation and reduction. o Biological molecules – carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. o Enzymes o Metabolic pathways o Regulation of metabolic pathways 2) Carbohydrate metabolism – o overview of carbohydrate ...
Chapter 3 Biochemistry Section 1 – Carbon Compounds Section 2
... Enzymes can be denatured-which causes them to change shape and they will no longer function ...
... Enzymes can be denatured-which causes them to change shape and they will no longer function ...
Vitamin-similar substances
... variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredient that replaces some of the natural antioxidant produced by the body, whether ingested or applied topically. When applied topically, Ubiquinone is thought to penetrate the skin easily, and reduce free radical damage via its antioxidant properties. • Ubi ...
... variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredient that replaces some of the natural antioxidant produced by the body, whether ingested or applied topically. When applied topically, Ubiquinone is thought to penetrate the skin easily, and reduce free radical damage via its antioxidant properties. • Ubi ...
Oxidation - medscistudents
... 1. Once the activated FA enter the mitochondria, flavoprotein linked acyl CoA dehydrogenase (DH) removes two hydrogen atoms from the , position, forming ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double ...
... 1. Once the activated FA enter the mitochondria, flavoprotein linked acyl CoA dehydrogenase (DH) removes two hydrogen atoms from the , position, forming ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double ...
Protein
... living things. They can store twice as many calories as polysaccharides can. Oils (mostly from plants) contain more unsaturated fatty acids, while fats (animals) contain more saturated fatty acids. Simple lipids also dissolve vitamins ...
... living things. They can store twice as many calories as polysaccharides can. Oils (mostly from plants) contain more unsaturated fatty acids, while fats (animals) contain more saturated fatty acids. Simple lipids also dissolve vitamins ...
Enzymes - flickbio
... • Larger molecules broken down into smaller molecules by the addition of water ...
... • Larger molecules broken down into smaller molecules by the addition of water ...
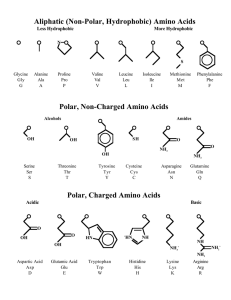
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
The fatty acid profile of muscle tissue of ram lambs with
... fat Soay breed and Welsh mountain sheep, slaughtered at the same life weight. Contrary to the results of the above-mentioned authors, the breed with less content of intramuscular fat in comparison to the fatter breed was characterized by a higher (P#0.05) amount of oleic acid and almost the same val ...
... fat Soay breed and Welsh mountain sheep, slaughtered at the same life weight. Contrary to the results of the above-mentioned authors, the breed with less content of intramuscular fat in comparison to the fatter breed was characterized by a higher (P#0.05) amount of oleic acid and almost the same val ...
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: metabolic
... A (CoA) related compounds. Apart from its primary function in the transport of long chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane [5], carnitine also plays a central role in buffering the intramitochondrial pool of CoA by exporting acylcarnitine esters from the intramitochondrial space t ...
... A (CoA) related compounds. Apart from its primary function in the transport of long chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane [5], carnitine also plays a central role in buffering the intramitochondrial pool of CoA by exporting acylcarnitine esters from the intramitochondrial space t ...
Biochemistry 423 Final Examination
... glycerate 2-phosphate to phosphoenolpyruvate glycerate 3-phosphate to glycerate 2-phosphate glycerate 1,3-bisphosphate to glycerate 3-phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone posphate ...
... glycerate 2-phosphate to phosphoenolpyruvate glycerate 3-phosphate to glycerate 2-phosphate glycerate 1,3-bisphosphate to glycerate 3-phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone posphate ...
Lecture 4
... Amino acids are organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Cell build their proteins from 20 kinds of amino acids with important functions in organisms, there are many other amino acids with important functions in organisms, but they are not incorporated into proteins. Most amino a ...
... Amino acids are organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Cell build their proteins from 20 kinds of amino acids with important functions in organisms, there are many other amino acids with important functions in organisms, but they are not incorporated into proteins. Most amino a ...
Metabolism
... How do we store Fat? • Fatty acids are stored as triglycerides • High fat diets: most go to straight to fat stores • High protein diets: body converts most of excess protein to fat • High carb diets: does not convert protein to fat; however, it shifts your body’s fuel preferences to burn more carbs ...
... How do we store Fat? • Fatty acids are stored as triglycerides • High fat diets: most go to straight to fat stores • High protein diets: body converts most of excess protein to fat • High carb diets: does not convert protein to fat; however, it shifts your body’s fuel preferences to burn more carbs ...
Tidbit Membrane Fluidity FINAL
... Which of the following would occur when a tropical fish suddenly finds itself in the Arctic? 1. Membranes are more rigid 2. Membranes are more fluid 3. Membranes maintain the same fluidity ...
... Which of the following would occur when a tropical fish suddenly finds itself in the Arctic? 1. Membranes are more rigid 2. Membranes are more fluid 3. Membranes maintain the same fluidity ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.